Developing a C# Event Function Using IDE
This section describes how to develop a C# event function using IDE. For details about the C# syntax, initializer and SDK APIs, see C# Function Development Overview.
Constraints
When calling a function using APIG, isBase64Encoded is valued true by default, indicating that the request body transferred to FunctionGraph is encoded using Base64 and must be decoded for processing.
{
"isBase64Encoded": true|false,
"statusCode": httpStatusCode,
"headers": {"headerName":"headerValue",...},
"body": "..."
}
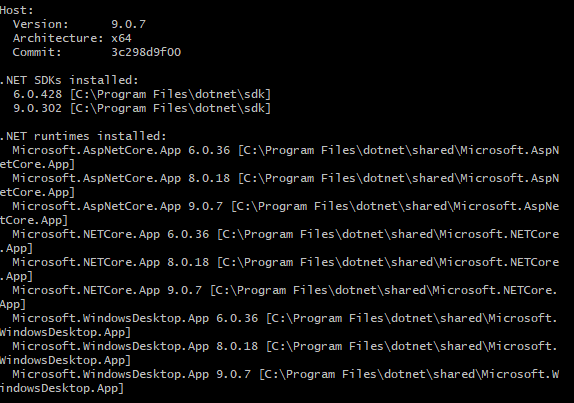
Viewing the.NET Version
Run the following command to view the installed .NET version:
dotnet --info
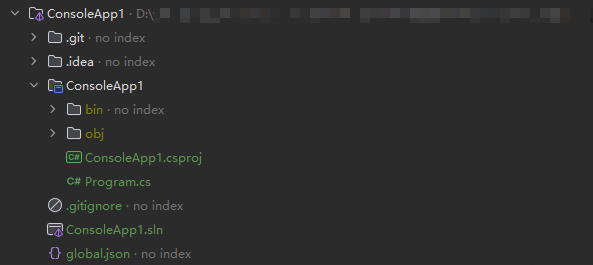
Step 1: Creating a Project
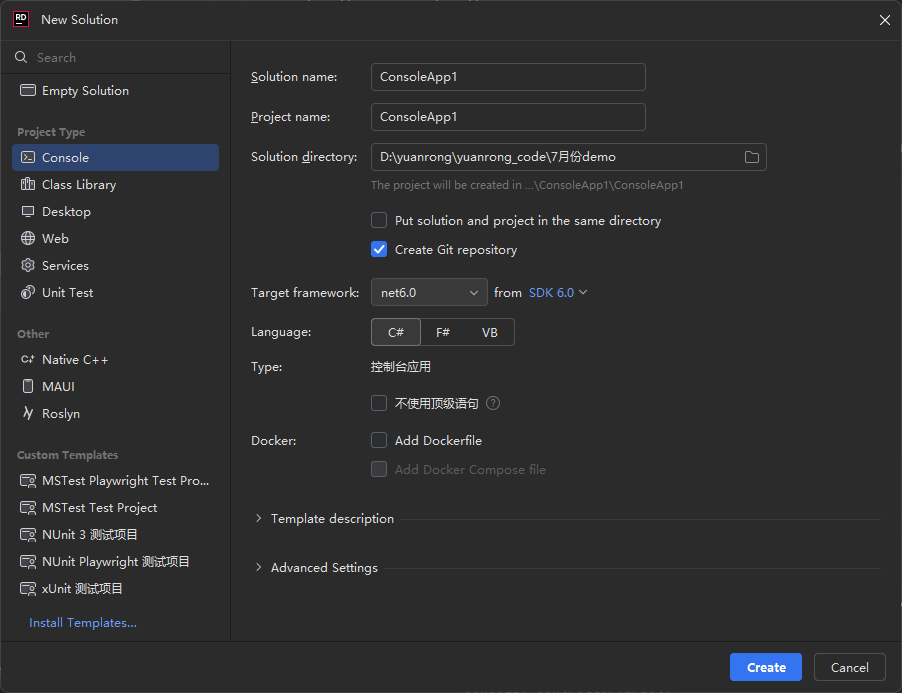
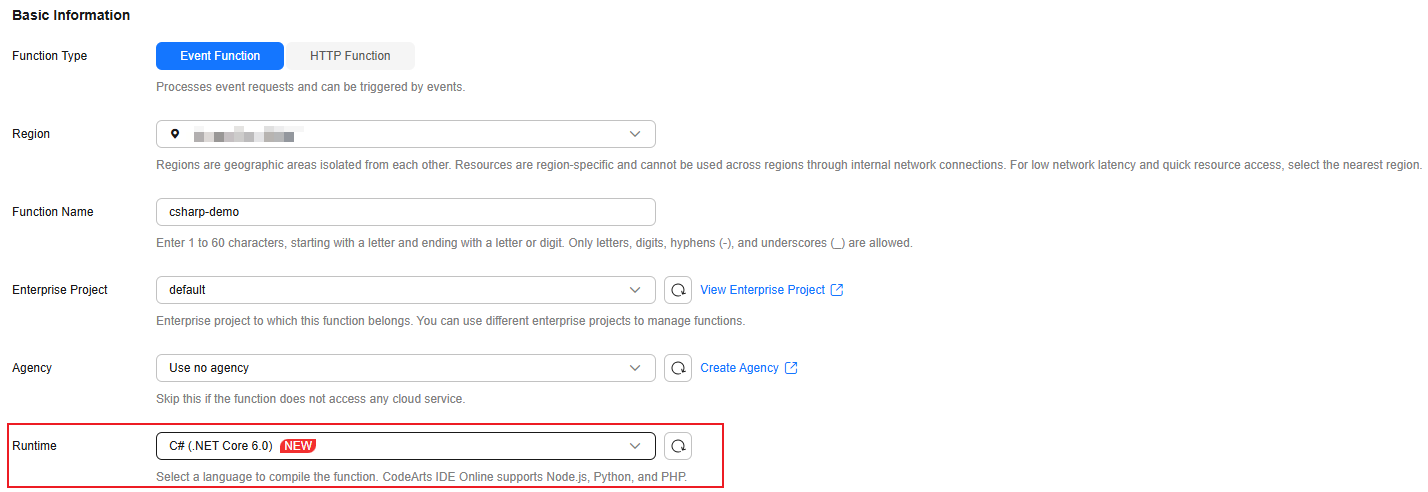
- Open the IDE and create a C# compilation project, as shown in Figure 2. Select net6.0 as the framework.
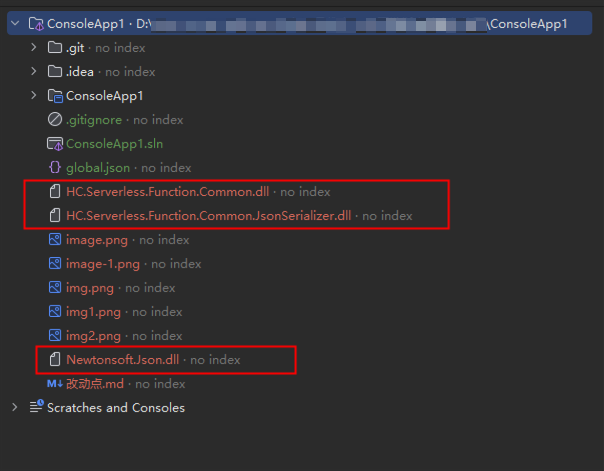
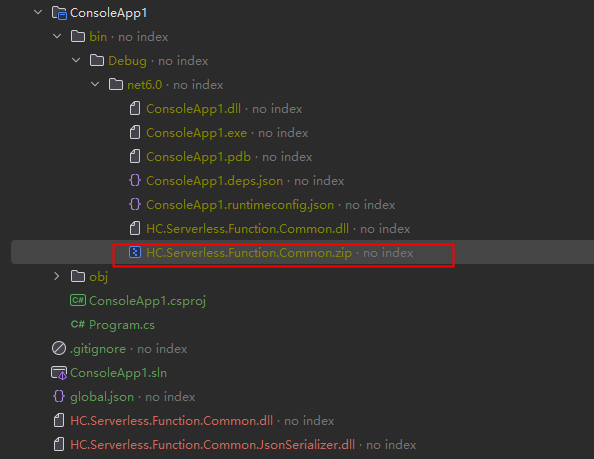
- Check the directory after the project is created.
