Help Center/
DataArts Lake Formation/
User Guide/
LakeFormation Metadata Management/
Managing LakeFormation Databases
Updated on 2025-07-31 GMT+08:00
Managing LakeFormation Databases
You can view, modify, authorize, and delete LakeFormation databases, and view tables in the databases.
Prerequisites
You have created a database. For details, see Creating a Database.
Managing Databases
- Log in to the LakeFormation console.
- Select the LakeFormation instance to be operated from the drop-down list on the left and choose Metadata > Database in the navigation pane.
- Select a catalog from the Catalog drop-down list box in the upper right corner. View the databases contained in this catalog.
Figure 1 Viewing databases
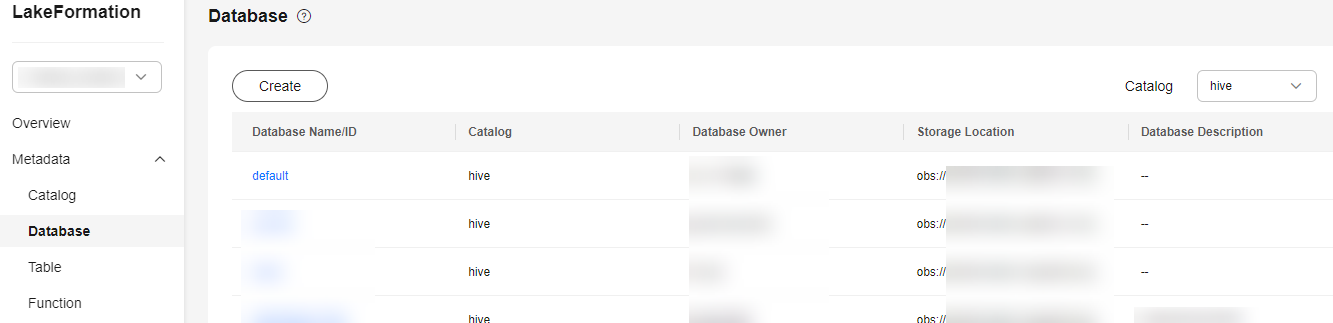
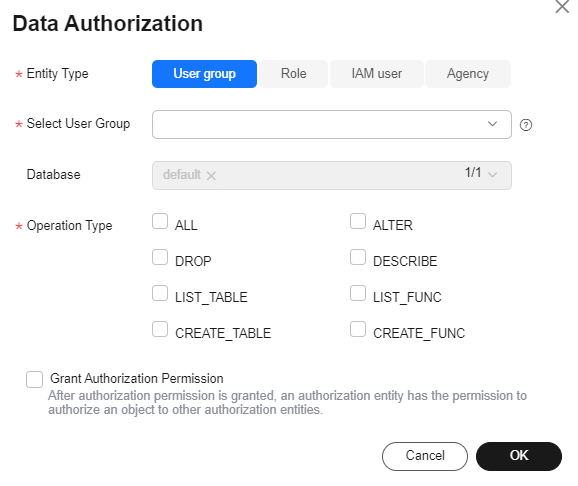
- Perform the following operations on a database.
Parent topic: LakeFormation Metadata Management
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
The system is busy. Please try again later.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot