Scaling Out a Cluster
When you need more compute and storage resources, add more nodes for cluster scale-out on the management console.
- When you scale out a storage-compute coupled data warehouse cluster, use the same storage specifications as the cluster.
- If the number of subnet IP addresses is insufficient, cross-subnet scale-out is allowed.
After the data in a DWS data warehouse is deleted, the occupied disk space may not be released, resulting in dirty data and disk waste. Therefore, if you need to scale out your cluster due to insufficient storage capacity, run the VACUUM command to reclaim the storage space first. If the used storage capacity is still high after you run the VACUUM command, you can scale out your cluster. For details about the VACUUM syntax, see "SQL Syntax Reference" > "DDL Syntax" > "VACUUM" in the Data Warehouse Service (DWS) SQL Syntax Reference.
Impact on the System
- Before the scale-out, disable the client connections that have created temporary tables because temporary tables created before or during the scale-out will become invalid and operations performed on these temporary tables will fail. Temporary tables created after the scale-out will not be affected.
- Certain cluster functions, including restarting, stopping, and starting, modifying specifications, adding or removing CNs, creating snapshots, and resetting the database administrator's password, cannot be performed while scaling out the cluster.
- During an offline scale-out, the cluster automatically restarts. Therefore, the cluster changes to Unavailable for a period of time. After the cluster is restarted, the status becomes Available. At the end of the scale-out, if you select automatic redistribution, the system dynamically redistributes user data in the cluster to all nodes. Otherwise, you need to start data redistribution.
- During offline scale-out, stop all services or run only a few query statements. During table redistribution, a shared lock is added to tables. All insert, update, and delete operations as well as DDL operations on the tables are blocked for a long time, which may cause a lock wait timeout. After a table is redistributed, you can access the table. Do not perform queries that take more than 20 minutes during the redistribution (the default time for applying for the write lock during redistribution is 20 minutes). Otherwise, data redistribution may fail due to lock wait timeout.
- If a new snapshot is created for the cluster after the scale-out, the new snapshot contains data on the newly added nodes.
- If the cluster scale-out fails, the database automatically performs the rollback operation in the background so that the number of nodes in the cluster can be restored to that before the scale-out.
- If the rollback is successful and the cluster can be normally used, you can perform again. If the scale-out still fails, contact the technical support.
- If the rollback fails due to some exceptions, the cluster may become Unavailable. In this case, you cannot perform or restart the cluster. Contact the technical support.
Prerequisites
- The cluster to be scaled out is in the Available, Read-only, or Unbalanced state.
- The number of nodes to be added must be less than or equal to the available nodes. Otherwise, system scale-out is not allowed.
Scaling Out a Cluster
- A cluster becomes read-only during scale-out. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- The cluster will be intermittently disconnected during scale-out. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- To ensure data security, you are advised to create a snapshot before the scale-out. For details about how to create a snapshot, see Manual Snapshots.
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters.
All clusters are displayed by default.
- In the Operation column of the target cluster, choose More > Scale Node > Scale Out. The scale-out page is displayed.
Before scaling out the cluster, it is crucial to verify if it meets the inspection conditions. Click Immediate Inspection to complete the inspection and proceed to the next step only if it passes. For more information, see Viewing Inspection Results.
- If the IP addresses of the original subnet are insufficient, you can expand the capacity across subnets.
- Specify the number of nodes to be added.
- DNs are added during scale-out. For details about how to add CNs, see Adding or Deleting a CN in a DWS Cluster.
- The number of nodes after scale-out must be at least three nodes more than the original number. The maximum number of nodes that can be added depends on the available quota. In addition, the number of nodes after the scale-out cannot exceed 256.
- Flavor of the new nodes must be the same as that of existing nodes in the cluster.
- The VPC and security group of the cluster with new nodes added are the same as those of the original cluster.
- Configure advanced parameters.
- If you choose Default, Auto Redistribution will be enabled and Redistribution Mode will be Offline by default.
- If you choose Custom, you can configure the following advanced configuration parameters for scale-out:
- Auto Redistribution: Automatic redistribution can be enabled. If automatic redistribution is enabled, data will be redistributed immediately after the scale-out is complete. If this function is disabled, only the scale-out is performed. In this case, to redistribute data, select a cluster and choose More > Scale Node > Redistribute.
