Overview
Security Group
A security group is a collection of access control rules for ECSs that have the same security protection requirements and that are mutually trusted. After a security group is created, you can create various access rules for the security group, these rules will apply to all ECSs added to this security group.
When creating an ECS, you must associate it with a security group. If no security group has been created yet, a default security group will be automatically created and associated with the ECS. You can also create a security group based on service requirements and associate it with the ECS. An ECS can be associated with multiple security groups, and traffic to and from the ECS is matched by priority in a descending order.
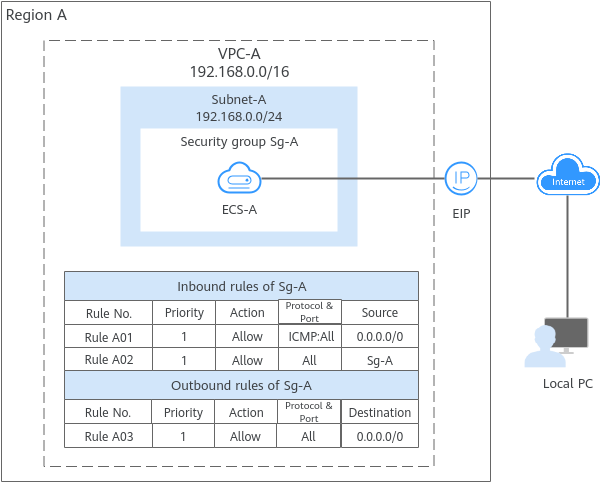
- Security group Sg-A has a custom inbound rule to allow ICMP traffic to ECS-A from your PC over all ports. However, the security group does not have rules that allow SSH traffic to ECS-A so you cannot remotely log in to ECS-A from your PC.
- If ECS-A needs to access the Internet through an EIP, the outbound rule of Sg-A must allow all traffic from ECS-A to the Internet.

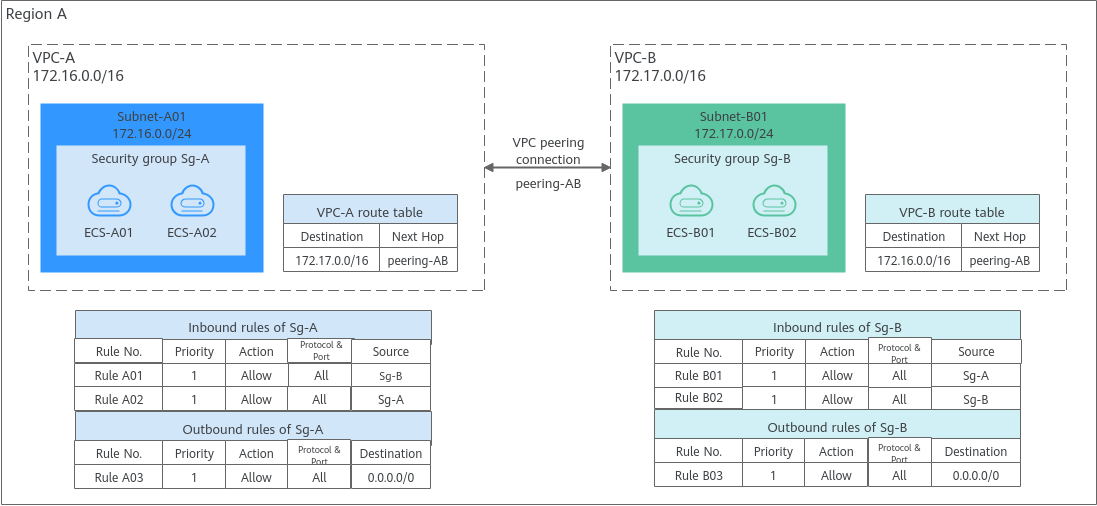
- A security group works only when the network communication is normal. If two ECSs are in the same security group but in different VPCs, the security group does not take effect. You can use a VPC peering connection to connect the two VPCs first. For details, see VPC Connectivity Options.
Security Group Rules
After a security group is created, you can add rules to the security group. A rule applies either to inbound traffic (ingress) or outbound traffic (egress). After ECSs are added to the security group, they are protected by the rules of that group. For details about how security group rules work, see How Security Groups Work.
Each security group has default rules. For details, see Default Security Groups and Rules. You can also customize security group rules. For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules.
- Inbound rules: control traffic to the instances in a security group.
