Certificate Validity Verification (OCSP)
Introduction
IoTDA uses Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) to verify the validity of certificates on the device and server. OCSP checks the revocation status of certificates at the Transport Layer Security (TLS) layer. It offers several advantages over the traditional Certificate Revocation List (CRL), including higher scalability, shorter response time, better real-time performance, and greater suitability for the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). Unlike CRL, which is updated less frequently and has a larger file size, OCSP provides more efficient and timely certificate verification.
Terms
OCSP verification: used for device certificate validity status check on the platform side. The IoT platform checks whether the device certificate has been revoked by the CA.
OCSP stapling: also known as server OCSP, is a TLS certificate status query extension that serves as an alternative to traditional OCSP for checking the status of X.509 certificates. With OCSP stapling, the server takes the initiative to check its certificate revocation status (continuously) and includes a cached OCSP response during the TLS handshake. This eliminates the need to send a separate request to the CA and speeds up the handshake process, as you only need to verify the validity of the response.
Constraints
- Only enterprise instances support this function.
- When OCSP verification is enabled, the platform will send a request to the OCSP server during the initial device connection to the platform. This may result in a longer duration for establishing the connection, which is a normal occurrence. Subsequent connection establishment is not affected.
- Cache duration for the OCSP response to the platform: 24 hours.
- Timeout interval for receiving a response from the OCSP server: 5 seconds. Max. response size: 4 KB.
Process
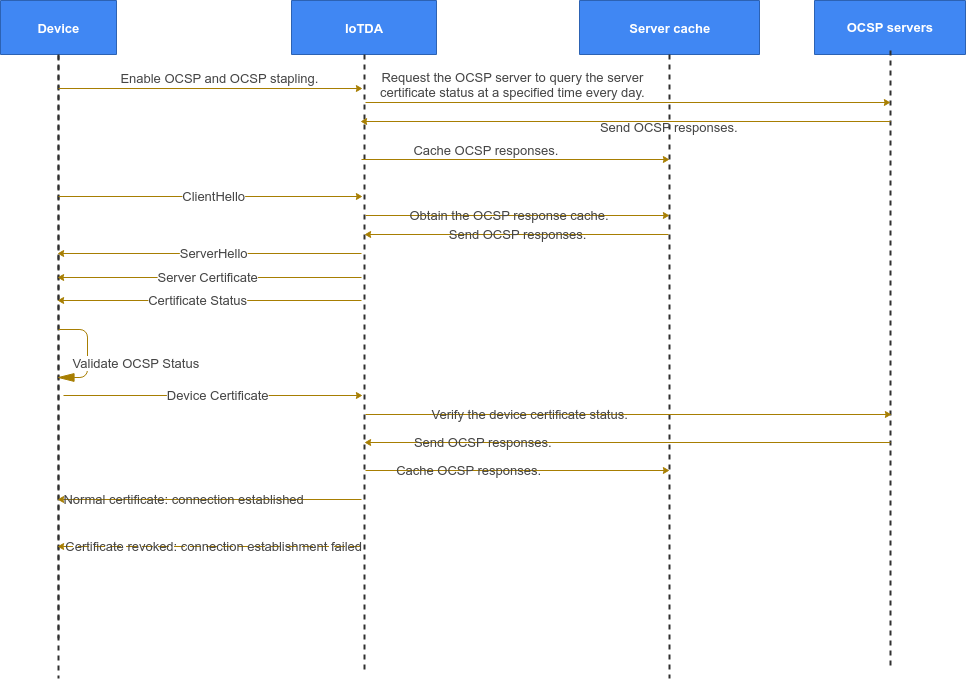
Procedure
- Access the IoTDA service page and click Access Console. Click the target instance card.
- In the navigation pane, choose Devices > Device Certificates. On the displayed page, click the corresponding CA certificate and click the button for certificate settings.
Figure 2 CA certificate - Enabling OCSP verification

- If the OCSP server access mode is HTTPS, choose Devices > Device Certificates > CA Certificates, click Upload Certificate, and upload the CA certificate of the OCSP server.
Return to the IoTDA console, locate the corresponding instance, and access its details page. Click the button of custom domain name details and click the modification button to enable OCSP stapling. If the OCSP server access mode is HTTPS, click SSL Verification and associate the server CA certificate.