Figure 3 Project directory structure
- Download the .dll file of the function and decompress the .dll file to the directory shown in Figure 4.
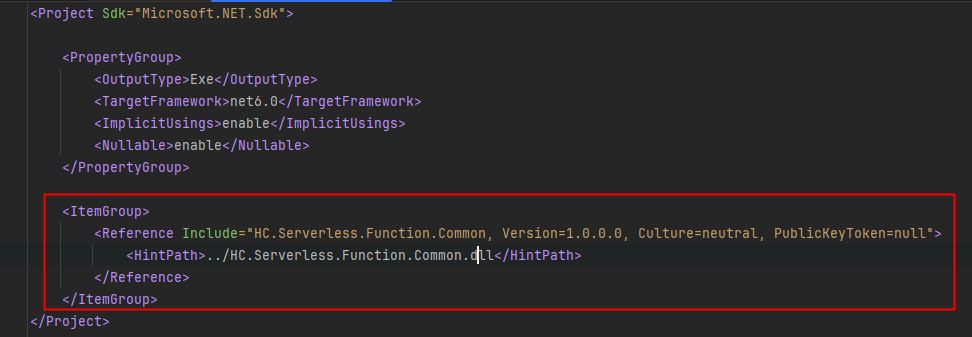
- Edit the ConsoleApp1.csproj file in the project to enable the project to reference the downloaded .dll file. The following information is added to the file:
<ItemGroup> <Reference Include="HC.Serverless.Function.Common, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null"> <HintPath>../HC.Serverless.Function.Common.dll</HintPath> </Reference> </ItemGroup>After the editing is complete, the content of the cspoj file is shown in Figure 5.
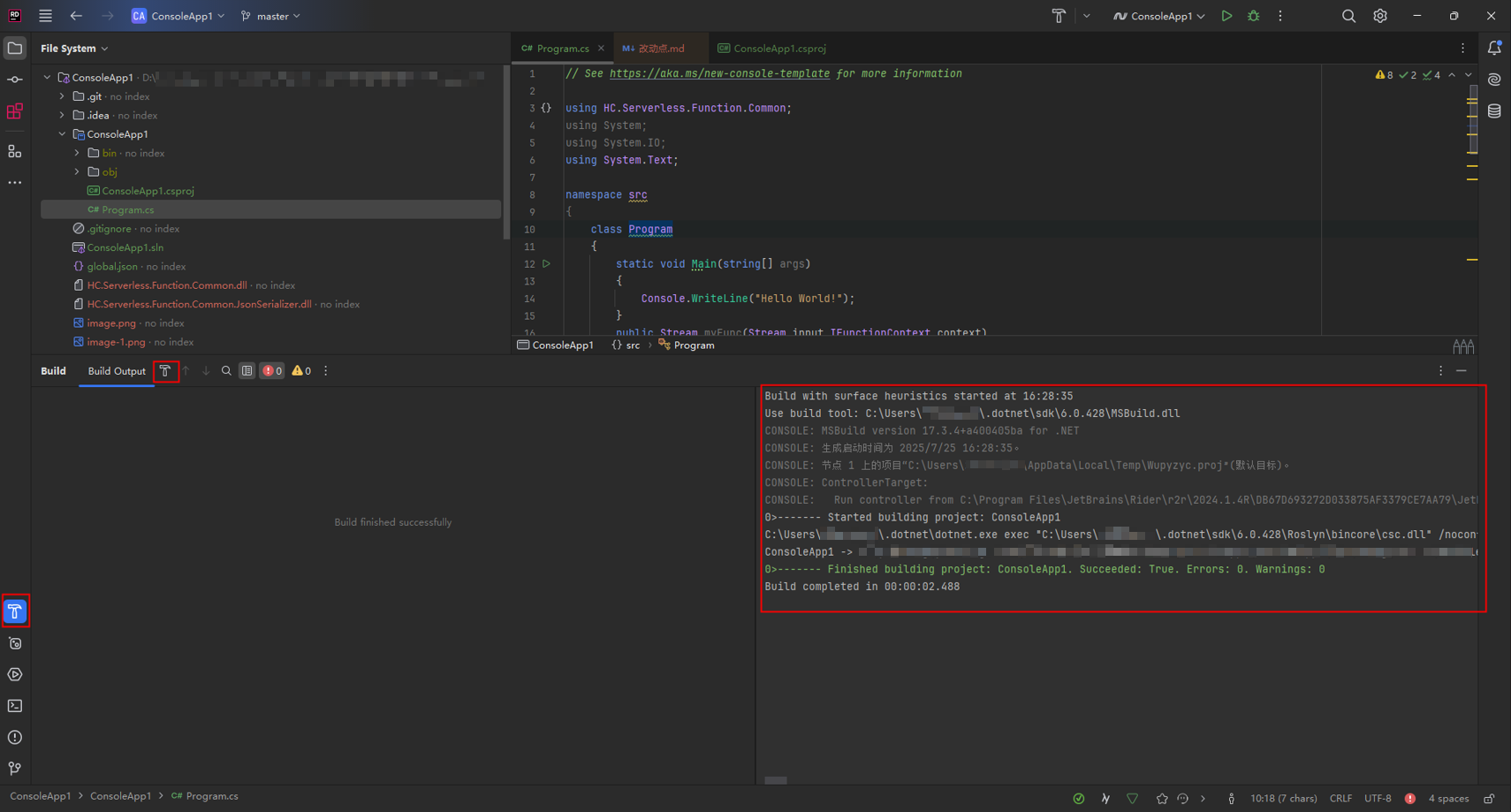
- Edit the Program.cs file in the project and replace the original code in the file with the following code:
using HC.Serverless.Function.Common; using System; using System.IO; using System.Text; namespace src { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); } public Stream myFunc(Stream input,IFunctionContext context) { string payload = ""; if (input != null && input.Length > 0) { byte[] buffer = new byte[input.Length]; input.Read(buffer, 0, (int)(input.Length)); payload = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer); } var ms = new MemoryStream(); using (var sw = new StreamWriter(ms)) { sw.WriteLine("CSharp runtime test(v1.0.2)"); sw.WriteLine("====================================="); sw.WriteLine("Request Id: {0}", context.RequestId); sw.WriteLine("Function Name: {0}", context.FunctionName); sw.WriteLine("Function Version: {0}", context.FunctionVersion); sw.WriteLine("Project: {0}", context.ProjectId); sw.WriteLine("Package: {0}", context.PackageName); sw.WriteLine("Security Access Key: {0}", context.SecurityAccessKey); sw.WriteLine("Security Secret Key: {0}", context.SecuritySecretKey); sw.WriteLine("Security Token: {0}", context.SecurityToken); sw.WriteLine("Token: {0}", context.Token); sw.WriteLine("User data(ud-a): {0}", context.GetUserData("ud-a")); sw.WriteLine("User data(ud-notexist): {0}", context.GetUserData("ud-notexist", "")); sw.WriteLine("User data(ud-notexist-default): {0}", context.GetUserData("ud-notexist", "default value")); sw.WriteLine("====================================="); var logger = context.Logger; logger.Logf("Hello CSharp runtime test(v1.0.2)"); sw.WriteLine(payload); } return new MemoryStream(ms.ToArray()); } } } - As shown in Figure 6, click the compilation button in the IDE to compile the C# project.
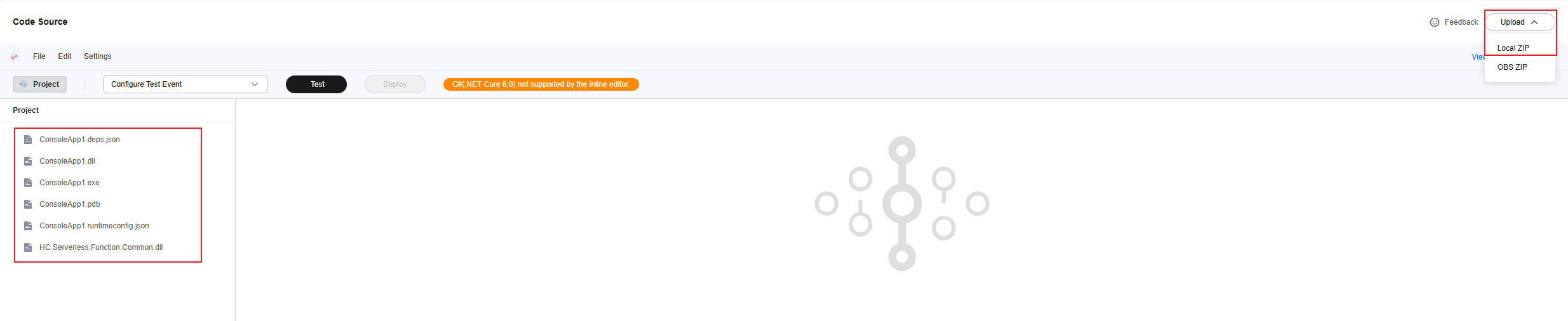
- Compress all compiled files in the ConsoleApp1\bin\Debug\net6.0 directory into a .zip file, as shown in Figure 7. Do not compress the entire folder. Ensure that files are displayed after the package is decompressed.
Step 2: Testing the Function
- Log in to the FunctionGraph console and click Create Function in the upper right corner.
- Create a C# event function from scratch and click Create Now as shown inFigure 8. The function details page is displayed.
- Upload the ZIP file compressed in 7. After the code package is uploaded, it will be automatically deployed on the FunctionGraph console, as shown in Figure 9.
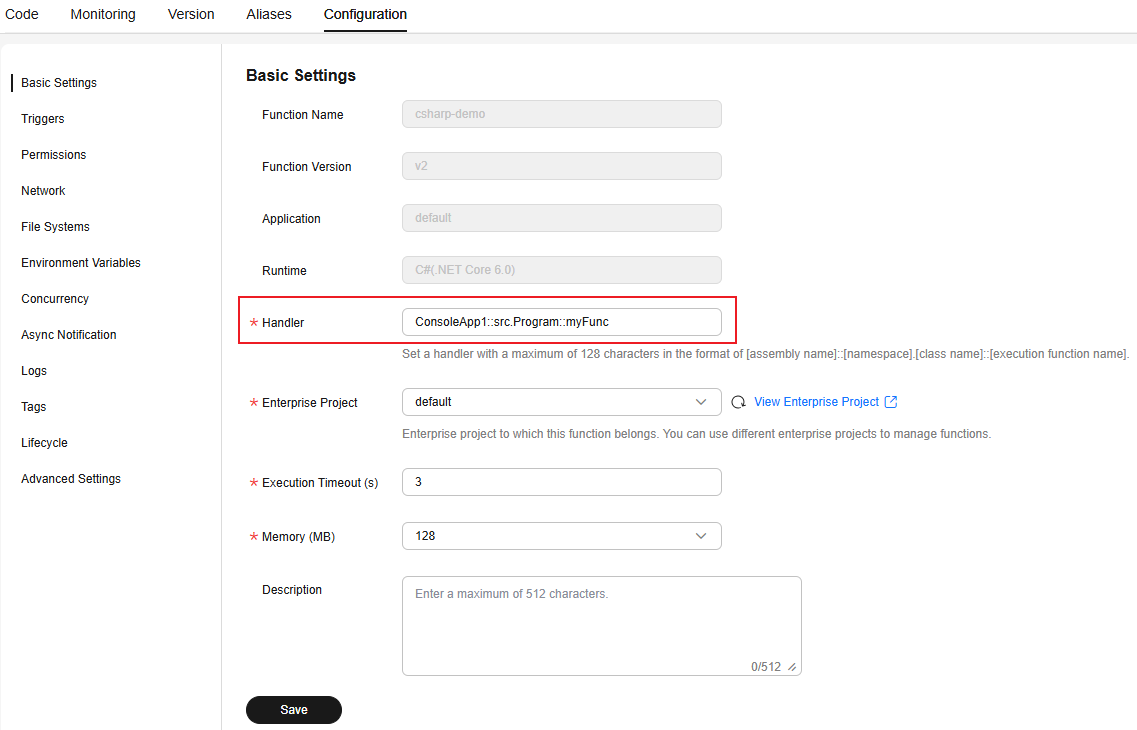
- Choose Configuration > Basic Settings, set Handler to ConsoleApp1::src.Program::myFunc, and click Save, as shown in Figure 10.
The file generated after the C# project in the sample project package is compiled is ConsoleApp1.dll. Therefore, the assembly name of the function handler is ConsoleApp1.
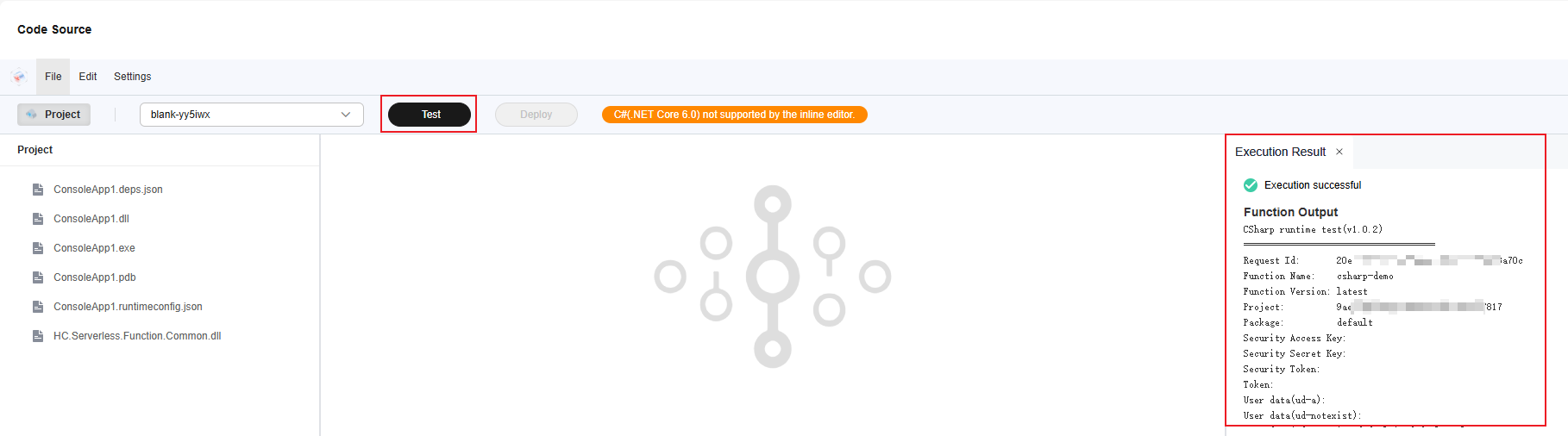
- Return to the Code tab page, click Test to configure a blank test event.
- Select the created blank test event, as shown in Figure 11, and click Test to view the function execution result.
Execution Result
The execution result consists of the function output, summary, and log output.
|
Parameter |
Successful Execution |
Failed Execution |
|---|---|---|
|
Function Output |
The defined function output information is returned. |
A JSON file that contains errorMessage and errorType is returned. The format is as follows: {
"errorMessage": "",
"errorType": ""
}
errorMessage: Error message returned by the runtime. errorType: Error type. |
|
Summary |
Request ID, Memory Configured, Execution Duration, Memory Used, and Billed Duration are displayed. |
Request ID, Memory Configured, Execution Duration, Memory Used, and Billed Duration are displayed. |
|
Log Output |
Function logs are printed. A maximum of 4 KB logs can be displayed. |
Error information is printed. A maximum of 4 KB logs can be displayed. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot