Configuring Expressions
You can reference pipeline contexts with expressions to specify the execution condition of a job. An expression can be any combination of contexts, operators, functions, or literals. Contexts can be accessed programmatically with expressions, so information such as pipeline runs, variables, and jobs can be transferred across pipelines.
- Create a pipeline.
- Add stage jobs or edit existing jobs.
- Click Job Configuration and set Execute to With expression to configure the expression for job execution. For a new stage and job, add an extension first and then click Job Configuration.
Figure 1 Expressions
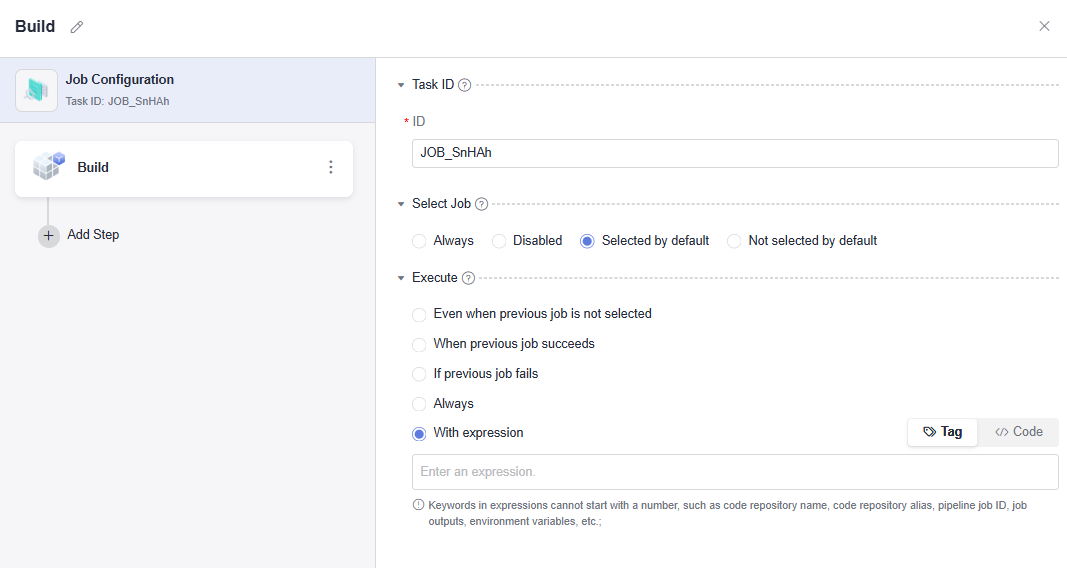
Example:
The following expression shows that a job runs only when the running branch of the specified code source is master.
${{ sources.my_repo.target_branch == 'master' }}
References
- Operator
The following table lists the operators that can be used in expressions.
Table 1 Operators Operator
Description
.
Attribute reference. For example, the ${{ pipeline.trigger_type }} expression can be used to obtain the trigger type.
!
False. For example, the ${{ !startsWith(sources.my_repo.target_branch, 'release') }} can be used to check whether the branch of the pipeline's code source does not start with "release".
==
Equal. For example, the ${{ pipeline.trigger_type == 'Manual' }} expression can be used to check whether a pipeline is triggered manually.
!=
Not equal. For example, the ${{ pipeline.trigger_type != 'Manual' }} expression can be used to check whether a pipeline is not triggered manually.
&&
And. For example, the ${{ pipeline.trigger_type == 'Manual' && sources.my_repo.target_branch == 'master' }} expression can be used to check whether a pipeline is triggered manually and the branch of the pipeline code source is master.
||
Or. For example, the ${{ pipeline.trigger_type == 'Manual' || sources.my_repo.target_branch == 'master' }} expression can be used to check whether a pipeline is triggered manually or the branch of the pipeline code source is master.
- Function
The following table lists the built-in functions that can be used in expressions.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