Figure 3 Instance management - Enabling OCSP stapling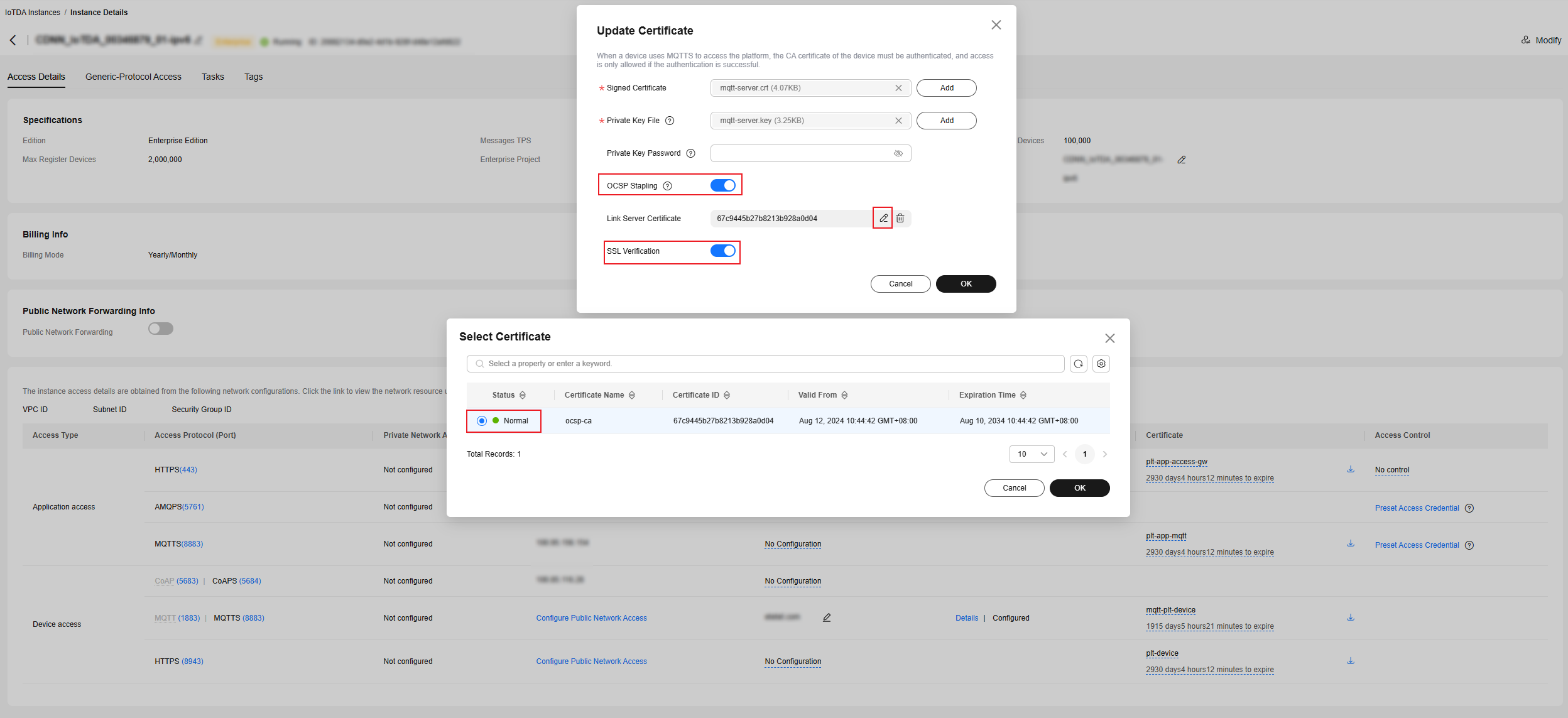
- To enable OCSP stapling, the certificate chain must contain the upper-layer CA certificate.
- The OCSP signature certificate information must contain the OCSP URL extension field.
- Use the MQTT simulator that supports OCSP to connect to the platform, check the OCSP stapling information of the platform certificate, use the packet capture tool to capture TLS handshake packets for connection establishment, and check the OCSP response of the platform certificate. There are three certificate status types: good, revoked, and unknown. The device determines whether to establish a connection based on the platform certificate status. For example, the device establishes a connection with the platform only when the certificate status is good.
Figure 4 TLS-Certificate Status good
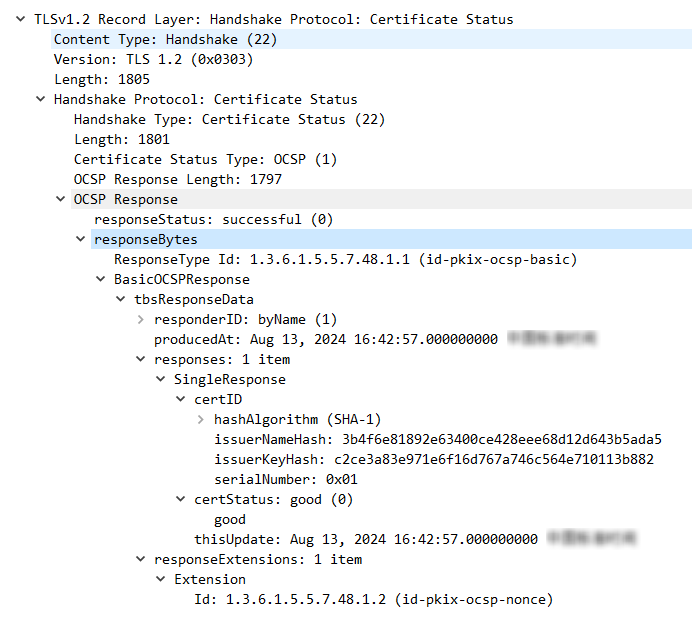 Figure 5 TLS-Certificate Status revoked
Figure 5 TLS-Certificate Status revoked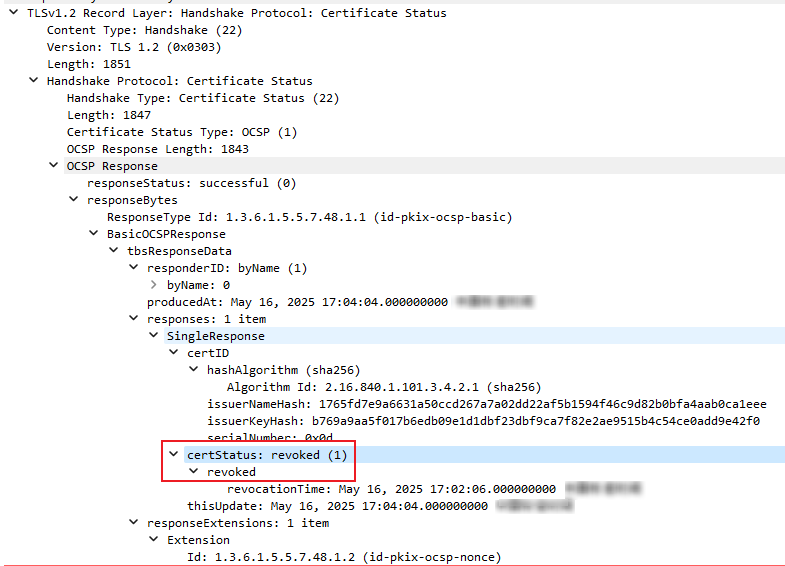 Figure 6 TLS-Certificate Status unknown
Figure 6 TLS-Certificate Status unknown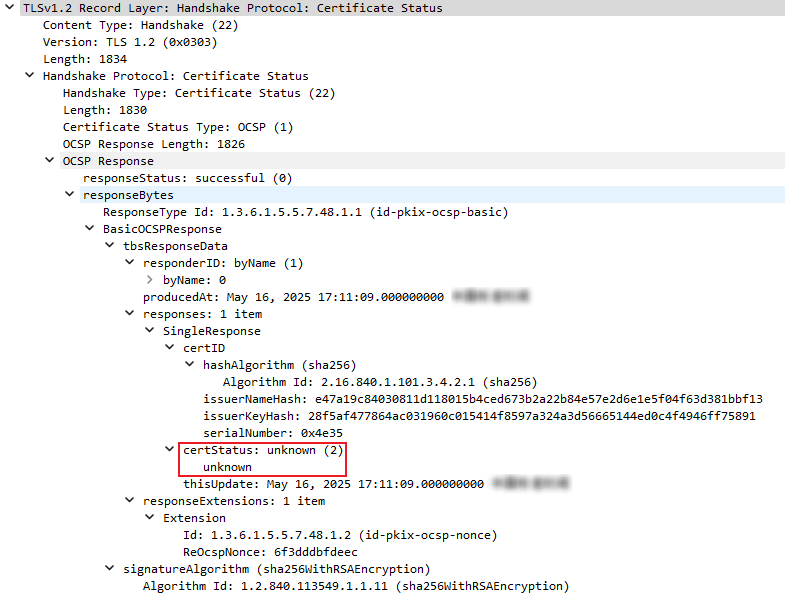
 The server returns certificate status only when the Client Hello packet sent by the client carries the status_request extended field.Figure 7 status request
The server returns certificate status only when the Client Hello packet sent by the client carries the status_request extended field.Figure 7 status request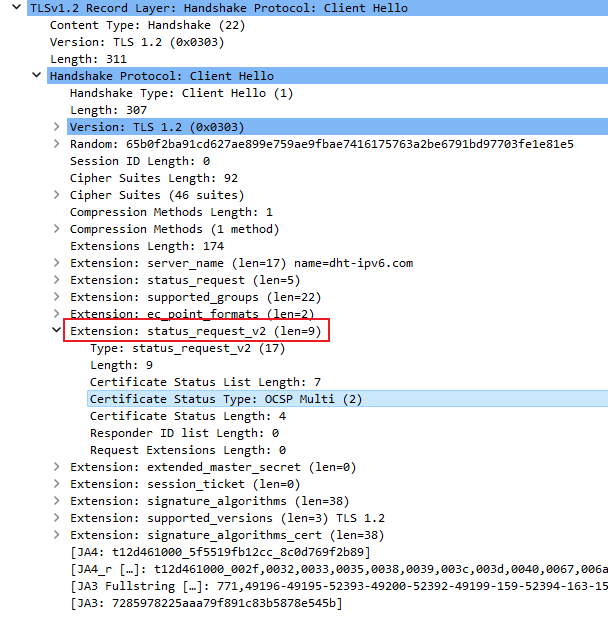
