A Cluster is Unavailable Due to Improper Shard Allocation
Symptom
The cluster status is Unavailable.


Possible Causes
Some index shards in the cluster are not properly allocated.
Procedure
- Use Kibana to access the faulty cluster. On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the GET /_recovery?active_only=true command to check whether the cluster is restoring the backup.
- If {"index_name":{"shards":[{"id":25,"type":"... is returned, there are indexes being restored using backup. Wait until the backup restoration is complete. If the cluster status is still Unavailable, go to the next step.
- If { } is returned, the cluster is not performing backup restoration. Go to the next step.
- Run the GET _cluster/allocation/explain?pretty command to check why some index shards are not allocated based on the returned information.
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
index
Index name
shard
Shard ID
current_state
Shard status
allocate_explanation
Shard allocation explanation
explanation
Explanation
Table 2 Faults description Symptom
Causes
Procedure
explanation: no allocations are allowed due to cluster setting [cluster.routing.allocation.enable=none]
The cluster allocation policy forbids the allocation of all shards.
For details, see cluster.routing.allocation.enable in Incorrect Shard Allocation Policy Configuration.
explanation: too many shards [3] allocated to this node for index [write08]index setting [index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node=3]
The number of shards that can be allocated to each data node from a single index in the cluster is too small, which does not meet the index shard allocation requirements.
For details, see index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node in Incorrect Shard Allocation Policy Configuration.
explanation: too many shards [31] allocated to this node, cluster setting [cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node=30]
The number of shards that can be allocated to each data node in the cluster is too small.
For details, see cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node in Incorrect Shard Allocation Policy Configuration.
explanation: node does not match index setting [index.routing. allocation. include] filters [box_type:"hot"]
Index shards can only be allocated to data nodes labeled with hot. If a cluster has no nodes labeled with hot, shards cannot be allocated.
For details, see index.routing.allocation.include in Incorrect Shard Allocation Policy Configuration.
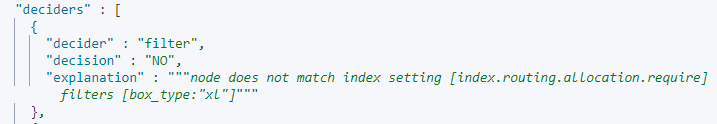
explanation: node does not match index setting [index.routing. allocation. require] filters [box_type:"xl"]
Index shards can only be allocated to data nodes with specified labels. If a cluster has no such nodes, shards cannot be allocated.
For details, see index.routing.allocation.require in Incorrect Shard Allocation Policy Configuration.
explanation: [failed to obtain in-memory shard lock]
Generally, this problem occurs when a node is removed from a cluster for a short time and then added back to the cluster. In addition, a thread is performing a long-term data writing to a shard, such as bulk or scroll. When the node is added to the cluster again, the master node cannot allocate the shard because the shard lock is not released.
For details, see shard lock error.
explanation: node does not match index setting [index.routing.allocation.include] filters [_tier_preference:"data_hot OR data_warm OR data_cold"]
The configuration of an index does not match the cluster version.
For details, see Inconsistent index parameter version.
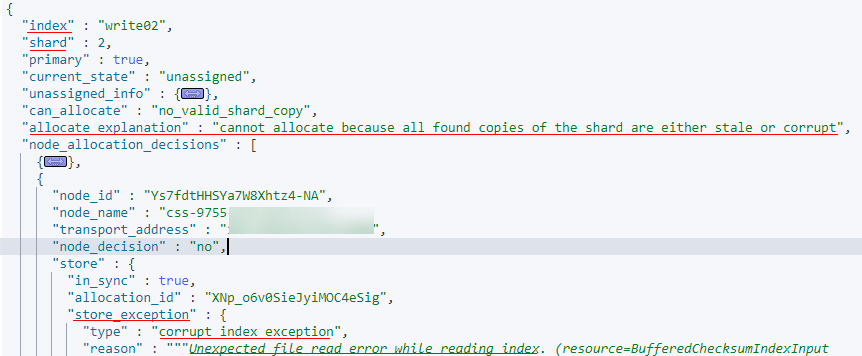
explanation: cannot allocate because all found copies of the shard are either stale or corrupt
The data on index shards is damaged.
For details, see Damaged primary shard data.
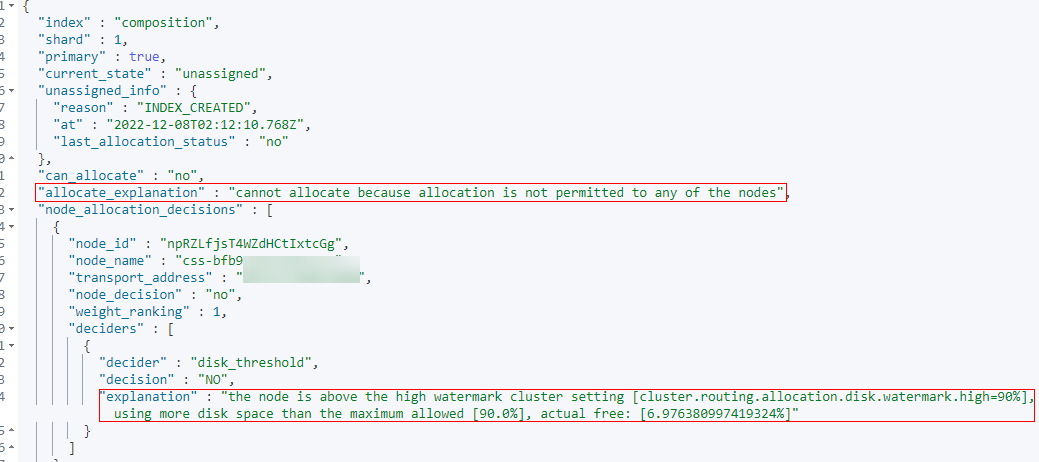
explanation: the node is above the high watermark cluster setting [cluster.routing. allocation. disk.watermark.high=90%], using more disk space than the maximum allowed [90.0%], actual free: [6.976380997419324%]
The node disk usage reaches the upper limit.
For details, see Excessive disk usage.
Step 2: Rectify the fault.
- Incorrect shard allocation policy
- cluster.routing.allocation.enable
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, the current allocation policy of the cluster forbids the allocation of all shards.
Figure 3 Incorrect configuration of allocation.enable

- On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the following command to set enable to all to allow all shards to be allocated:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent": { "cluster": { "routing": { "allocation.enable": "all" } } } }
The index-level configuration overwrites the cluster-level configuration. The parameters are described as follows:
- all: Default value. All types of shards can be allocated.
- primaries: Only the primary shards can be allocated.
- new_primaries: Only the primary shards of the newly created index can be allocated.
- none: No shards can be allocated.
- Run the POST _cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true command to manually allocate shards. Wait until all index shards are allocated and the cluster status changes to Available.
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, the current allocation policy of the cluster forbids the allocation of all shards.
- index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, the value of index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node is too small and does not meet the index shard allocation requirements.
Figure 4 Incorrect configuration of index total_shards_per_node

- On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the following command to change the number of index shards that can be allocated to each node:
PUT index_name/_settings { "index": { "routing": { "allocation.total_shards_per_node": 3 } } }
Value of index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node = Number of index_name index shards/(Number of data nodes - 1)
Set this parameter to a relative large value. Assume that a cluster has 10 nodes, including five data nodes, two client nodes, and three master nodes. The number of shards of an index is 30. If total_shards_per_node is set to 4, the total number of shards that can be allocated is: 4 x 5 = 20. Not all shards cannot be allocated. To allocate all shards in this index, at least six shards should be allocated to each data node (30 shards in total). In case a data node is faulty, at least eight shards should be allocated to each node.
- Run the POST _cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true command to manually allocate shards. Wait until the index shards are allocated and the cluster status changes to Available.
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, the value of index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node is too small and does not meet the index shard allocation requirements.
- cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, the number of shards that can be allocated to each data node in the cluster is too small.
Figure 5 Incorrect configuration of cluster total_shards_per_node

- The value of cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node indicates the maximum number of shards that can be allocated to each data node in a cluster. The default value of this parameter is 1000. On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the following command to specify the cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node parameter:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent": { "cluster": { "routing": { "allocation.total_shards_per_node": 1000 } } } } - In most cases, the problem occurs because index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node is mistakenly set to cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node. Run the following command to specify the index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node parameter:
PUT index_name/_settings { "index": { "routing": { "allocation.total_shards_per_node": 30 } } } Both of the following parameters are used to limit the maximum number of shards that can be allocated to a single data node:
Both of the following parameters are used to limit the maximum number of shards that can be allocated to a single data node:- cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node is used to limit shard allocation at the cluster level.
- index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node is used to limit shard allocation at the index level.
- Run the POST _cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true command to manually allocate shards. Wait until the index shards are allocated and the cluster status changes to Available.
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, the number of shards that can be allocated to each data node in the cluster is too small.
- index.routing.allocation.include
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, index shards can only be allocated to data nodes with the hot label. If no data nodes in the cluster are labeled with hot, shards cannot be allocated.
Figure 6 Incorrect configuration of include

- On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the following command to cancel the configuration:
PUT index_name/_settings { "index.routing.allocation.include.box_type": null } - Run the POST _cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true command to manually allocate shards. Wait until the index shards are allocated and the cluster status changes to Available.
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, index shards can only be allocated to data nodes with the hot label. If no data nodes in the cluster are labeled with hot, shards cannot be allocated.
- index.routing.allocation.require
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, shards can only be allocated to data nodes with specified labels. If no nodes in the cluster have such labels, the shards cannot be allocated.
Figure 7 Incorrect configuration of require
- On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the following command to cancel the configuration:
PUT index_name/_settings { "index.routing.allocation.require.box_type": null } - Run the POST _cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true command to manually allocate shards. Wait until the index shards are allocated and the cluster status changes to Available.
- If the value of explanation in the output is as follows, shards can only be allocated to data nodes with specified labels. If no nodes in the cluster have such labels, the shards cannot be allocated.
- cluster.routing.allocation.enable
- Shard lock error
- In the output, explanation contains [failed to obtain in-memory shard lock]. This problem usually occurs when a node is removed from a cluster for a short time and then added back to the cluster, and a thread is performing a long-term data writing to a shard, such as bulk or scroll. When the node is added to the cluster again, the master node cannot allocate the shard because the shard lock is not released.
- This problem does not cause fragment data loss. You only need to allocate the shard again. On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the POST /_cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true command to manually allocate the unallocated shard. Wait until the index shards are allocated and the cluster status changes to Available.
- Inconsistent index setting and node version
- The value of index and explanation in the output are as follows, indicating that the parameter configuration of an index does not match the node version.
Figure 8 Inconsistent index configuration

- Run the GET index_name/_settings command to check the index configuration. In the output, check whether the index features match the node version.
Figure 9 Index configuration
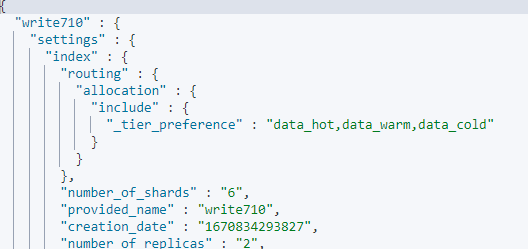
For example, assume that a cluster version is 7.9.3. The index feature index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference is supported by clusters of the version later than 7.10. If you use this feature in a cluster of the version earlier than 7.10, index shards cannot be allocated. As a result, the cluster is unavailable.
- Determine whether the inapplicable feature is mandatory for the cluster.
- If yes, create a cluster of the required version and restore the data of the old cluster to the new cluster using the backup.
- If no, go to the next step.
- Run the following command to remove the inapplicable index feature:
PUT /index_name/_settings { "index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference": null } - Run the POST /_cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true command to manually allocate the unallocated shards. Wait until the index shards are allocated and the cluster status changes to Available.
- The value of index and explanation in the output are as follows, indicating that the parameter configuration of an index does not match the node version.
- Damaged primary shard data
- The values of index, shard, allocate_explanation, and store_exception in the output are as follows, indicating that the data of a shard in an index is damaged.
Figure 10 Damaged primary shard data
- When the index data is damaged or the primary backup of a shard is lost, run the following command to define an empty shard and specify the node to be allocated:
POST /_cluster/reroute { "commands" : [ { "allocate_empty_primary" : { "index" : "index_name", "shard" : 2, "node" : "node_name", "accept_data_loss":true } } ] }
Data in the corresponding shard will be completely cleared. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- After index shards are reallocated, the cluster status becomes Available.
- The values of index, shard, allocate_explanation, and store_exception in the output are as follows, indicating that the data of a shard in an index is damaged.
- Excessive disk usage
- The output is as follows. The value of allocate_explanation indicates that shards of an index cannot be allocated to any data node, and the value of explanation indicates that node disk usage reaches the upper limit.
Figure 11 Query result
- If the disk usage of a node exceeds 85%, new shards will not be allocated to this node.
- If the disk usage of a node exceeds 90%, the cluster attempts to migrate the shards of this node to other data nodes with low disk usage. If data cannot be migrated, the system forcibly sets the read_only_allow_delete attribute for each index in the cluster. In this case, data cannot be written to indexes, and the indexes can only be read or deleted.
- A node may be disconnected due to high disk usage. After the node automatically recovers, once the cluster is overloaded, the cluster may fail to respond when you call the Elasticsearch API to query the cluster status. If the cluster status cannot be updated in a timely manner, the cluster becomes Unavailable.
- Increase the available disk capacity of the cluster.
- On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the DELETE index_name command to clear invalid data in the cluster to release disk space.
- Temporarily reduce the number of index copies. After the disk or node capacity is expanded, change the number of index copies back to the original value.
- On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the following command to temporarily reduce the number of index copies:
PUT index_name/_settings { "number_of_replicas": 1 }The output is as follows.Figure 12 Index status of read-only-allow-delete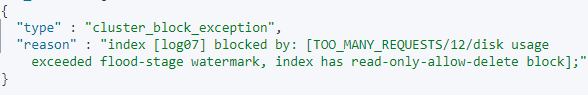
The disk usage exceeds the maximum value allowed by the disk space. The system forcibly sets the read_only_allow_delete attribute for all indexes in the cluster. Run the following command to set the attribute value to null, and then run the command in 2.a to reduce the number of index copies:
PUT /_settings { "index.blocks.read_only_allow_delete": null } - Increase the number of nodes or node storage capacity of the cluster by referring to Scaling Out a Cluster.
- After the scale-out is complete, run the command in step 2.a to change the number of index copies back. After all index shards are allocated, the cluster status changes to Available.
- On the Dev Tools page of Kibana, run the following command to temporarily reduce the number of index copies:
- The output is as follows. The value of allocate_explanation indicates that shards of an index cannot be allocated to any data node, and the value of explanation indicates that node disk usage reaches the upper limit.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





