Customizing APIs
You can encapsulate scripts and flows into custom REST APIs and publish them. After encapsulation, URLs are more standard for easy calling by third-party systems.
Customizing APIs
- Log in to the application designer by referring to Logging In to the Application Designer.
- In the navigation pane, choose Integrations. Click the plus sign (+) next to Open API.
Alternatively, choose Home > Open APIs.
- Complete the configuration and click Save.
Figure 1 Creating an open API
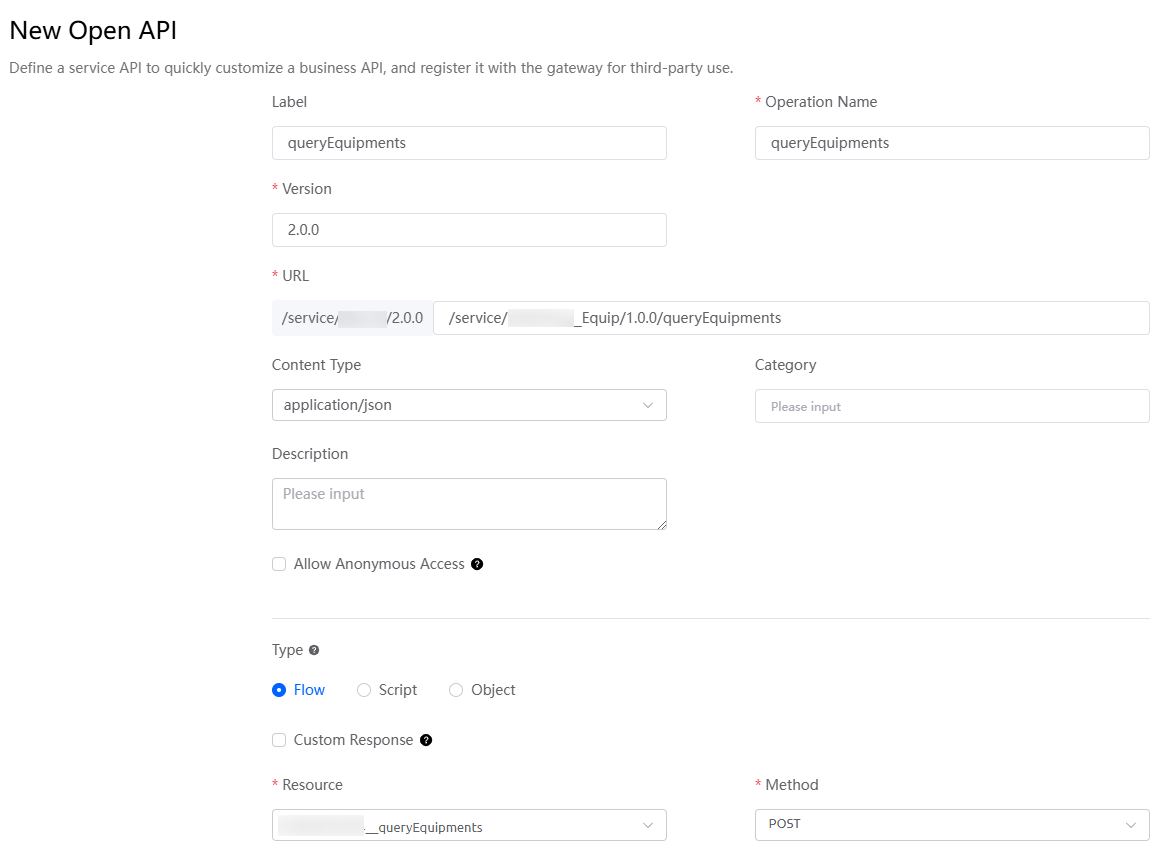
Table 1 Parameters for creating an open API Parameter
Description
Label
API label.
Value: 1–64 characters.
Operation Name
API operation name. The naming requirements are as follows:
- The value contains a maximum of 40 characters.
- Start with a letter and can contain letters, digits, and underscores (_). It cannot end with an underscore (_).
Version
API version, which is in the x.y.z format.
URL
API path, which starts with /service/{namespace}__{application name}/{version}.
Content Type
Body type in a request.
multipart/form-data and binary-data are used for the file upload API. If either of them is selected, only POST scripts can be invoked.
Category
Category to which this API belongs.
Description
Description of this API.
Allow Anonymous Access
Indicates whether the API can be accessed anonymously in the runtime environment.
If this option is selected, anonymous access is allowed. If you access the API using a subdomain name of the runtime environment with invalid token authentication information, you can access it as an anonymous user without CSRF verification. The profile of anonymous users is Anonymous User Profile. Ensure that this profile has the service permission credential or related resource permissions for accessing the API. For example, add a service permission credential required by the API to Anonymous User Profile to access the API anonymously using the subdomain name of the runtime environment.
For example, the URL of the login API (used to log in to applications) is /service/namespace__MyApp/1.0.0/login, and the subdomain name of the runtime environment is test.example.com. To allow anonymous access to this API, select Allow Anonymous Access. If the API's service permission credential is configured for Anonymous User Profile, anonymous users can access the API through https://test.example.com/service/namespace__MyApp/1.0.0/login.
When configuring anonymous access, comply with the following rules:
- If an account needs to support anonymous access to the custom API, the subdomain name of the runtime environment must be set.
- A custom API that allows anonymous access is preferentially accessed with valid authentication profiles.
- CSRF verification is not required for anonymous users to access custom APIs.
- Regardless of the access mode, profile verification after identity authentication is the same. If the API has service permission credentials, the system checks whether the user profile has the credentials.
Type
Resource type. Only Flow APIs can be called in flows. Other APIs can only be called through API request.
- Flow: indicates that a flow is called using this API.
- Script: indicates that a script is called using this API.
- Object: indicates that the custom URL is used to operate object data, including adding, deleting, modifying, and querying object data.
Custom Response
Indicates whether to format the response returned after the URL is called. If this option is selected, the response is formatted. The resCode, resMsg, and result outer information is deleted, and only the returned messages are transparently transmitted.
- If Custom Response is not selected, the following response is returned:
{ "resCode": "0", "resMsg": "Success", "result": [ { "equipments": [ { "createdBy": "aaa", "createdBy.__objectType": "User" }, { "createdBy": "aaa", "createdBy.__objectType": "User" } ], "total": "2" } ] } - If Custom Response is selected, only the following response is returned:
{ "equipments": [ { "createdBy": "aaa", "createdBy.__objectType": "User" }, { "createdBy": "aaa", "createdBy.__objectType": "User" } ], "total": "2" }
Resource
Select the resource to be bound based on Type, such as script, flow, or object name.
If the flow or script to be bound cannot be found, check if it is activated. If not, go to the flow or script design page and click
 in the upper-left corner to activate it.
in the upper-left corner to activate it.Object Operation
This parameter is displayed only when Type is set to Object.- Insert Record: Add object data.
- Update or Insert Record: Update or add object data.
- Update By ID: Update object data by record ID.
- Delete By ID: Delete object data by record ID.
- Query By ID: Query object data by record ID.
- Update By Condition: Update object data by condition.
- Delete By Condition: Delete object data by condition.
- Query By Condition: Query object data by condition.
Method
HTTP method of the API.- GET: Requests a server to return specified resources.
- PUT: Requests a server to update specified resources.
- POST: Requests a server to add resources or perform special operations.
- DELETE: Requests a server to delete specified resources.
- PATCH: Requests a server to update parts of specified resources. If the resource was not found, a new resource will be created.
- Choose Integrations from the navigation pane, click
 next to the created API, and select Check. The preview page is displayed.
next to the created API, and select Check. The preview page is displayed. - Click
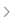 to view the API information.
to view the API information. - Click the try button to simulate API calling.
Request parameters and the response body of the API are the input and output parameters configured for the bound resources, such as scripts and flows.Figure 2 API request parameters
 Figure 3 API returned messages
Figure 3 API returned messages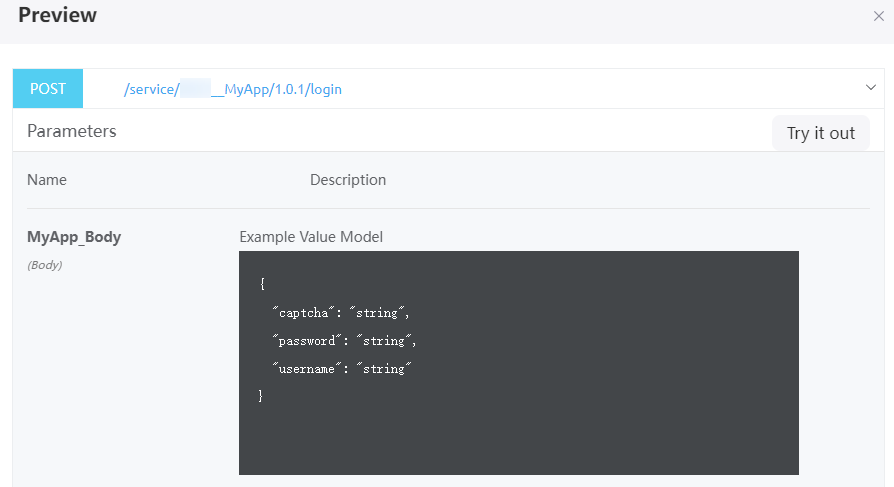
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