- Outbound rules: control traffic from the instances in a security group to access external networks.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Action |
Allow or deny. If the protocol, port, and source or destination of the traffic matches a security group rule, the traffic will be allowed or denied. |
|
Priority |
The value range is from 1 to 100. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. Security group rules are matched by priority and then by action. Deny rules take precedence over allow rules. To learn more, see Security Group and Security Group Rule Overview. |
|
Type |
IPv4 or IPv6. |
|
Protocol & Port |
Network protocol type and port range.
|
|
Source/Destination |
Source address of traffic in the inbound direction or destination address of traffic in the outbound direction.
The source or destination can be an IP address, security group, or IP address group.
|
Security Group Examples
You can allow given IP addresses to access instances in a security group, or allow access from another security group to enable instances in different security groups to communicate with each other. You can add security group rules to flexibly control the traffic in and out of a network to ensure network security. Here are some examples on how security groups can be used.
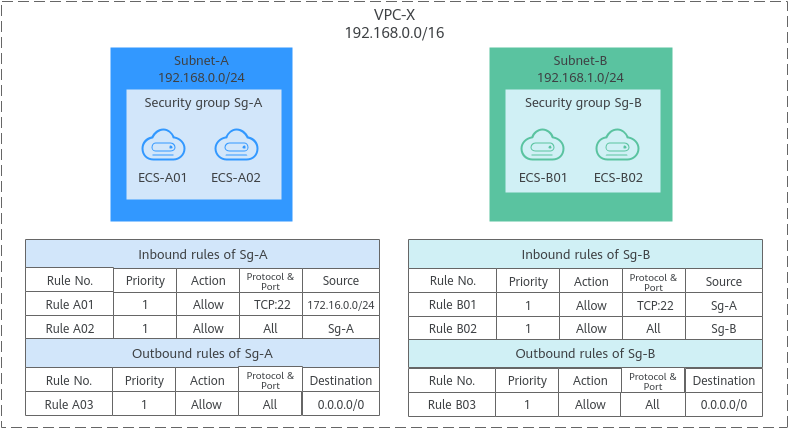
- Inbound rule A01 of Sg-A allows traffic from IP addresses in 172.16.0.0/24 to access SSH port 22 of the ECSs in Sg-A for remotely logging in to these ECSs.
- Inbound rule A02 of Sg-A allows the ECSs in this security group to communicate with each other using any protocol and port.
- Inbound rule B01 of Sg-B allows the ECSs in Sg-A to access the ECSs in Sg-B SSH port 22. That is, ECSs in Subnet-A can remotely log in to the ECSs in Subnet-B.
- Inbound rule B02 of Sg-B allows the ECSs in this security group to communicate with each other using any protocol and port. That is, ECSs in Subnet-B can communicate with each other.
- The outbound rules of both security groups allow all traffic from the ECSs in the security groups.
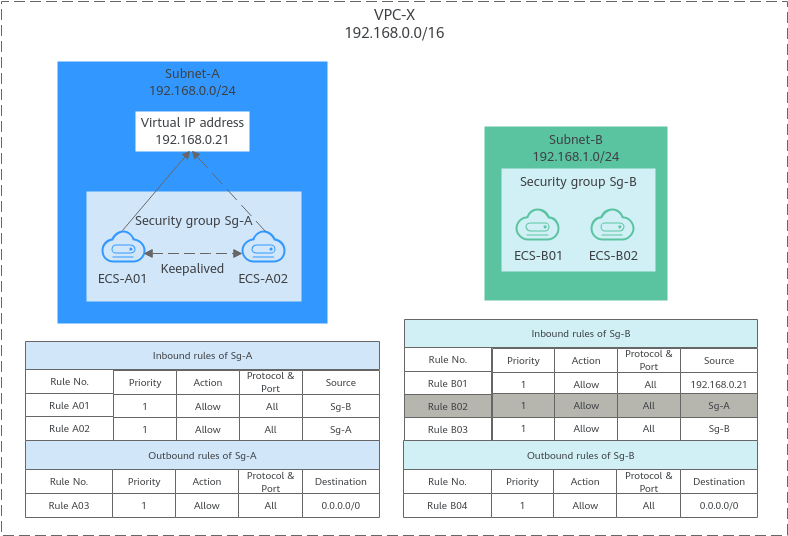
If you use an intermediate network instance to forward traffic between instances in different subnets, setting the source of the inbound rule to the security group associated with the peer instance does not allow the instances to communicate with each other. If you set the source of inbound rules to the security groups associated with the ECSs, the ECSs in the two security groups cannot communicate with each other. To enable communication between them, set the source to the private IP address or subnet CIDR block of the virtual IP address.
- Inbound rule A01 of Sg-A allows ECSs in Sg-B to access ECSs in Sg-A using any protocol over any port.
- Sg-B has the following inbound rules:
- Rule B02: Allows ECSs in Sg-A to use private IP addresses to access ECSs in Sg-B. However, in this network, ECSs in Sg-A are supposed to communicate with ECSs in Sg-B through virtual IP address 192.168.0.21. However, rule B02 does not allow traffic from this virtual IP address.
- Rule B01: Allows traffic from virtual IP address 192.168.0.21 to ECSs in Sg-B using any protocol over port. In this networking, you can also set the source to 192.168.0.0/24, the CIDR block of Subnet-A.
- Rule A01 with Source to Sg-B to allow ECSs in Sg-B to access ECSs in Sg-A.
- Rule B01 with Source to Sg-A to allow ECSs in Sg-A to access ECSs in Sg-B.
Security Group Configuration Guide
If you use security groups for the first time, you are advised to perform the following operations.
|
Scenario |
Description |
Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Creating a security group |
If the default security group and existing custom security groups do not meet service requirements, you can create a security group. |
NOTE:
When creating an ECS, you can use templates to quickly create security groups. For details, see Creating a Security Group. |
|
Configuring security group rules |
After a security group is created, if the rules in the security group cannot meet service requirements, you can add or delete inbound and outbound rules, and modify the action, priority, protocol & port of the existing security group rules as required. |
|
|
Associating an ECS with a security group |
When creating an ECS, associate it with at least one security group. The inbound and outbound traffic of the ECS is protected by the security group. If the security group does not meet service requirements, you can change the security group associated with the ECS. |
Constraints on Using Security Groups
- For better network performance, you are advised to associate an instance with no more than five security groups.
- A security group can have no more than 6,000 instances associated, or its performance will deteriorate.
- For inbound rules of a security group, the sum of the rules with Source set to Security group, of the rules with Source set to IP address group, and of the rules with inconsecutive ports, cannot exceed 120. Excess rules will not take effect. If there are both IPv4 and IPv6 security group rules, up to 120 rules can be added for each type.
The limits on outbound security group rules are the same as those on inbound rules.
For example, to add inbound IPv4 rules to a security group (Sg-A), you can refer to Table 3 for rules that meet the restrictions. Of these rules, rule A02 uses inconsecutive ports (TCP: 22,25,27) and security group Sg-B as the source. In this case, only one quota is occupied.
Table 3 Inbound security group rules Rule No.
Action
Type
Protocol & Port
Source
Rule A01
Allow
IPv4
All
Current security group: Sg-A
Rule A02
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 22,25,27
Another security group: Sg-B
Rule A03
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 80-82
IP address group: ipGroup-A
Rule A04
Allow
IPv4
TCP: 22-24,25
IP address: 192.168.0.0/16
- If you specify an IP address group or inconsecutive ports for a security group rule, the rule is only applied for certain ECSs. For details, see Table 4.
Table 4 Scenarios that security group rules do not take effect Rule Configuration
ECS Type
Source or Destination is set to IP address group.
The following x86 ECS types are not supported:- General computing (S1, C1, and C2 ECSs)
- Memory-optimized (M1 ECSs)
- High-performance computing (H1 ECSs)
- Disk-intensive (D1 ECSs)
- GPU-accelerated (G1 and G2 ECSs)
- Large-memory (E1, E2, and ET2 ECSs)
Port is set to non-consecutive ports.
The following x86 ECS types are not supported:
- General computing (S1, C1, and C2 ECSs)
- Memory-optimized (M1 ECSs)
- High-performance computing (H1 ECSs)
- Disk-intensive (D1 ECSs)
- GPU-accelerated (G1 and G2 ECSs)
- Large-memory (E1, E2, and ET2 ECSs)
Kai1 Kunpeng ECSs do not support inconsecutive ports.
If you use inconsecutive port numbers in a security group rule of a Kai1 Kunpeng ECS, this rule and rules configured after this one do not take effect.
If you configure security group rule A with inconsecutive ports 22,24 and then configure security group rule B with port 9096, both rule A and rule B do not take effect.

- For details about x86 ECSs, see ECS Specifications (x86).
- For details about Kunpeng ECSs, see ECS Specifications (Kunpeng).
- Traffic from load balancers is not restricted by network ACL and security group rules if:
Transfer Client IP Address is enabled for the listeners of a load balancer.
The load balancer can still forward traffic to backend servers, even if there is a rule that denies traffic from the load balancer to the backend servers.
Helpful Links
- Default Security Groups and Rules
- Security Group Configuration Examples
- Common ECS Ports
- Configuring Security Group Rules
- Changing a Security Group
- Adding ECSs to One or More Security Groups
- Removing Instances from One or More Security Groups
- Viewing the Details of a Security Group
- Why Cannot My Windows ECS Access the Internet?
- Firewall Configuration Issues
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot