FunctionGraph and IaC
Combination of FunctionGraph and IaC
Most FunctionGraph functions do not run independently, but work with storage, gateways, databases, and message queues to form serviceless applications. Infrastructure as code (IaC) automates the frequent deployments and updates of functions and triggers. This approach shortens the development cycle, simplifies configuration management, and maintains the consistency of resource deployment.
Suitable IaC Tools for FunctionGraph
Resource Formation Service (RFS) is a new final-state cloud resource orchestration engine that fully supports Terraform (HCL and Provider), the industry's de facto standard for infrastructure as code. It automatically builds cloud resources in batches based on open ecosystem templates that use the HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) syntax. With RFS, you can create, manage, and upgrade cloud resources (such as FunctionGraph functions, APIG gateways, and database instances) efficiently, securely, and consistently.
Getting Started with RFS for FunctionGraph
- Create the Python script file index.py with the following content:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import json def handler (event, context): return { "statusCode": 200, "isBase64Encoded": False, "body": json.dumps(event), "headers": { "Content-Type": "application/json" } } - Compress index.py into index.zip, upload the ZIP file to an OBS bucket, and obtain the file's object link in the bucket.
- Create the variables.tf file using the following content to define the parameters to be used in your RFS template.
variable "enterprise_project_id" { type = string description = " Specifies enterprise_project_id" default = "0" } variable "agency_name" { type = string description = " Specifies the agency to which the function belongs." default = "" } variable "region" { type = string description = " Specifies the region." default = "cn-north-7" } variable "code_url" { type = string description = "code_url" } variable "apig_id" { type = string description = "apig_id" default = "" } - Create the RFS template file main.tf using the following content to define functions and triggers.
variable "enterprise_project_id" { type = string description = " Specifies enterprise_project_id" default = "0" } variable "agency_name" { type = string description = " Specifies the agency to which the function belongs." default = "" } variable "region" { type = string description = " Specifies the region." default = "cn-north-7" } variable "code_url" { type = string description = "code_url" } variable "apig_id" { type = string description = "apig_id" default = "" } - Compress main.tf and variables.tf into the components.zip file.
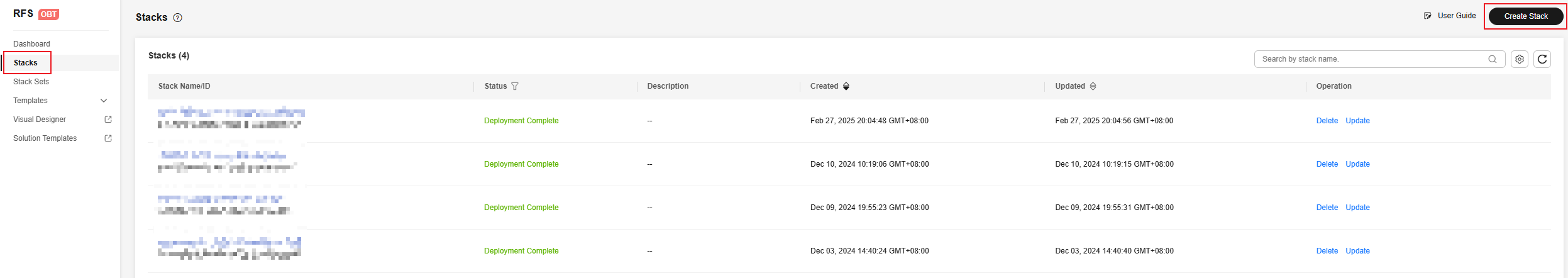
- Log in to the RFS console, and choose Stacks > Create Stack as shown in Figure 1. For details, see Creating a Stack.
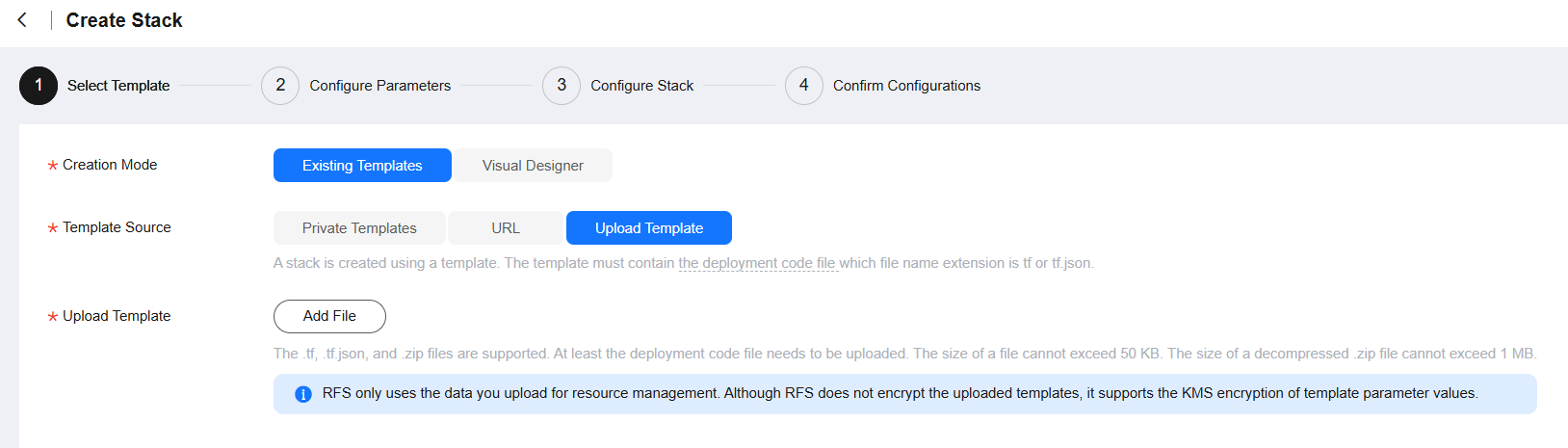
- Set parameters as shown in Figure 2, and upload components.zip. Then click Next.
- On the Configure Parameters page, set the following parameters, and click Next.
- enterprise_project_id: enterprise project ID
- agency_name: function agency name
- region: region ID. Obtain it from Regions and Endpoints.
- code_url: OBS object link obtained in step 2
- apig_id: APIG gateway ID
- On the Configure Stack page, specify an IAM agency, retain the default values for other parameters, and click Next to confirm the deployment of this stack. The specified function and resource are automatically created on the FunctionGraph console.
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console, and click the function name in the function list to go to the details page. Choose Configuration > Triggers, locate the APIG trigger, copy its calling URL, and paste the URL into your browser or run the following curl command.
curl -s <Trigger_Invoke_URL> # Replace <Trigger_Invoke_URL> with the calling URL of your APIG trigger.
The response is a JSON representation of the selected attributes in the original event object. It contains information about the request sent to the APIG endpoint. The following is an example response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Length: 658 Connection: keep-alive Content-Type: application/json Date: Wed, 12 Mar 2025 08:59:18 GMT Server: api-gateway Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubdomains; X-Apig-Latency: 52 X-Apig-Ratelimit-Api: remain:97,limit:100,time:1 minute X-Apig-Ratelimit-Api: remain:29973,limit:30000,time:1 second X-Apig-Ratelimit-Api-Allenv: remain:199,limit:200,time:1 second X-Apig-Ratelimit-Api-Allenv: remain:29973,limit:30000,time:1 second X-Apig-Ratelimit-User: remain:3995,limit:4000,time:1 second X-Apig-Upstream-Latency: 14 X-Cff-Billing-Duration: 1 X-Cff-Invoke-Summary: {"funcDigest":"e6e9c99b8f5b9d6f9408d5210263330","duration":0.756,"billingDuration":1,"memorySize":128,"memoryUsed":33.207,"podName":"pool22-300-128-fusion-844bdc7755-bh55w","gpuMemorySize":0,"ephemeralStorage":512} X-Cff-Request-Id: b43781ee-49f3-4762-8c24-236c718d3391 X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff X-Download-Options: noopen X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN X-Func-Err-Code: 0 X-Is-Func-Err: false X-Request-Id: 90a48d7a4c699780579f4edc8983cdaf X-Xss-Protection: 1; mode=block; {"requestContext": {"requestId": "90a48d7a4c699780579f4edc8983cdaf", "apiId": "01127600bb9f4d2ca8e532d1c378d8c8", "stage": ":DEBUG"}, "queryStringParameters": {}, "path": "/nxy-sasa", "httpMethod": "GET", "isBase64Encoded": true, "headers": {"host": "47f32d1efa1742f5a7ee5b720ca9c4a5.apig.cn-east-3.huaweicloudapis.com", "content-type": "application/json", "x-forwarded-host": "47f32d1efa1742f5a7ee5b720ca9c4a5.apig.cn-east-3.huaweicloudapis.com", "user-agent": "APIGatewayDebugClient/1.0", "x-forwarded-port": "443", "x-forwarded-proto": "https", "x-request-id": "90a48d7a4c699780579f4edc8983cdaf", "x-apig-mode": "debug"}, "body": "", "pathParameters": {}}
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot