Making an API Request
This section describes how a REST API is formed and uses the IAM API for obtaining a user token as an example to describe how to call an API. A token authenticates the calling of other APIs.
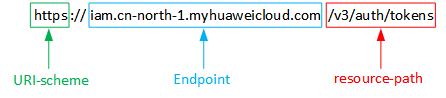
Request URI
A request URI is in the following format:
{URI-scheme}://{Endpoint}/{resource-path}?{query-string}
Although a request URI is included in the request header, most programming languages and frameworks require the request URI to be transmitted separately.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
URI-scheme |
Protocol used to transmit requests. All APIs use HTTPS. |
|
Endpoint |
Domain name or IP address of the server bearing the REST service. The endpoint varies between services in different regions. It can be obtained from Regions and Endpoints. For example, the endpoint of IAM in the CN North-Beijing1 region is iam.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com. |
|
resource-path |
The access path of an API for performing a specified operation. Obtain the path from the URI of an API. For example, the resource-path of the API used to obtain a user token is /v3/auth/tokens. |
|
query-string |
(Optional) Query parameter. Not all APIs have a query parameter. Ensure that a question mark (?) is included before each query parameter that is in the format of "Parameter name=Parameter value". For example, limit=10 indicates that a maximum of 10 data records will be displayed. |
For example, to obtain an IAM token in the CN North-Beijing1 region, obtain the endpoint of IAM (iam.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com) for this region and the resource-path (/v3/auth/tokens) in the URI of the API used to obtain a user token. Then, construct the URI as follows:
1
|
https://iam.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com/v3/auth/tokens |
To simplify the URI display in this document, each API is provided only with a resource-path and a request method. The URI-scheme of all APIs is HTTPS, and the endpoints of all APIs in the same region are identical.
Request Methods
|
Method |
Description |
|---|---|
|
GET |
Requests the server to return specified resources. |
|
PUT |
Requests the server to update specified resources. |
|
POST |
Requests the server to add resources or perform special operations. |
|
DELETE |
Requests the server to delete specified resources, for example, an object. |
|
HEAD |
Same as GET except that the server must return only the response header. |
|
PATCH |
Requests the server to update partial content of a specified resource. If the resource does not exist, the PATCH method may create one. |
For example, in the case of the API used to obtain a user token, the request method is POST. The request is as follows:
1
|
POST https://iam.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com/v3/auth/tokens |
Request Headers
You can also add additional fields to a request, such as the fields required by a specified URI or HTTP method. For example, to request for the authentication information, add Content-Type, which specifies the request body type.
|
Name |
Description |
Mandatory |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Host |
Server domain name and port number of the resource being requested. The value can be obtained from the URL of the service API. The value is hostname[:port]. If the port number is not specified, the default port is used. The default port number for HTTPS is 443. |
No This parameter is mandatory for AK/SK-based authentication. |
code.test.com or code.test.com:443 |
|
Content-Type |
MIME type of the response body. You are advised to use the default value application/json. For APIs used to upload objects or images, the value can vary depending on the flow type. |
Yes |
application/json |
|
Content-Length |
Specifies the length of the request body. The unit is byte. |
No |
3495 |
|
X-Project-Id |
Specifies a project ID. Obtain the project ID by following the instructions in Obtaining a Project ID. |
No This field is mandatory for requests that use AK/SK-based authentication in the DeC scenario or multi-project scenario. |
e9993fc787d94b6c886cbaa340f9c0f4 |
|
X-Auth-Token |
Specifies the user token. The user token is a response to the API used to obtain a user token. This API is the only one that does not require authentication. After the request is processed, the value of X-Subject-Token in the header is the token value. |
No This field is mandatory for token-based authentication. |
The following is part of an example token: MIIPAgYJKoZIhvcNAQcCo...ggg1BBIINPXsidG9rZ |
In addition to supporting token-based authentication, cloud service APIs also support authentication using the AK/SK. During AK/SK-based authentication, an SDK is used to sign the request, and the Authorization (signature information) and X-Sdk-Date (time when the request is sent) header fields are automatically added to the request.
For more information, see "AK/SK-based Authentication" in Authentication.
The API used to obtain a user token does not require authentication. Therefore, only the Content-Type field needs to be added to requests for calling the API. An example of such requests is as follows:
1 2 |
POST https://iam.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com/v3/auth/tokens Content-Type: application/json |
(Optional) Request Body
This part is optional. The body of a request is often sent in a structured format (for example, JSON or XML) as specified in the Content-Type header field. The request body transfers content except the request header. The request body can contain Chinese characters in the UTF-8 encoding format.
The request body varies depending on APIs. Some APIs do not require the request body, for example, the APIs requested using the GET and DELETE methods.
In the case of the API used to obtain a user token, the request parameters and parameter description can be obtained from the API request. The following provides an example request with a body included. Replace username, domainname, ******** (login password), and xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx (project ID) with the actual values. To learn how to obtain a project ID, see Obtaining a Project ID.
The scope parameter specifies where a token will take effect. You can set scope to an account or a project under an account. In the following example, the token takes effect only for the resources in a specified project. For more information about this API, see Obtaining a User Token.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
POST https://iam.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com/v3/auth/tokens Content-Type: application/json { "auth": { "identity": { "methods": [ "password" ], "password": { "user": { "name": "username", "password": "********", "domain": { "name": "domainname" } } } }, "scope": { "project": { "id": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" } } } } |
If all data required for the API request is available, you can send the request to call an API through curl, Postman, or coding. In the response to the API used to obtain a user token, x-subject-token is the desired user token. You can use this token to authenticate the calling of other APIs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





