What Is EVS?
Overview
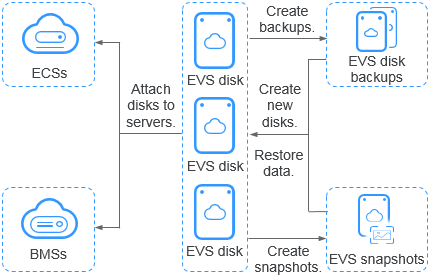
Elastic Volume Service (EVS) offers scalable block storage for cloud servers. EVS disks provide high reliability, high performance, and come with a variety of disk types. They can be used for distributed file systems, development and test environments, data warehouses, and high-performance computing (HPC) applications. Cloud servers that EVS supports include Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs) and Bare Metal Servers (BMSs).
Just like the physical disks in local PC need to be installed before they can be used, EVS disks need to be attached to servers before they can be used. They cannot be used alone. You also need to partition and create file systems on them before they can be used for persistent data storage.
In this document, EVS disks are sometimes just referred to as "disks".
Introduction Video
EVS Advantages
EVS has the following advantages.
|
Advantage |
Description |
Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Various disk types |
EVS provides a variety of disk types for you to choose from. They can be used as data disks or system disks for cloud servers. You can select whichever disk type that has the specifications best suited to your budget and service requirements. |
|
|
Elastic scalability |
The EVS disk capacity ranges from 10 GiB to 32 TiB. You can start with 10 GiB, and if, later on, that no longer meets your needs, you can expand the disk capacity to up to 32 TiB in increments of 1 GiB, without interrupting your applications. |
|
|
In addition to the disk capacity limit, there is an EVS capacity quota. The additional space you add cannot exceed the remaining quota. However, if this happens, you can apply for a higher quota. |
||
|
High security and reliability |
Both system disks and data disks support data encryption to ensure data security. |
|
|
High security and reliability |
Data protection functions, such as backups, safeguard the disk data. If your data is ever damaged by a software exception or online attack, you can restore your data from backups. |
|
|
High security and reliability |
Data protection functions, such as snapshots, safeguard the disk data. If your data is ever damaged by a software exception or online attack, you can restore your data from snapshots. |
|
|
Real-time monitoring |
On Cloud Eye, you can monitor the disk health and operating status at any time. |
Differences Among EVS, SFS, and OBS
There are three types of storage available for you to choose from: EVS, Scalable File Service (SFS), and Object Storage Service (OBS). Their differences are described in the following table.
|
Dimension |
SFS |
OBS |
EVS |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Concept |
SFS provides on-demand high-performance file storage that can be shared by multiple servers. SFS can be used like a remote directory for Windows or Linux servers. |
OBS provides massive, secure, reliable, and cost-effective data storage for you to store data of any type and size. |
EVS provides scalable, high-performance, high-reliability, block storage that can be used to meet a wide variety of service requirements. EVS disks are like physical disks on PCs. |
|
Data storage logic |
Stores files. Data is sorted and displayed in files and folders. |
Stores objects. Files are saved directly to OBS. The files automatically generate corresponding system metadata. You can also customize the metadata if needed. |
Stores binary data and cannot directly store files. To store files, you need to format the disk with a file system first. |
|
Access method |
SFS file systems need to be mounted to cloud servers through the Network File System (NFS) or Common Internet File System (CIFS) protocol before they can be accessed. A network address must be specified or mapped to a local directory for access. |
OBS buckets can be accessed through the Internet or Direct Connect. The bucket address must be specified for access, and transfer protocols HTTP and HTTPS are used. |
EVS disks can only be used and accessed from applications after being attached to cloud servers and initialized. |
|
Application scenarios |
High-performance computing, media processing, file sharing, content management, and web services
NOTE:
Mainly suitable for high-performance computing workloads like gene sequencing and image rendering that require high bandwidth for file sharing. |
Big data analytics, static website hosting, online video on demand (VoD), gene sequencing, and intelligent video surveillance |
High-performance computing, enterprise critical clustered applications, enterprise application systems, and development and testing
NOTE:
Mainly suitable for high-performance workloads like industrial design and energy exploration that require high speed and high IOPS for high-performance storage. |
|
Capacity |
PiB-level |
EiB-level |
TiB-level |
|
Latency |
3–10 ms |
Milliseconds |
Sub-millisecond |
|
IOPS/TPS |
10,000 per file system |
Tens of millions |
128,000 per disk |
|
Bandwidth |
GiB/s |
TiB/s |
MiB/s |
|
Data sharing |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
|
Remote access |
Supported |
Supported |
Not supported |
|
Used independently |
Supported |
Supported |
Not supported |
Access Methods
EVS provides a web-based console and HTTPS-based APIs that you can use to access the EVS service.
- APIs
Use APIs if you need to integrate EVS into a third-party system for secondary development. For details, see Elastic Volume Service API Reference.
- Console
Use the console if you do not need to integrate EVS with a third-party system. Sign in to the console with your account and choose Elastic Volume Service from the service list. If you do not have an account, sign up with Huawei Cloud.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





