Connecting to a DB Instance from a Linux ECS
You can connect to your DB instance using a Linux ECS installed with a MySQL client over a public network.
This section describes how to connect to a DB instance with SSL disabled. To connect to a DB instance with SSL enabled, see Using MySQL CLI to Connect to an Instance Through a Public Network.
- Step 1: Buy an ECS
- Step 2: Test Connectivity and Install a MySQL Client
- Step 3: Connect to the DB Instance Using Commands (Non-SSL Connection)
Step 1: Buy an ECS
- Log in to the management console and check whether there is an ECS available.
- If there is a Linux ECS, go to 3.
- If there is a Windows ECS, see Connecting to a DB Instance from a Windows Server.
- If no ECS is available, go to 2.
Figure 1 ECS
- Buy an ECS and select Linux (for example, CentOS) as its OS.
To download a MySQL client to the ECS, bind an EIP to the ECS.
For details about how to purchase a Linux ECS, see "Purchasing an ECS" in Elastic Cloud Server Getting Started.
- On the ECS Information page, view the region and VPC of the ECS.
Figure 2 ECS information

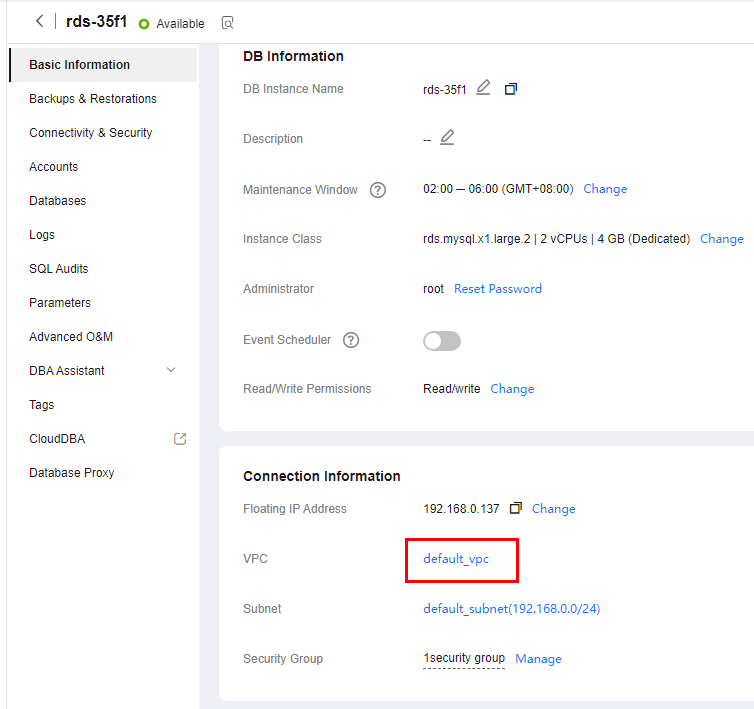
- On the Basic Information page of the RDS for MySQL instance, view the region and VPC of the DB instance.
Figure 3 DB instance information
Step 2: Test Connectivity and Install a MySQL Client
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see Login Using VNC in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
- On the Instances page, click the DB instance name.
- Choose Connectivity & Security from the navigation pane. In the Connection Information area, obtain the EIP and database port of the DB instance.
Figure 4 Connection information
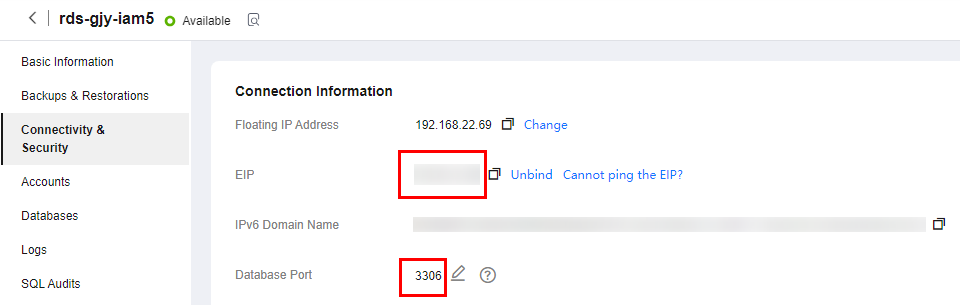
If no EIP has been bound to the DB instance, see Binding an EIP.
- On the ECS, check whether the EIP and database port of the DB instance can be connected.
- If yes, network connectivity is available.
- If no, check the security group rules.
- If in the security group of the ECS, there is no outbound rule with Destination set to 0.0.0.0/0 and Protocol & Port set to All, add an outbound rule for the EIP and port of the DB instance.
Figure 5 ECS security group

- If in the security group of the DB instance, there is no inbound rule allowing the access from the private IP address and port of the ECS, add an inbound rule for the private IP address and port of the ECS. For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules.
- If in the security group of the ECS, there is no outbound rule with Destination set to 0.0.0.0/0 and Protocol & Port set to All, add an outbound rule for the EIP and port of the DB instance.
- Download the MySQL client installation package for Linux on the ECS. The mysql-community-client-5.7.38-1.el6.x86_64.rpm package is used as an example.
A MySQL client running a version later than that of the DB instance is recommended.
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-community-client-5.7.38-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
- Install the MySQL client.
rpm -ivh --nodeps mysql-community-client-5.7.38-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
- If any conflicts occur during the installation, add the replacefiles parameter to the command and install the client again.
rpm -ivh --replacefiles mysql-community-client-5.7.38-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
- If a message is displayed prompting you to install a dependency package during the installation, add the nodeps parameter to the command and install the client again.
rpm -ivh --nodeps mysql-community-client-5.7.38-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
- If any conflicts occur during the installation, add the replacefiles parameter to the command and install the client again.
Follow-up Operations
After logging in to the DB instance, you can create or migrate databases.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot









