Automatically Adjusting Air Conditioner Temperature Through Device Shadow
Scenarios
Using a constant-temperature control system, you can adjust the default temperature of air conditioners (regardless of whether they are powered on). After being powered on, the air conditioners automatically run at the default temperature. This is achieved by using the device shadow of the IoT platform. For any connected air conditioner, you can set the device shadow on the application or IoTDA console to deliver the preset temperature to the air conditioner. The air conditioner automatically adjusts the temperature after receiving the property modification request.
Developing a Product
- Visit the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose Products. In the search box, select the resource space to which the new product belongs.
- Click Create Product to create a constant-temperature air conditioner product, set the parameters, and click OK.
Basic Information
Product Name
Enter a value, for example, aircondition.
Protocol
Select MQTT.
Data Type
Select JSON.
Industry
Customize the values.
Device Type
- After the product is created, click the corresponding product to access its details.
- On the Basic Information tab page, click Customize Model and configure the product model based on the table below.
Service data
Service
Service ID: Enter temperature.
Service Type: You are advised to set this parameter to the same value as Service ID.
Property
Property Name: Enter temperature.
Data Type: Select Integer.
Access Permissions: Select Read and Write.
Length: Enter 1.
- In the navigation pane, choose , and click Register Device. In the dialog box displayed, set the parameters based on the table below.
Figure 1 Registering a device - MQTT

Parameter
Description
Product
Select the product created in 3.
Node ID
Set this parameter to the IMEI, MAC address, or serial number of the device. If the device is not a physical one, set this parameter to a custom character string that contains letters and digits.
Device Name
Customize the value.
Authentication Type
Select Secret.
Secret
Customize the secret used for device access. If the secret is left blank, the platform automatically generates a secret.
Configuring a Device Shadow
You can set a device shadow on the IoTDA console or by calling the API for configuring desired properties in a device shadow on the application side. This section describes how to set a device shadow on the IoTDA console.
- Log in to the IoTDA console, choose Devices > All Devices in the navigation pane, and click View in the row of the device registered in 6 to access its details.
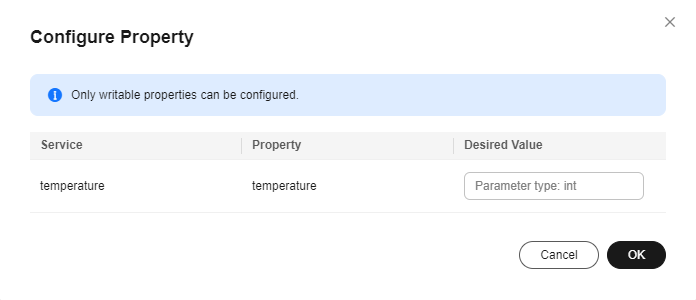
- On the Device Shadow tab page, click Configure Property.
- In the dialog box displayed, enter the desired value of a property. In this example, the value of temperature is set to 25.
Figure 2 Configuring a device shadow
Verifying Configurations
Method 1:
You can use MQTT.fx to simulate device verification.
- Use MQTT.fx to simulate a constant-temperature air conditioner and connect it to the platform. For details, see Developing an MQTT-based Simulated Smart Street Light Online.
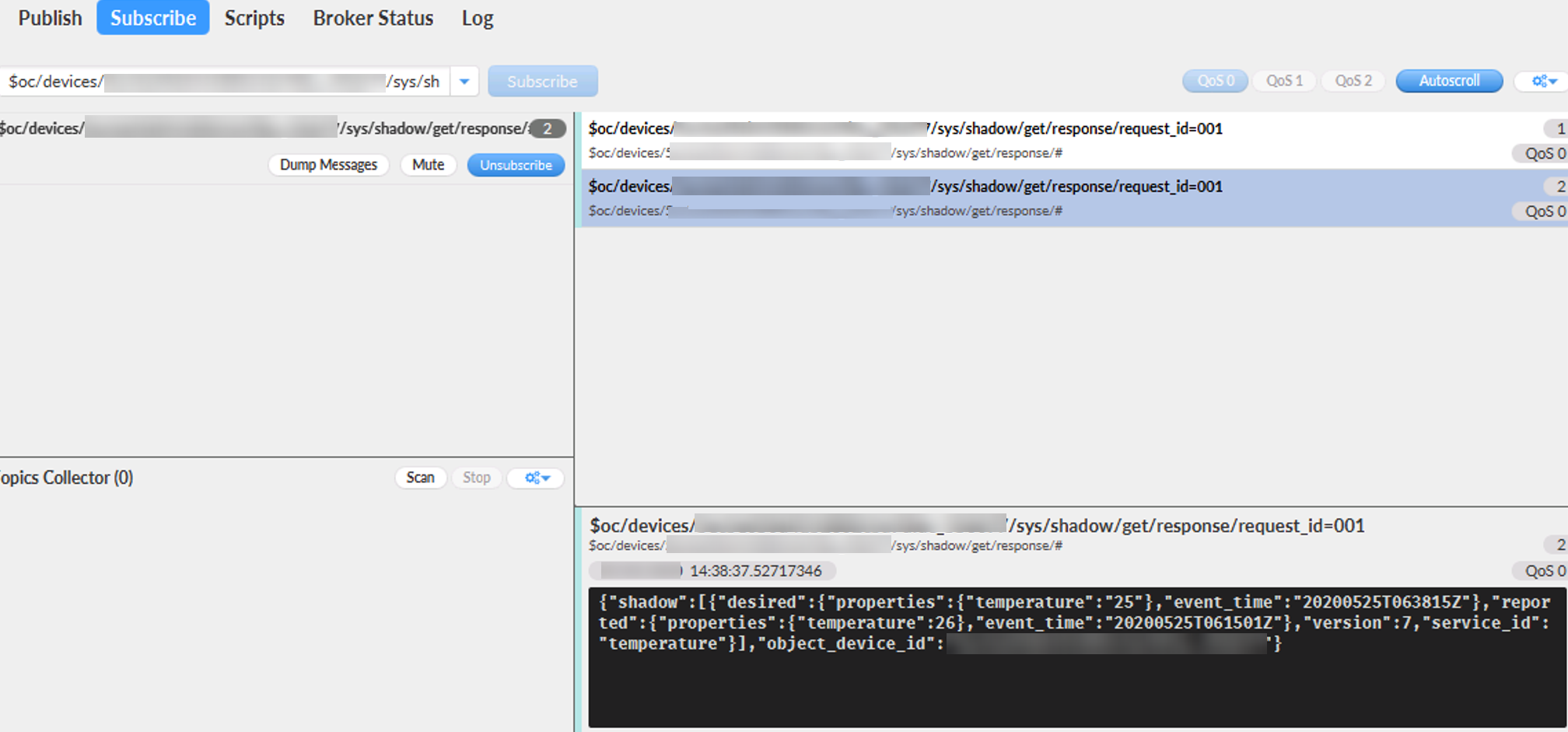
- On the Subscribe tab page, enter topic=$oc/devices/{device_id}/sys/shadow/get/response/# of the device shadow (replace {device_id} with the device ID in 6), and click Subscribe.

- On the Publish tab page, enter Topic=$oc/devices/{device_id}/sys/shadow/get/request_id={request_id} of the device shadow.
- Enter a request for obtaining the device shadow and click Publish.
Example:
{ "object_device_id": "**********", "service_id": temperature" }
- Click the Subscribe tab. The device shadow data delivered by the platform is displayed.
Method 2:
You can connect a physical device to the platform. The device will receive the device shadow configuration delivered by the platform and change the preset temperature accordingly.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