- Redistribution Concurrency: If automatic redistribution is enabled, you can set the number of concurrent redistribution tasks. The value range is 1 to 200. The default value is 4.
- Auto Redistribution: Select Offline.
- Confirm the settings, select the confirmation check box, and click Next: Confirm.
- Click Submit.
- After you submit the scale-out application, task information of the cluster changes to Scaling out and the process will take several minutes.
- During the scale-out, the cluster automatically restarts. Therefore, the cluster status will stay Unavailable for a while. After the cluster is restarted, the status will change to Available.
- After the scale-out is complete, the system dynamically redistributes user data in the cluster, during which the cluster is in the Read-only state.
- A cluster is successfully scaled out only when the cluster is in the Available state and task information Scaling out is not displayed. Then you can use the cluster.
- If Scale-out failed is displayed, the cluster fails to be scaled out.
Scaling Out with Idle Nodes
To ensure reliability, prepare ECS first by referring to Adding Nodes for a large-scale cluster, and scale out the cluster using idle nodes.
- Disable automatic redistribution when you scale out a large-scale cluster to facilitate retries upon failures for improved reliability.
- After the scale-out is complete, manually perform redistribution to ensure that multiple retries can be performed in this phase.
Precautions
- A number of available nodes must be added to the cluster in advance so that idle nodes can be created and added for scale-out.
- The anti-affinity rule dictates that the number of idle nodes to be added must be an integer multiple of the cluster ring size.
- Make sure to configure the scale-out task before submitting it. This involves completing the scale-out preparation. Once done, wait for a moment.
Procedure
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters. All clusters are displayed by default.
- In the Operation column of the target cluster, choose More > Scale Node > Scale Out.
Before scaling out the cluster, it is crucial to verify if it meets the inspection conditions. Click Immediate Inspection to complete the inspection and proceed to the next step only if it passes. For more information, see Viewing Inspection Results.
If there are idle nodes in the cluster, the system displays a message asking you whether to add nodes.
- Click the corresponding button to make scale-out preparations and wait until the preparation is complete.
- Configure the parameters as required. For details, see Scaling Out a Cluster.
After setting the scale-out and redistribution parameters, select the confirmation check box, and click Next: Confirm.
- Confirm the information and click Submit.
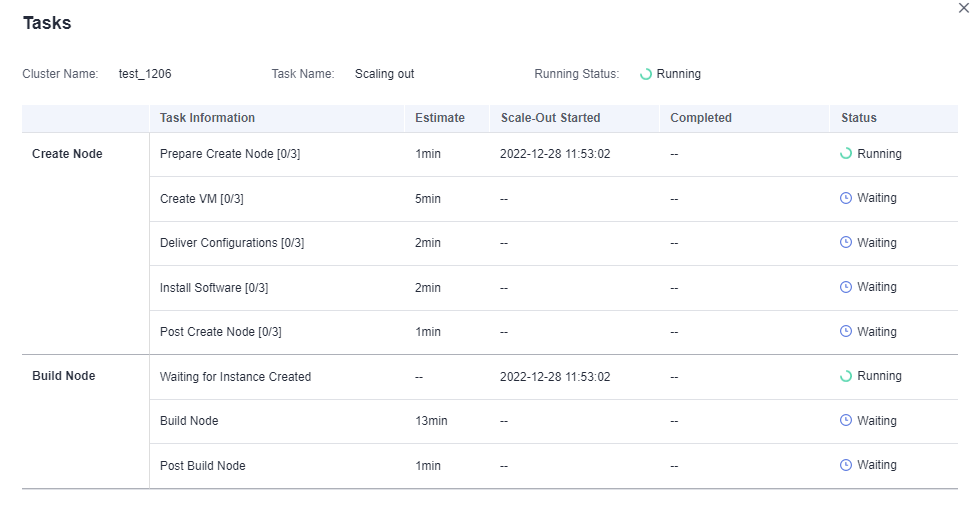
Viewing Scaling Details
- Log in to the DWS console.
- Choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters. By default, all clusters of the user are displayed.
- In the Task Information column of a cluster, click View Details.
- Check the scale-out status of the cluster on the scaling details page.
Figure 1 Viewing scale-out details
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





