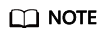Fast Access
This section uses the smoke detector demo to create a product model, configure and start the demo, and use basic SDK functions. A smoke detector product model is provided to help you understand the product model. This smoke detector can report the smoke density, temperature, humidity, and smoke alarms, and execute the ring alarm command. The following uses the smoke detector as an example to introduce the procedures of message reporting, property reporting, and command response.
Creating a Product
A smoke detector product model is provided to help you understand the product model. This smoke detector can report the smoke density, temperature, humidity, and smoke alarms, and execute the ring alarm command. The following uses the smoke detector as an example to introduce the procedures of message reporting and property reporting.
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- Choose Products in the navigation pane and click .
Figure 1 Creating a product
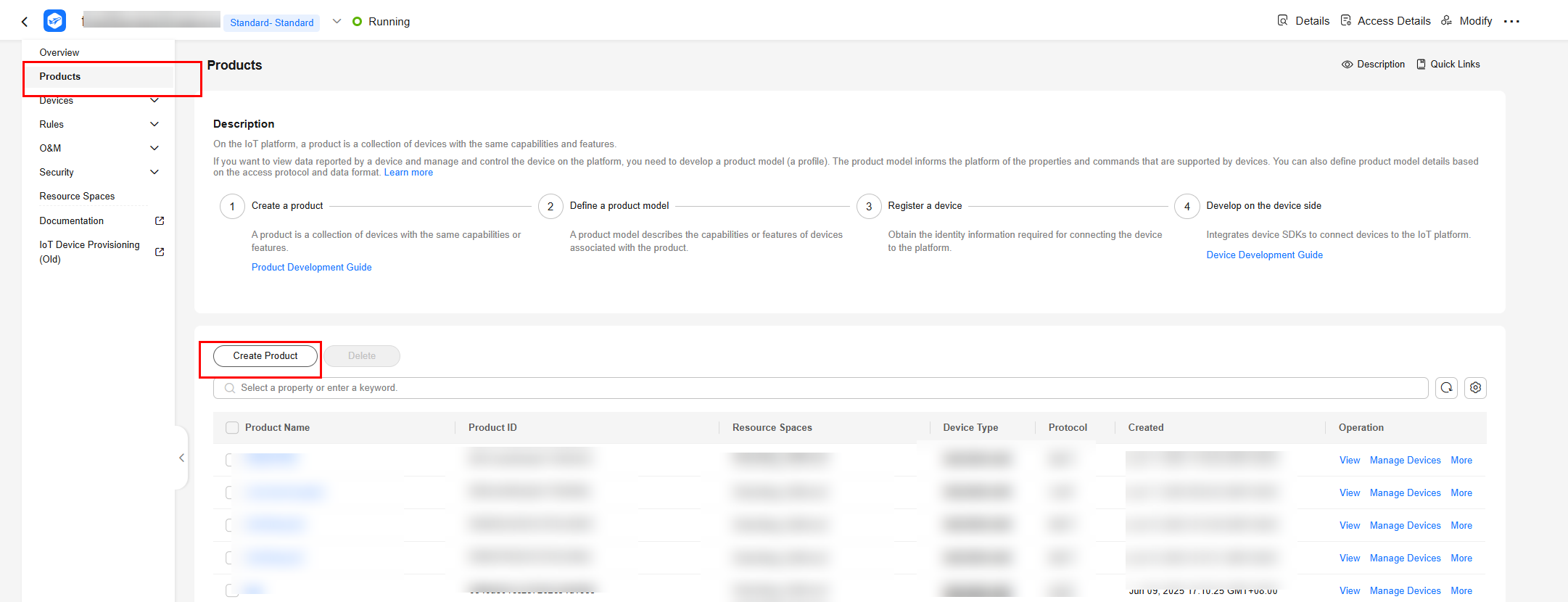
- Set the parameters as prompted and click OK.
Basic Info
Resource Space
The platform automatically allocates the created product to the default resource space. You can also select an existing resource space from the drop-down list or create one.
Product Name
Customize the product name. The name can contain letters, numbers, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
Protocol
Select MQTT.
Data Type
Select JSON.
Device Type Selection
Select Custom.
Device Type
Select smokeDetector.
Advanced Settings
Product ID
Leave this parameter blank.
Description
Set this parameter based on service requirements.
Figure 2 Creating a product - MQTT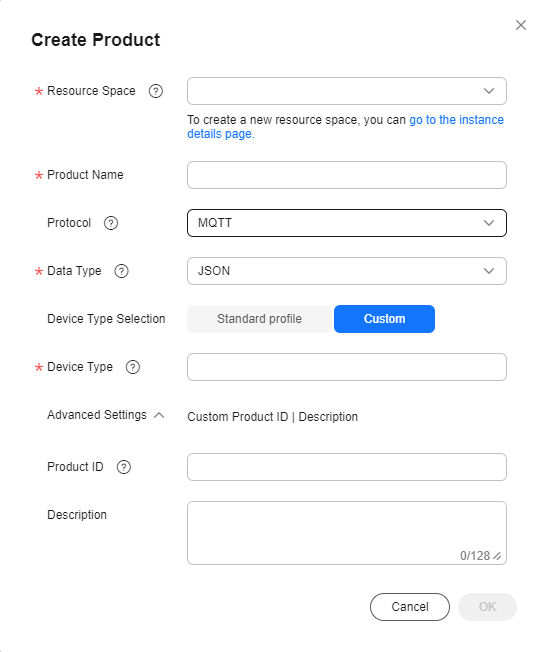
Uploading a Product Model
- Download the smokeDetector product model file.
- Click the name of the created product to access its details page.
- On the Basic Information tab page, click Import from Local to upload the product model file obtained in 1.
Figure 3 Product - Uploading a product model

Registering a Device
- In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices, and click Register Device.
- Set the parameters as prompted and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Resource Space
Ensure that the device and the created product belong to the same resource space.
Product
Select the created product.
Node ID
Customize a unique physical identifier for the device. The value consists of letters and digits.
Device Name
Customize the device name.
Authentication Type
Select Secret.
Secret
Customize the device secret. If this parameter is not set, the platform automatically generates a secret.
After the device is registered, save the node ID, device ID, and secret.
Accessing the Device
- Obtain the access address by choosing Overview > Access Details on the console.
Figure 4 Access information - MQTT access address on the device side
- Open the samples/rule /rule_demo.go file and enter the obtained access address, device ID, and device secret in the corresponding positions.
// Create a device and initialize it. authConfig := &config2.ConnectAuthConfig{ Id: "your device id", Servers: "mqtts://{MQTT_ACCESS_ADDRESS}:8883", Password: "your password", ServerCaPath: "iotda server ca path", } authConfig.RuleEnable = true device := device2.NewMqttDevice(authConfig) if device == nil { glog.Warningf("create mqtt device failed.") return } - Write and run the code. The following is an example of the command output. If connect result is : true exists, the connection is successful.
Figure 5 Connection succeeded

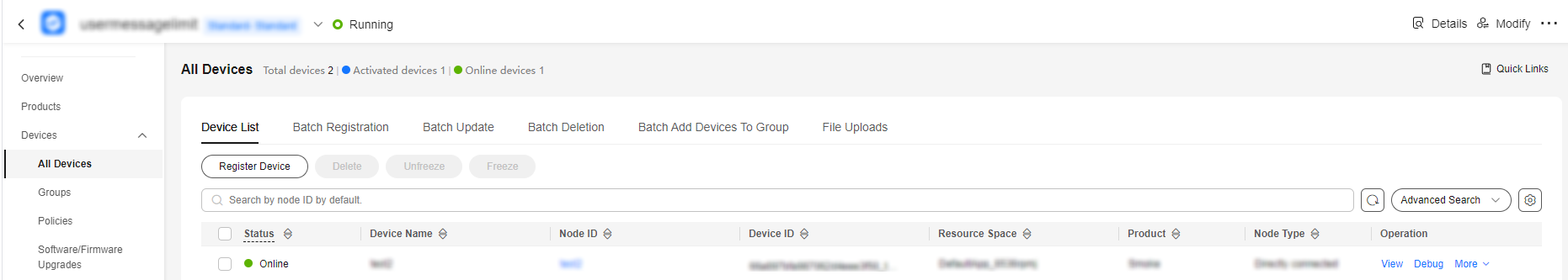
- Check the device running status. On the device details page of the console, check whether the device is online and the reported product model data.
Figure 6 Device list - Device online status

The SDK provides automatic reconnection by default. After the device is initialized, if the connection fails due to an unstable or unreachable network, or proactive disconnection by the platform, the SDK automatically initiates reconnection in the backend. To disable this function, see Disconnection and Connection.
Reporting a Message
Message reporting is the process in which a device reports messages to the platform.
- Report messages with custom topic with the SendMessage method in the example of ./samples/message/message_demo.go. If no topic is specified in the message, the message will be reported with the default topic of the platform.
""" create device code here """ // Send a message to the platform. message := model.Message{ Topic: "{custom topic}", Payload: "first message", } for { sendMsgResult := device.SendMessage(message) glog.Infof("send message %v", sendMsgResult) time.Sleep(1 * time.Second) } - On the IoTDA console, choose Devices > All Devices and check whether the device is online.
Figure 7 Device list - Device online status

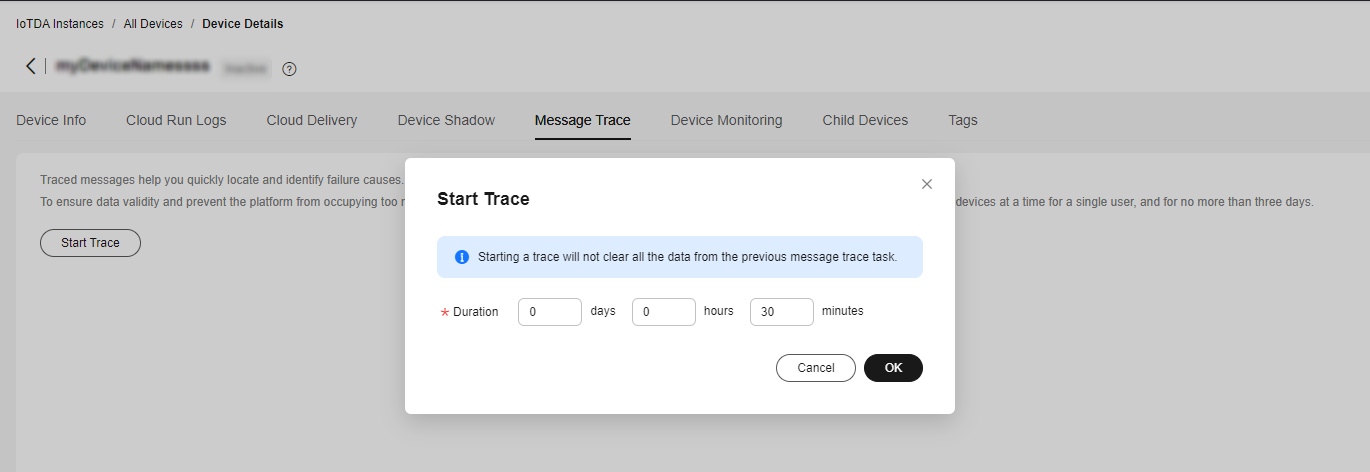
- Select the device, click View, and enable message trace on the device details page.
Figure 8 Message tracing - Starting message tracing
- Check the message tracing result to see whether the platform has received messages from the device.

Message tracing may be delayed. If no data is displayed, wait for a while and refresh the page.
Figure 9 Message tracing - Viewing device_sdk_java tracing result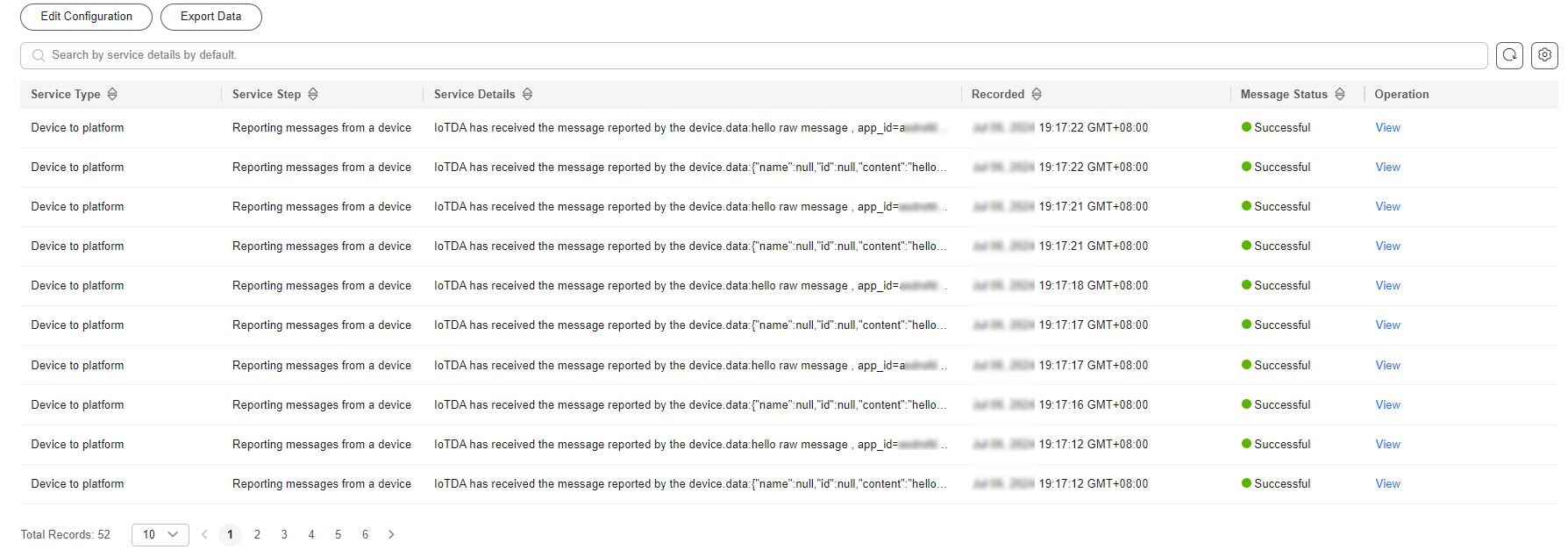
Reporting Properties
A device can report current property values to the platform.
- Report properties to the platform with the ReportProperties method in the example of ./samples/properties/device_properties.go.
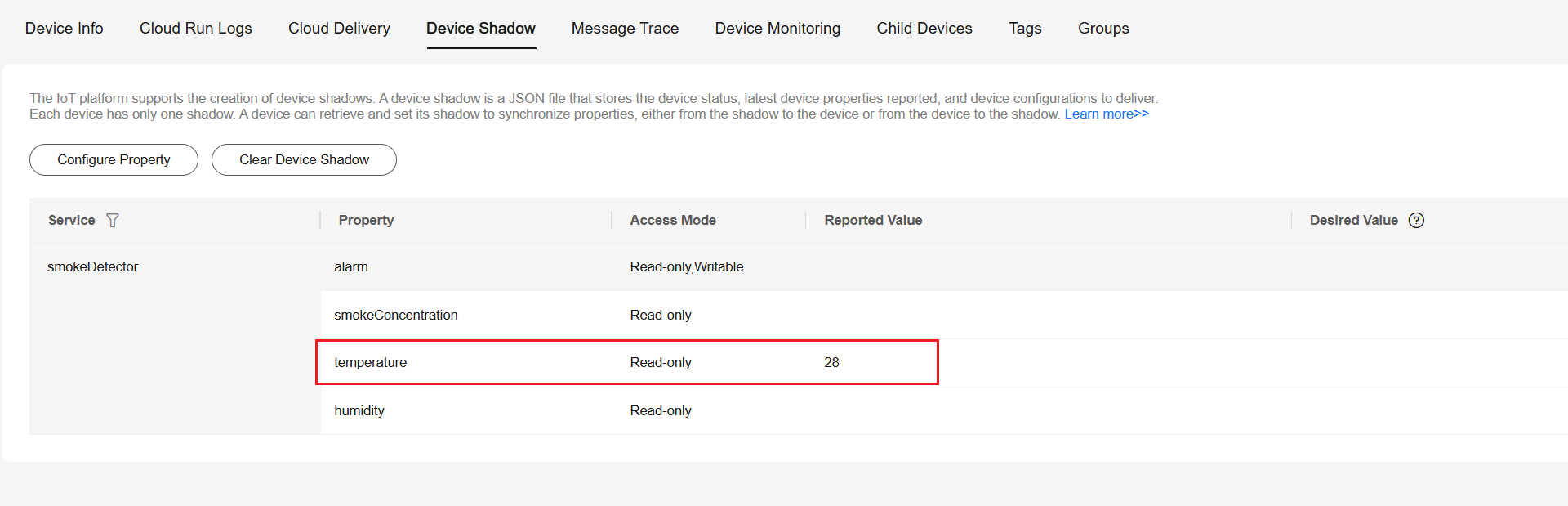
< create device code here ... > // Report properties. props := model.DevicePropertyEntry{ ServiceId: "smokeDetector", EventTime: iot.GetEventTimeStamp(), Properties: test_model.DemoProperties{ Temperature: 28, }, } var content []model.DevicePropertyEntry content = append(content, props) services := model.DeviceProperties{ Services: content, } device.ReportProperties(services) - In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices, select the registered device, and click the Device Shadow tab to view the reported property values.
Figure 10 Device shadow - temperature
Delivering Commands
You can set a command listener to receive commands delivered by the platform. The callback API needs to process the commands and report responses.
- ./samples/command/platform_command.go is an example of processing platform command delivery. Use the CommandHandler function as the command listener.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
mqttDevice.Client.AddCommandHandler(func(command model.Command) (bool, interface{}) { glog.Infof("I get command from platform") glog.Infof("command device id is %s", command.ObjectDeviceId) glog.Infof("command name is %s", command.CommandName) glog.Infof("command serviceId is %s", command.ServiceId) glog.Infof("command params is %v", command.Paras) return true, map[string]interface{}{ "cost_time": 12, } })
- When the device receives a command, the CommandHandler function is automatically called and the function response result is returned to the platform.
- Execute the main method, deliver a command from the platform to the device, and check the code logs.
Figure 11 Command delivery in Go

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot