Migration Operations
Migrate CentOS 7.9 to HCE 1.1.
Preparing Dependent Packages
- Remotely connect to the source OS.
Remotely log in to the ECS to be migrated and verify that it can be accessed from the Internet. For details, see Login Overview.
- Disable all repository configurations in /etc/yum.repos.d of CentOS. This ensures that the repositories of CentOS and HCE do not conflict.
Figure 1 Disabling repository configurations

Take Centos_Base.repo as an example. Add enabled=0 under each item, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 2 Adding the configuration item enabled=0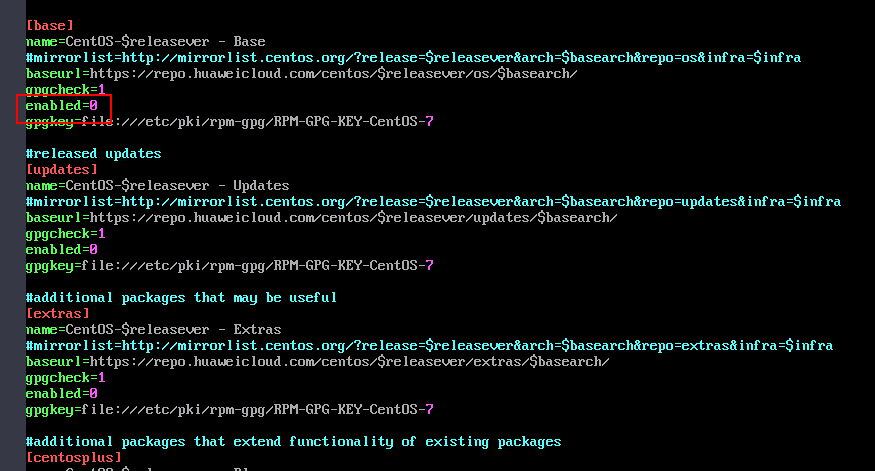
- Configure the repository of HCE.
Add the following content to hce.repo and then store it in the /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory:
[centos7_everything] name=centos7_everything baseurl=https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/os/x86_64/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 priority=1 #released updates [updates] name=hce1_updates baseurl=https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/updates/x86_64/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 gpgkey=
- Check whether CentOS 7.9 can access the repository of HCE.
Run the curl https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/os/x86_64/ command to check whether the repository of HCE can be accessed. If information similar to the following is displayed, the repository can be accessed:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 100 3417 0 3417 0 0 373 0 --:--:-- 0:00:09 --:--:-- 696 <!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/repository/static/css/style.css" type="text/css"/> <style> * { font-family: 'Verdana', sans-serif; margin: 0; padding: 0; -webkit-box-sizing: border-box; -moz-box-sizing: border-box; box-sizing: border-box; } ...... - Install Python 3.0.
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y python 3 //Run this command in any directory you want.
If Python 3 has been installed on CentOS 7.9, skip this step.
- Disable SELinux.
Installing the Migration Tool
- Download tool package centos2hce1-*.rpm from the Huawei Cloud open-source image site. Contact customer service to obtain the download link from O&M engineers.
The asterisk (*) indicates the version of the migration tool. In this example, centos2hce1-1.0.0-0.0.2.x86_64.rpm is used.
[root@localhost test]# wget https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/updates/x86_64/Packages/centos2hce1-1.0.0-0.0.2.x86_64.rpm //Download the centos2hce1-*.rpm package. [root@localhost test]# ls //Check whether the download is successful. centos2hce1-1.0.0-0.0.2.x86_64.rpm
- Install the migration tool.
- Configure the centos2hce1.conf file.
Configure the repository of HCE. It will be used for checking whether the repository can be accessed and updating RPM packages.
#iso as yum source link [repo_info] base_yum_url =https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/os/x86_64/ #iso as yum source repostr_hce1_1 = [base] name=hceversion baseurl=https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/os/x86_64/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 #released updates [updates] name=hce1_updates baseurl=https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/updates/x86_64/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 gpgkey=
To learn more about the parameters in the centos2hce1.conf file, see Appendix: Description of the .conf File.
Migrating the OS
- Back up the OS.
The migration to HCE 1.1 cannot be rolled back. Before performing the migration, you should back up CentOS including its system disk and data disks.
- Run the centos2hce1.py command to migrate the OS.
The migration takes 20 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the number and size of RPM packages to be updated and the download speed of RPM packages from the repository. Reserve sufficient time for the migration based on your environment.
[root@localhost home]# centos2hce1.py
If the following information is displayed, the migration was complete. If the migration failed, use the backup to restore data.
Figure 3 Command output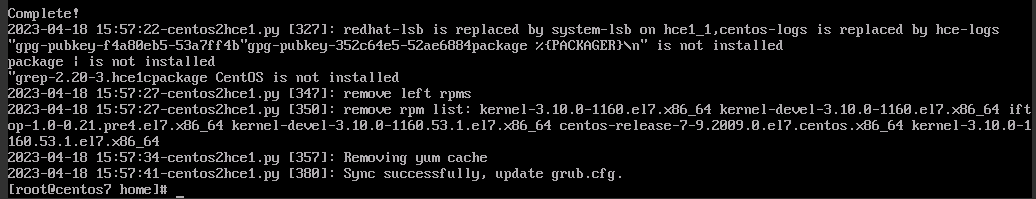
CentOS contains some RPM packages that are not provided by HCE 1.1. After you run the centos2hce1.py command to migrate the OS, these RPM packages are automatically deleted. If you want to retain them, run the -s skip command to migrate the OS.
- (Optional) Delete unnecessary RPM packages.
The following two RPM packages are not used during the migration and do not affect how the system runs. You can delete them.
Figure 4 Unused RPM packages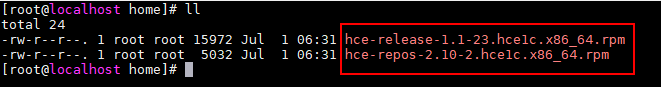 Figure 5 Deleting unused RPM packages
Figure 5 Deleting unused RPM packages
- Run the reboot command to restart the OS.
- Run the cat /etc/os-release command to check whether the migration was successful.
If the following information is displayed, the migration was successful.
Figure 6 Successful migration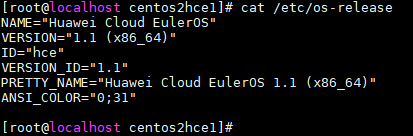
- (Optional) Enable SELinux.
Appendix: Description of the .conf File
#rpm lists for os migration
[rpm_lists]
#origin system must need rpms
baserpms_list = "basesystem initscripts hce-logos plymouth grub2 grubby" //The RPM packages required for the OS migration.
#old rpm and default conflict rpms //The conflicting RPM packages that may exist in the source OS during the migration.
oldrpms_list = centos-backgrounds centos-release-cr desktop-backgrounds-basic \
centos-release-advanced-virtualization centos-release-ansible26 centos-release-ansible-27 \
centos-release-ansible-28 centos-release-ansible-29 centos-release-azure \
centos-release-ceph-jewel centos-release-ceph-luminous centos-release-ceph-nautilus \
centos-release-ceph-octopus centos-release-configmanagement centos-release-dotnet centos-release-fdio \
centos-release-gluster40 centos-release-gluster41 centos-release-gluster5 \
centos-release-gluster6 centos-release-gluster7 centos-release-gluster8 \
centos-release-gluster-legacy centos-release-messaging centos-release-nfs-ganesha28 \
centos-release-nfs-ganesha30 centos-release-nfv-common \
centos-release-nfv-openvswitch centos-release-openshift-origin centos-release-openstack-queens \
centos-release-openstack-rocky centos-release-openstack-stein centos-release-openstack-train \
centos-release-openstack-ussuri centos-release-opstools centos-release-ovirt42 centos-release-ovirt43 \
centos-release-ovirt44 centos-release-paas-common centos-release-qemu-ev centos-release-qpid-proton \
centos-release-rabbitmq-38 centos-release-samba411 centos-release-samba412 \
centos-release-scl centos-release-scl-rh centos-release-storage-common \
centos-release-virt-common centos-release-xen centos-release-xen-410 \
centos-release-xen-412 centos-release-xen-46 centos-release-xen-48 centos-release-xen-common \
python3-syspurpose python-oauth sl-logos yum-rhn-plugin centos-indexhtml \
libreport-centos libreport-web libreport-plugin-mantisbt libreport-plugin-rhtsupport \
libreport hunspell-en-US hunspell-en policycoreutils-gui libcanberra-gtk2 cups \
NetworkManager-libreswan-gnome plymouth-graphics-libs avahi cups-lpd pinentry-qt \
librsvg2-devel libcanberra-gtk3 gnome-themes-standard wodim gsettings-desktop-schemas-devel \
avahi-ui-gtk3 freerdp-libs pulseaudio-utils gstreamer1-plugins-bad-free-gtk ghostscript-cups \
setools-console libxkbcommon-x11 cups plymouth-plugin-two-step pulseaudio-module-x11 ImageMagick-c++ \
cups-devel policycoreutils-sandbox PackageKit-gstreamer-plugin gtk3-immodule-xim avahi-glib avahi-autoipd \
mesa-libGLES foomatic libcanberra-devel plymouth-plugin-label PackageKit-gtk3-module colord avahi-gobject \
pinentry-qt4 avahi-ui-gtk3 plymouth-plugin-two-step ghostscript-cups ImageMagick-perl firewall-config \
plymouth-plugin-label redhat-redhat-lsb-corelsb vim-X11 dbus-x11 pulseaudio PackageKit-command-not-found libproxy-mozjs \
pinentry-gtk nm-connection-editor gtk2-immodule-xim wireshark-gnome pulseaudio-module-bluetooth pidgin-sipe freerdp kmod-kvdo \
redhat-lsb-core
#The following list contains the same symbol as centos/redhat
dstrpms_list = "hce-release hce-repos"
[log_conf]
# migration tool log common dir
migrate_common_dir = "/var/log/migrate-tool/" //The path for storing logs.
# migration tool classification log dir
migrate_classification_dir = %(migrate_common_dir)s/centos2hce1/
#iso as yum source link
[repo_info]
base_yum_url =https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/os/x86_64/ //The base yum URL used for checking the network connection.
#iso as yum source
repostr_hce1_1 = //The source path that provides the migration method.
[base]
name=hceversion
baseurl=https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/1.1/os/x86_64/ //The base yum URL used for obtaining the RPM packages.
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
gpgkey=
#released updates
[updates]
name=hce1_updates
baseurl=
gpgcheck=0
enabled=0
gpgkey=
#additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=hce1_extras
baseurl=
gpgcheck=0
enabled=0
gpgkey=
# plus packages provided by Huawei Linux dev team
[plus]
name=hce1_plus
baseurl=
gpgcheck=0
enabled=0
gpgkey=
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





