Collecting CCI Logs Using LTS
CCI 2.0 works with LTS to collect application logs and report these logs to LTS so that you can use them for troubleshooting.
Log Collection Reliability
The log system's main purpose is to record all stages of data for service components, including startup, initialization, exit, runtime details, and exceptions. It is primarily employed in O&M scenarios for tasks like checking component status and analyzing fault causes.
Standard streams (stdout and stderr) and local log files use non-persistent storage. However, data integrity may be compromised due to the following risks:
- Log rotation and compression potentially deleting old files
- Temporary storage volumes being cleared when Kubernetes pods end
- Automatic OS cleanup triggered by limited node storage space
While the Cloud Native Log Collection add-on employs techniques like multi-level buffering, priority queues, and resumable uploads to enhance log collection reliability, logs could still be lost in the following situations:
- The service log throughput surpasses the collector's processing capacity.
- The service pod is abruptly terminated and reclaimed by CCE.
- The log collector pod experiences exceptions.
The following lists some recommended best practices for cloud native log management. You can review and implement them thoughtfully.
- Use dedicated, high-reliable streams to record critical service data (for example, financial transactions) and store the data in persistent storage.
- Avoid storing sensitive information like customer details, payment credentials, and session tokens in logs.
Constraints
|
Scenario |
Instruction |
|---|---|
|
CCE container logs and CCI container logs |
You can collect the following three types of logs:
NOTICE:
For the pods of workloads scheduled to CCI, only container standard output and container file logs can be collected. |
|
Types of logs that cannot be collected |
|
|
Overlong logs |
A single log cannot exceed 250 KB. If multi-line logs are collected, the length of each line will be calculated separately. If the length of a line exceeds 250 KB, the log will be discarded. |
|
Overlong log file name |
In a container, if a log name exceeds 190 characters, the log will not be collected. If there are logs whose name contains 180 to 190 characters, only the first log can be collected. |
|
Maximum number of collected files |
In a single pod, no more than 2,000 log files can be collected by all log collection policies. |
|
Log collection rate |
In a single pod, up to 20,000 single-line logs can be collected per second, up to 2,000 multi-line logs can be collected per second, and the log size cannot exceed 10 MiB per second. Service quality cannot be ensured if any of these limits is exceeded. |
|
Log collection performance consumption |
To better collect logs, reserve the required amount of memory for the pod.
|
|
Log collection before a container is stopped |
When a container is stopped, if log collection is delayed due to network latency or high resource usage, some logs generated before the container is stopped may be lost. |
|
Log collection of init containers |
Logs of init containers cannot be collected. |
|
Logs of CCI Kunpeng pods |
Logs of Kunpeng pods cannot be collected. |
Procedure
- Install two add-ons: CCE Cloud Bursting Engine for CCI and Cloud Native Log Collection.
- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the name of the target CCE cluster to go to the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons.
- Select the CCE Cloud Bursting Engine for CCI add-on and click Install.
The version must be v1.5.61 or later.
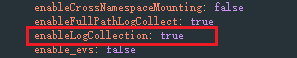
- Click Edit for the add-on to edit the YAML file, change the value of enableLogCollection to true, and click Submit.
- On the Add-ons page, select the Cloud Native Log Collection add-on and click Install.
- Create a workload on the CCE console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Workloads.
- Click Create Workload. For details, see Creating a Workload.
- Configure the parameters. For details, see Scheduling Workloads to CCI 2.0.
- Create a log collection policy.
- In the navigation pane, choose Logging.
- Click View Log Policy. On the displayed page, click Create Logging Policy.
- Configure the parameters and click OK.
Workloads scheduled to CCI do not support hot update of log policies. After a log collection policy is updated, redeploy the pods to apply the modification.
- View the reported logs in Logging.
For details about logging, see Cloud Native Log Collection.
Enabling Full-Path Collection
If the collected container logs have the same name but different collection paths, the correct logs cannot be located. You can enable full path collection.
- To collect the logs of pods of workloads scheduled to CCI, the version of the Cloud Native Log Collection must be v1.7.6 or later, and full-path log connection is enabled through this add-on.
- Enabling full-path collection affects performance. If the current log volume is close to or exceeds the log collection performance specifications, you are advised not to enable this function.
- On the CCE console, select a CCE cluster and click its name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons.
- Select the CCE Cloud Bursting Engine for CCI add-on and click Edit.
- In the upper left corner, click Edit YAML.
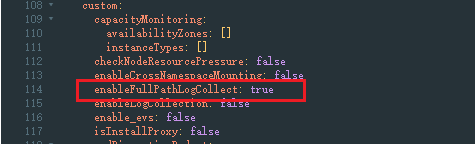
- Change the value of enableFullPathLogCollect to true and click Submit.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