- In the navigation pane, choose Devices > All Devices. On the displayed page, find the target device to access its details page. Click the Message Trace tab and enable message tracing. Use the MQTT simulator to simulate two-way certificate authentication. Check the message tracing error details. If the device certificate has been revoked, use a new valid certificate for access. Ensure to promptly revoke any leaked certificates.
Figure 8 Device certificate - Revoked
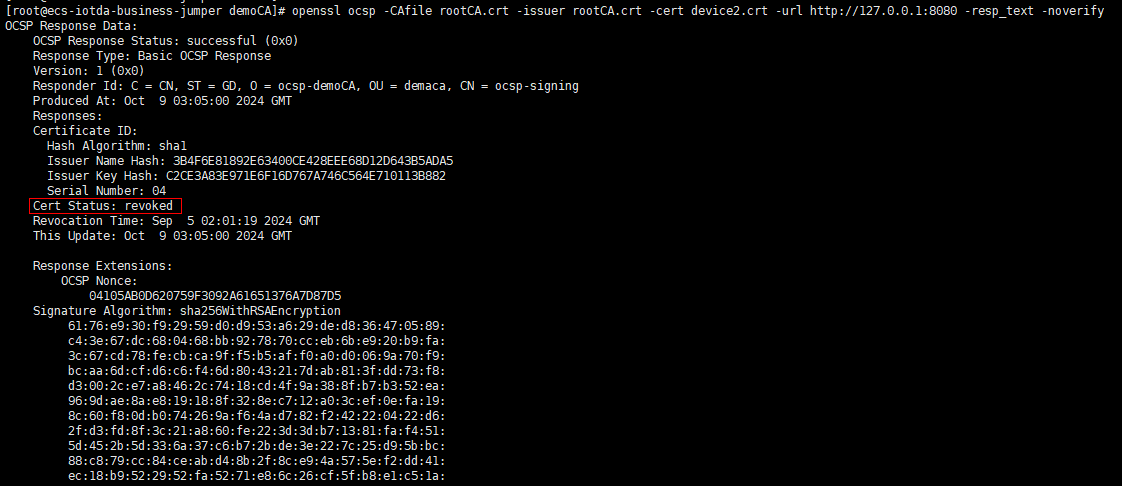 Figure 9 Message tracing - OCSP verification failure details
Figure 9 Message tracing - OCSP verification failure details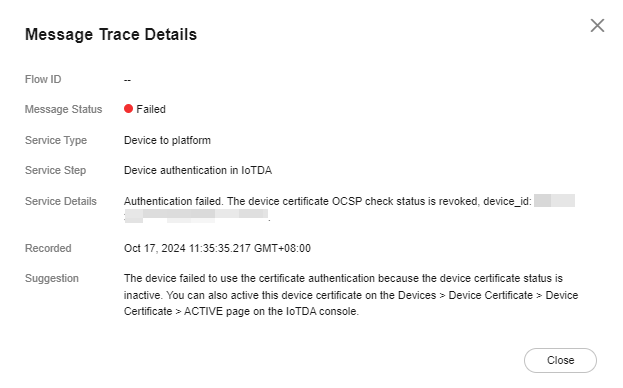
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





