Getting Started
(Optional) Modifying Security Group Rules

- By default, IP addresses from the VPC subnet CIDR block created in this solution are allowed to access the MySQL database through port 3306. Configure an IP address whitelist by referring to Modifying a Security Group Rule.
- This solution uses port 22 to remotely log in to the cloud server. By default, the VPC subnet created in this solution allows access from port 22. Configure an IP address whitelist by referring to Modifying a Security Group Rule.
A security group is a collection of access control rules for cloud resources, such as cloud servers, containers, and databases, to control inbound and outbound traffic. Cloud resources associated with the same security group have the same security requirements and are mutually trusted within a VPC.
If the rules of the security group associated with your instance cannot meet your requirements, for example, you need to add, modify, or delete a TCP port, do as follows:
- Adding a security group rule: Add an inbound rule and enable a TCP port if needed.
- Modifying a security group rule: Inappropriate security group settings can be a serious security risk. You can modify security group rules to ensure the network security of your instances.
- Deleting a security group rule: If the source or destination IP address of an inbound or outbound security group rule changes, or a port does not need to be enabled, you can delete the security group rule.
- Log in to the ECS console and view the instances created through one-click deployment and the EIPs bound to the instances.
Figure 1 Instances

- Open the Subnets where the cloud server is located and click the IP Addresses tab to view the virtual IP address.
Figure 2 Virtual IP address

- Check the security group rules. On the Security Groups page, locate the security group prefixed with the VPC name, and click the security group to view the security group rules. By default, ports 22 and 3306 are enabled in the inbound rules. Perform operations to modify the security group rules by referring to (Optional) Modifying Security Group Rules.
Figure 3 Security group rules

- Log in to the three cloud servers respectively as the administrator root.
Figure 4 Logging in to cloud servers

- Unbind the EIPs bound to the primary database and standby database suffixed with master and slave1. Log in to the ECS console, locate the target database server, choose More > Manage Network > Unbind EIP in the Operation column, and click Yes in the displayed dialog box. Do not release the EIP bound to the standby database (suffixed with slave2) with MHA Manager installed. Otherwise, an alarm email will fail to be sent during a failover.
Figure 5 Unbinding an EIP
 Figure 6 Confirming unbinding
Figure 6 Confirming unbinding
- Release the EIPs. Locate the two EIPs whose Status is Unbound, choose More > Release, and click Yes in the displayed dialog box.
Figure 7 Releasing the EIPs
 Figure 8 Confirming the release of the EIPs
Figure 8 Confirming the release of the EIPs
Initializing the Environment
Restarting ECSs may cause the MHA MySQL cluster to stop. You need to manually start MHA monitoring. Refer to the following operations.
- Reconfigure the VIP. Log in to the ECS where the primary database is deployed and run the ifconfig eth0:1 VIP/24 command. VIP is the virtual IP address obtained in 2 or 9.
Figure 9 Reconfiguring the VIP

- Enable the MHA service. Log in to the ECS (suffixed with slave2) with MHA Manager installed and run the mha_app1_start command to start MHA monitoring. If the MHA status is running, the cluster service is started.
Figure 10 Enabling MHA

Working with MySQL Databases
In this solution, three cloud servers are created by default, each of which has a MySQL 5.7.34 database installed. The databases include one primary database (suffixed with master) and two standby databases (suffixed with slave1 and slave2). By default, a user group mysql is created, the mysql user is added to the user group, and the service port 3306 is enabled. You need to create account repl on the primary database for primary/standby replication. Set the account password to be the same as the initial password. Allow only the IP addresses from 192.168.100.0/24 to access the primary database. Install MHA Manager on the standby database (suffixed with slave2). The default administrator account is mha and the password is the same as the initial password.
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G;

Create a replication account on the primary database. (By default, the repl user has been created, and the password is set to the initial password.)
mysql -uroot -S /tmp/mysql.sock -e "grant replication slave on *.* to Account@' %' identified by'Password'"; Example: mysql -uroot -S /tmp/mysql.sock -e "grant replication slave on *.* to repl@'192.168.100.%' identified by '123'";
Create an MHA administrator account on the primary database. (By default, the mha user has been created, and the password is set to the initial password.)
mysql -uroot -e "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO Account@'Allowed login address'IDENTIFIED BY'Password'"; Example: mysql -uroot -e "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO mha@'192.168.100.%' IDENTIFIED BY '123'";
Change the password of a MySQL database account.
update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('Password') where user='Account' and Host = 'localhost';
Example:
update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='repl' and Host = '192.168.100.%';
- If the password of the primary/standby replication account is changed, reconfigure the primary database information for the standby databases.
> CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST='192.168.100.111',
MASTER_USER='repl',
MASTER_PASSWORD='Password',
MASTER_PORT=3306,
MASTER_CONNECT_RETRY=10,
MASTER_AUTO_POSITION=1;
> START SLAVE;
- After changing the passwords of the primary/standby replication account and MHA administrator account, change the passwords in the app1.cnf configuration file on the ECS (suffixed with slave2) with MHA Manager installed.
Run the vim /datadisk/mha/conf/app1.cnf command to change the value of password.
Working with MHA
Install MHA Manager on the standby database (suffixed with slave2). An MHA program can manage multiple sets of primary and standby databases. You need to create a different configuration file for each set. In the initial solution, a configuration file for only one set of primary and standby databases is available, the default MHA administrator account is mha, the password is the initial password, and the configuration file is stored in /datadisk/mha/conf/app1.cnf.
MHA commands:
masterha_check_ssh --conf=/datadisk/mha/conf/app1.cnf If "All SSH connection tests passed successfully" is displayed, the three cloud servers can access each other without entering a password.

masterha_check_repl --conf=/datadisk/mha/conf/app1.cnf If "MySQL Replication Health is OK" is displayed, the primary/standby replication status is normal.

mha_app1_start
mha_app1_status
mha_app1_stop
tail -f /datadisk/mha/logs/manager
Simulating a Fault
- View log changes on the MHA Manager.
tail -f /datadisk/mha/logs/manager
Figure 14 Log changes
- Stop the primary database service.
systemctl stop mysqld
- Return to the ECS with MHA Manager installed, view the logs, and check whether the information "Master failover to xxxx completed successfully." is displayed.
Figure 15 Failover

- Log in to the standby database suffixed with slave1 and check whether the VIP is successfully bound.
Figure 16 VIP bound successfully

- Check the status of the MHA Manager. Its status is stopped.
mha_app1_status
Figure 17 Completing a failover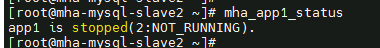
- Log in to the recipient's mailbox to view the alarm email.
Figure 18 Alarm email

Rectifying a Fault
- Restart the MySQL service for the original primary database and add it to the cluster as a standby database. (The IP address of the primary database has been updated.)
systemctl start mysqld.service mysql -uroot > CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='192.168.100.112', MASTER_USER='repl', MASTER_PASSWORD='Password', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_CONNECT_RETRY=10, MASTER_AUTO_POSITION=1; > START SLAVE; > SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G; - Modify the MHA Manager configuration file to add the original primary database to the cluster.
vim /datadisk/mha/conf/app1.cnf [server1] candidate_master=1 check_repl_delay=0 hostname=192.168.100.111 port=3306
- Restart the MHA service.
mha_app1_start mha_app1_status
Performing a Manual Switchover
Before performing a switchover, stop the MHA service.
mha_app1_stop
Run the following command on the MHA Manager to switch the primary and standby databases online:
masterha_master_switch --conf=/datadisk/mha/conf/app1.cnf --master_state=alive --new_master_host=192.168.100.111 --orig_master_is_new_slave --running_updates_limit=10000 --interactive=0 If the information "Switching master to 192.168.0.111(192.168.0.111:3306) completed successfully." is displayed, the switchover is successful.

Check whether the VIP is bound to the new primary database (192.168.100.111).
ifconfig
Restart MHA on the ECS where MHA Manager is installed.
mha_app1_start mha_app1_status
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





