Creating an Enterprise Router
Scenarios
Create an enterprise router.
Procedure
- Go to the enterprise router list.
- Click Create Enterprise Router in the upper right corner.
The Create Enterprise Router page is displayed.
Figure 1 Create Enterprise Router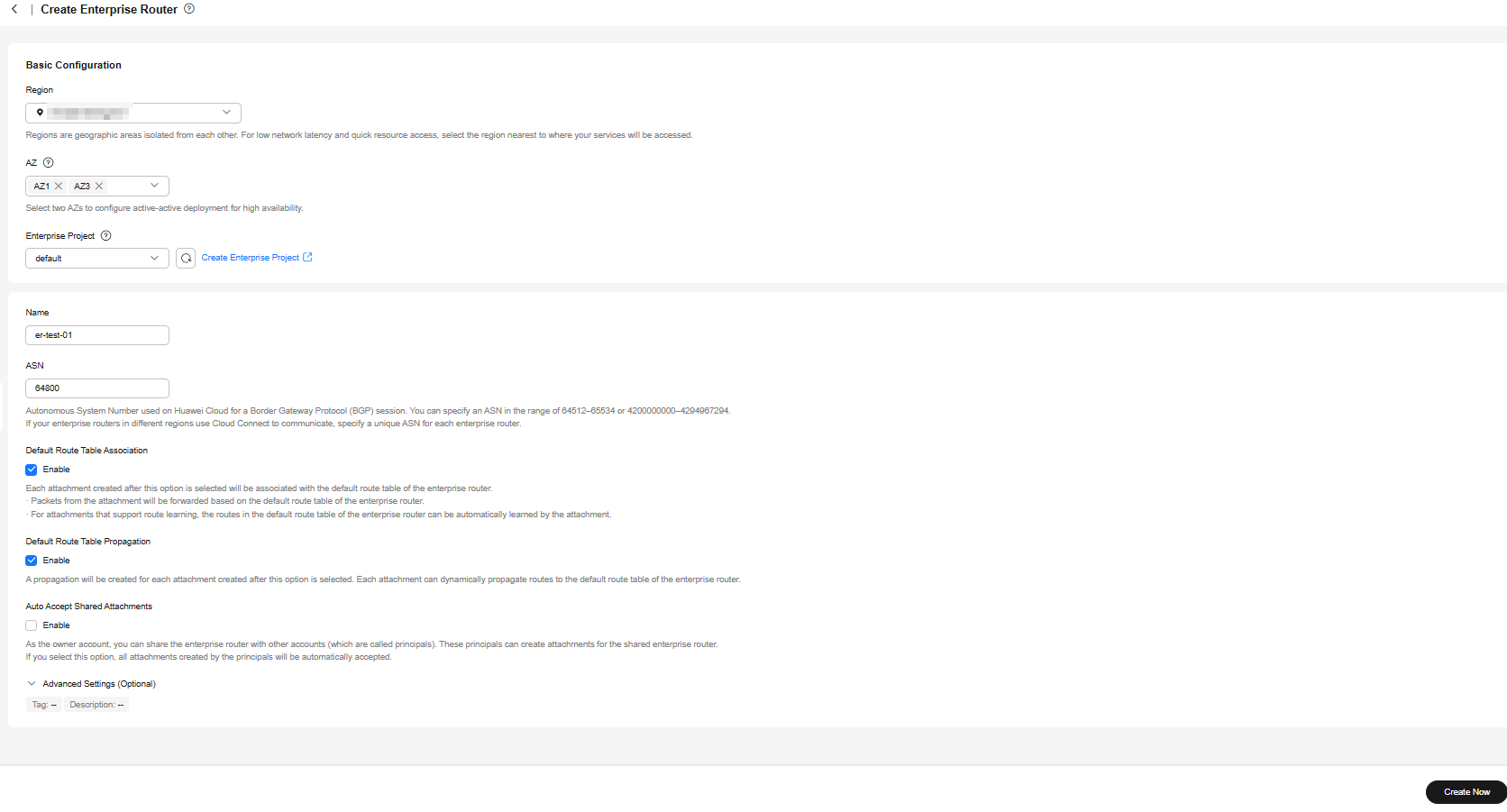
- Configure the parameters based on Table 1.
Table 1 Parameters for creating an enterprise router Parameter
Setting
Example Value
Region
Mandatory
Select the region nearest to you to ensure the lowest latency possible.
CN-Hong Kong
AZ
Mandatory
An AZ is a physical location where resources use independent power supplies and networks. AZs are physically isolated but interconnected through an internal network. Each region contains multiple AZs. If one AZ is unavailable, the other AZs in the same region continue to provide services.
We recommend you to select two AZs. The enterprise router will be deployed in both AZs that work in active-active mode, ensuring reliability and disaster recovery.
Traffic in an AZ is preferentially transmitted to the enterprise router in the same AZ to reduce latency.
AZ1
AZ2
Name
Mandatory
Enter a name for the enterprise router. The name:- Must contain 1 to 64 characters.
- Can contain letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.).
er-test-01
ASN
Mandatory
An autonomous system is an IP network that is managed by an entity and has the same route policy. On a BGP network, each autonomous system is assigned a unique ASN to differentiate them.
Specify a dedicated ASN in the range of 64512-65534 or 4200000000-4294967294.
Networks in the same region can be considered as an AS.
When Direct Connect and Enterprise Router are used to set up a hybrid cloud network, it is recommended that you set the ASN of the enterprise router different from the BGP ASN of the Direct Connect virtual gateway. If there are multiple Direct Connect connections associated with the enterprise router and the connections do not work in load balancing or active/standby mode, set different BGP ASNs for the virtual gateways of these connections.
If your enterprise routers in different regions use a central network to communicate, you need to specify a unique ASN for each router.
64800
Default Route Table Association
Optional
Enabled by default
Enabling Default Route Table Association can simplify network configurations. After this function is enabled:- An enterprise router automatically comes with a route table named defaultRouteTable. By default, this route table is the default association route table.
After the enterprise router is created, you can create a custom route table and set it as the default association route table to replace the original one if needed. For details, see Modifying an Enterprise Router.
- If you create an attachment to this enterprise router, the attachment will be automatically associated with the default association route table.
After the association:
- Packets from the attachment are forwarded through the routes specified in the associated route table.
- If the type of the attachment is peering connection, virtual gateway, or VPN gateway, the attachment automatically learns routes from the enterprise router.
For more types of attachments that support route learning, see How Enterprise Routers Work.
- If the type of the attachment is VPC, you need to add routes to the route table of the VPC for traffic to route through the enterprise router.
Enable
Default Route Table Propagation
Optional
Enabled by default
Enabling Default Route Table Propagation can simplify network configurations. After this function is enabled:
- An enterprise router automatically comes with a route table named defaultRouteTable. By default, this route table is the default propagation route table.
If both Default Route Table Association and Default Route Table Propagation are enabled, defaultRouteTable is not only the default association route table but also the default propagation route table.
After the enterprise router is created, you can create a custom route table and set it as the default propagation route table to replace the original one if needed. For details, see Modifying an Enterprise Router.
- If you create an attachment to this enterprise router, the attachment will be automatically propagated to the default propagation route table.
After the propagation:
- If it is a peering connection, virtual gateway, or VPN gateway attachment, the enterprise router automatically learn routes from the attachment.
For details about route learning of more types of attachments, see How Enterprise Routers Work.
- If the type of the attachment is VPC, the enterprise router uses the VPC CIDR block as the destination of a route.
- If it is a peering connection, virtual gateway, or VPN gateway attachment, the enterprise router automatically learn routes from the attachment.
Enable
Auto Accept Shared Attachments
Optional
As the owner, you can share your enterprise router with the principals. These principals can create attachments for your enterprise router.- If you do not select this option, you must manually accept attachments to this enterprise router from the accounts that this enterprise router is shared with.
- If you select this option, the attachments from the accounts that this enterprise router is shared with will be automatically accepted.
For details, see Sharing Overview.
Disable
Enterprise Project
Mandatory
Select an enterprise project that the enterprise router will be added to.
An enterprise project facilitates project-level management and grouping of cloud resources and users. The default project is default.
default
Tag
Optional
Add tags to help you quickly find your enterprise router.
For details, see Overview.
NOTE:If you have configured tag policies for enterprise routers, you need to add tags to your enterprise routers based on the tag policies. If you add a tag that does not comply with the tag policies, enterprise routers may fail to be created. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies. For details about tag policies, see Tag Policy Overview.
Tag key: test
Tag value: 01
Description
Optional
Describe the enterprise router for easy identification.
-
- Click Create Now.
- Confirm the enterprise router configurations and click Submit.
The enterprise router list is displayed.
- Check the enterprise router status.
If the status changes from Creating to Normal, the enterprise router is successfully created.
Follow-Up Operations
- After an enterprise router is created, attach network instances to the enterprise router and configure routes. For details, see Getting Started.
- If Default Route Table Association and Default Route Table Propagation are not enabled for an enterprise router, you need to:
- Create a custom route table for the enterprise router. For details, see Creating a Route Table.
- Create associations for the attachments of the enterprise router. For details, see Creating an Association for an Attachment in a Route Table.
- Use either of the following methods to add routes for the attachment to the route table:
- Create a propagation in the route table. For details, see Creating a Propagation for an Attachment in the Route Table.
After the propagation is created, routes of the attachments to the enterprise router will be automatically propagated to the route table of the enterprise router.
- Add static routes to the route table. For details, see Creating a Static Route.
- Create a propagation in the route table. For details, see Creating a Propagation for an Attachment in the Route Table.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





