Managing Intelligent Analysis Assistants
You can manage intelligent analysis assistants in a personalized manner. This includes viewing basic information, editing or deleting them, and exporting their Q&A.
Viewing Basic Information About an Intelligent Analysis Assistant
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > Intelligent Analysis Assistants.
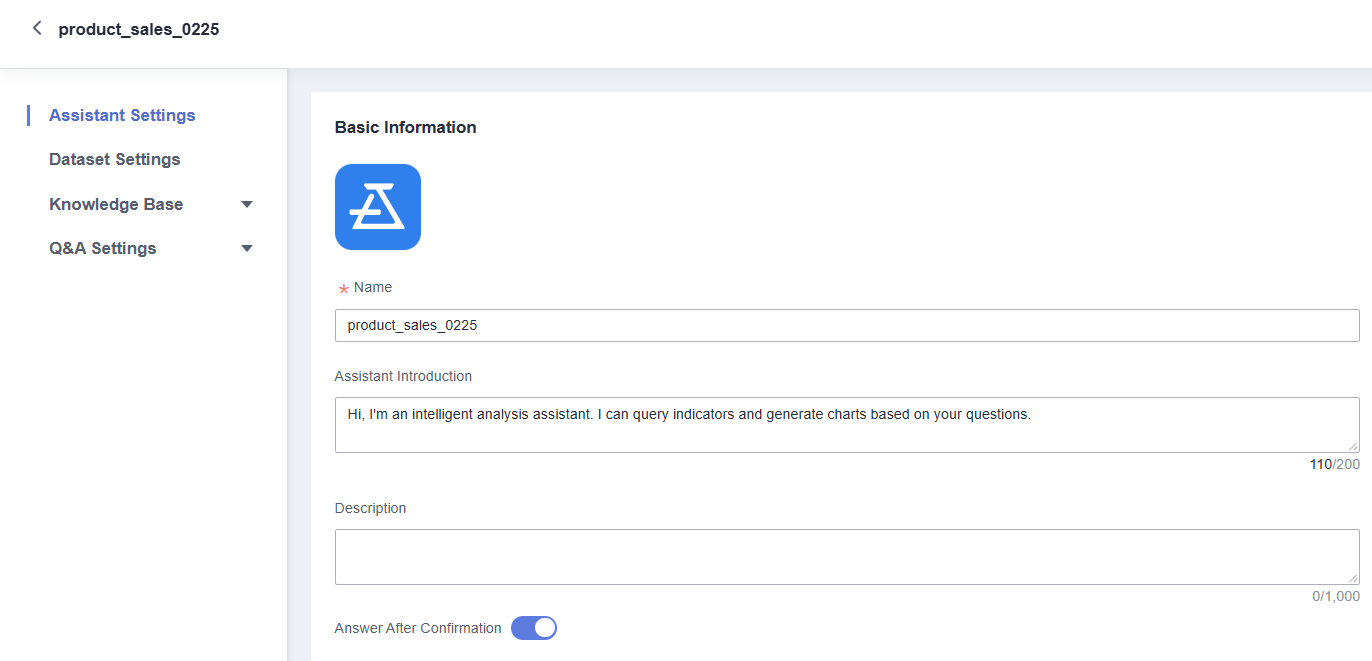
- Locate the intelligent analysis assistant whose basic information you want to view and click Edit in the Operation column. On the displayed page, view its basic information (Figure 1). For the basic information parameters, see Table 1.
Table 1 Basic information parameters Parameter
Description
Name
Name of the intelligent analysis assistant. The name can contain up to 32 characters. Only letters, numbers, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed.
Assistant Introduction
Custom greeting for the intelligent analysis assistant on the Q&A page. The greeting can contain up to 200 characters.
Description
Description of the intelligent analysis assistant. Enter up to 1,000 characters. You can enter the purpose and use case of the intelligent analysis assistant to facilitate subsequent management.
Answer After Confirmation
Whether to first verify if the intelligent assistant accurately understands the user's question before generating an answer.
Editing an Intelligent Analysis Assistant
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > Intelligent Analysis Assistants.
- Locate the intelligent analysis assistant you want to edit and click Edit in the Operation column.
- Edit parameters and click Synchronization in the upper right corner of the page to re-synchronize the table structure semantic configuration.
Figure 2 Editing an intelligent analysis assistant
Deleting an Intelligent Analysis Assistant
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > Intelligent Analysis Assistants.
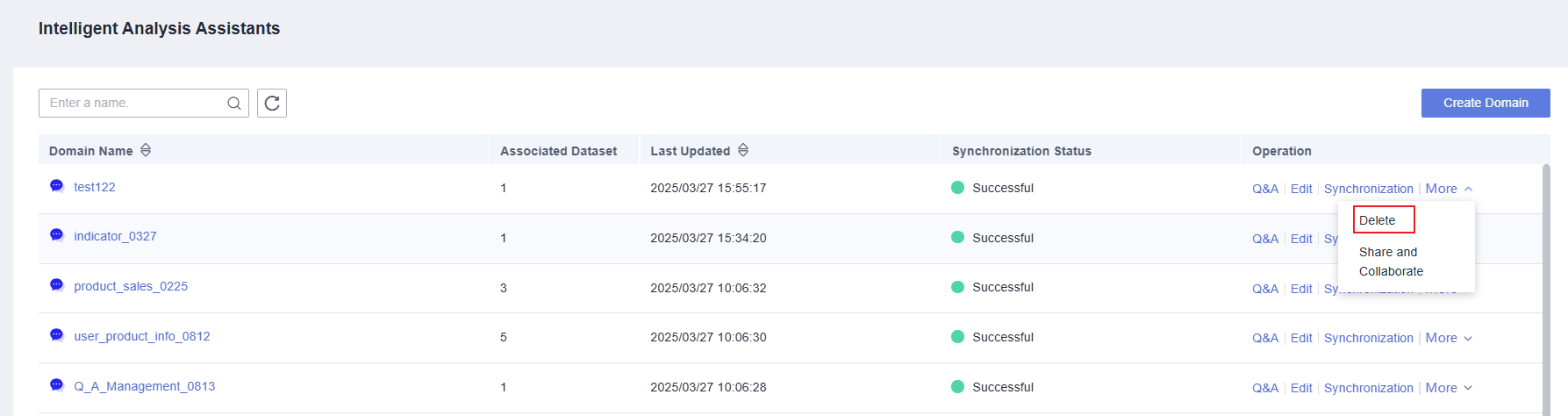
- Locate the intelligent analysis assistant you want to delete, click More in the Operation column, and select Delete (Figure 3).
- In the dialog box that appears, click OK.
Exporting Questions from an Intelligent Analysis Assistant
You can export the questions and analysis process of an intelligent analysis assistant. The analysis process includes keyword rewriting, retrieval results, prompts, semantic SQL, DQE, and SQL.
- Constraints:
- To use this function, you must have the administrator permissions.
- Procedure:
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > Question Management.
Figure 4 Question management page
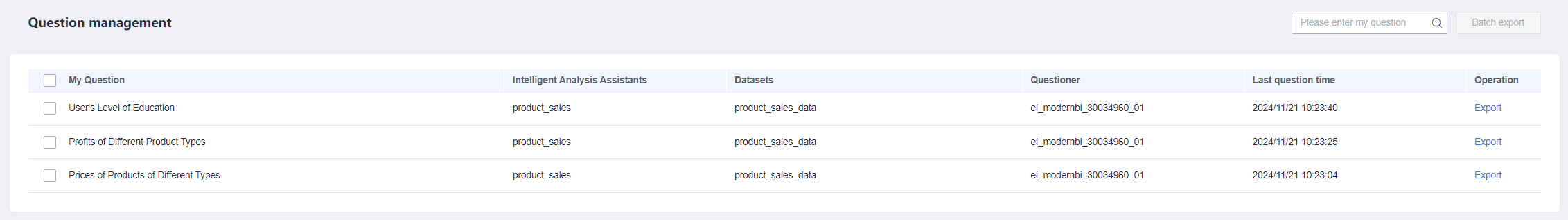
- On this page, locate the question you want to export and click Export in the Operation column. In the dialog box that appears, click OK. Then, the questions and analysis process of the intelligent analysis assistant are exported. Table 2 describes the parameters in the analysis process.
Table 2 Analysis process parameters Parameter
Description
Keyword Rewrite
You can configure question and answer keywords in the assistant. After multi-turn rewriting, the system will check if the question contains any user-defined keywords. If so, the keywords in the question will be replaced with the configured replacement content.
Grounded
The assistant will search and retrieve relevant data tables, fields, and enumerations based on your query. This search step simplifies the input for the model compared to directly inputting all dataset schemas and enumeration information. It improves the effectiveness of the NL2SQL model and reduces inference latency.
Prompt
Based on prompt word templates and user instructions, as well as search results, the assistant dynamically generates corresponding prompt words for each user query.
Semantics SQL
The foundation model performs inference for the NL2SQL task based on prompt words, generating semantic SQL. Note that semantic SQL is generated based on the dataset schema and is not directly executable physical SQL.
Semantic DQE
Semantic SQL is transformed into data query expressions (DQEs). Compared to SQL, DQE is a more structured data structure and is a universal data query structure in DataArts Insight. During the transformation, semantic SQL is post-processed to validate and correct any illusions or errors, improving the accuracy of the entire data query.
Physical SQL
DQE is further transformed into physical SQL that can be executed by the target data source. This transformation includes mapping the dataset schema to the physical table schema, adapting to the target data source dialect, injecting default filtering conditions and access control conditions.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Q&A Management > Question Management.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot