SELECT INTO
Description
SELECT INTO creates a table based on the query result and inserts data retrieved by the query to the new table. Different from common SELECT, SELECT INTO does not return data to the client. The columns of the new table have the same names and data types as the output columns of SELECT.
Precautions
CREATE TABLE AS provides functions similar to SELECT INTO in functions and provides a superset of functions provided by SELECT INTO. You are advised to use CREATE TABLE AS, because SELECT INTO cannot be used in a stored procedure.
Syntax
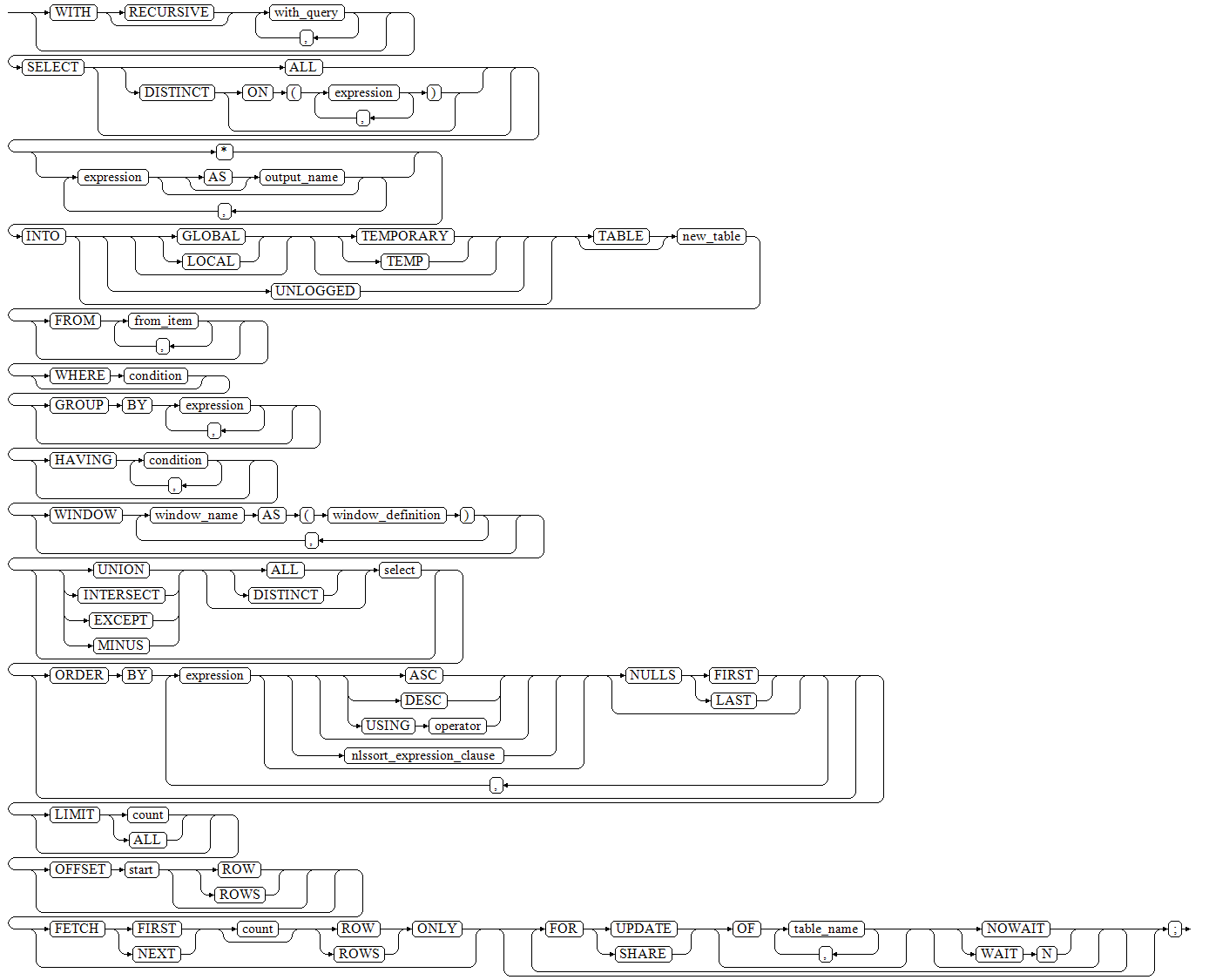
[ WITH [ RECURSIVE ] with_query [, ...] ]
SELECT [ ALL | DISTINCT [ ON ( expression [, ...] ) ] ]
{ * | {expression [ [ AS ] output_name ]} [, ...] }
INTO [ [ GLOBAL | LOCAL ] [ TEMPORARY | TEMP ] | UNLOGGED ] [ TABLE ] new_table
[ FROM from_item [, ...] ]
[ WHERE condition ]
[ GROUP BY expression [, ...] ]
[ HAVING condition [, ...] ]
[ WINDOW {window_name AS ( window_definition )} [, ...] ]
[ { UNION | INTERSECT | EXCEPT | MINUS } [ ALL | DISTINCT ] select ]
[ ORDER BY {expression [ [ ASC | DESC | USING operator ] | nlssort_expression_clause ] [ NULLS { FIRST | LAST } ]} [, ...] ]
[ LIMIT { count | ALL } ]
[ OFFSET start [ ROW | ROWS ] ]
[ FETCH { FIRST | NEXT } [ count ] { ROW | ROWS } ONLY ]
[ {FOR { UPDATE | SHARE } [ OF table_name [, ...] ] [ NOWAIT |WAIT N]} [...] ];
Parameters
- new_table
Specifies the name of the new table.
- UNLOGGED
Specifies that the table is created as an unlogged table. Data written to unlogged tables is not written to the WALs, which makes them considerably faster than ordinary tables. However, an unlogged table is automatically truncated after a crash or unclean shutdown. The contents of an unlogged table are also not replicated to standby servers. Any indexes created on an unlogged table are automatically unlogged as well.
- Usage scenario: Unlogged tables do not ensure data security. Users can back up data before using unlogged tables; for example, users should back up the data before a system upgrade.
- Troubleshooting: If data is missing in the indexes of unlogged tables due to some unexpected operations such as an unclean shutdown, users should rebuild the indexes with errors.
- GLOBAL | LOCAL
When creating a temporary table, you can specify the GLOBAL or LOCAL keyword before TEMP or TEMPORARY. If the keyword GLOBAL is specified, GaussDB creates a global temporary table. Otherwise, GaussDB creates a local temporary table.
- TEMPORARY | TEMP
If TEMP or TEMPORARY is specified, the created table is a temporary table. Temporary tables are classified into global temporary tables and local temporary tables. If the keyword GLOBAL is specified when a temporary table is created, the table is a global temporary table. Otherwise, the table is a local temporary table.
The metadata of the global temporary table is visible to all sessions. After the sessions end, the metadata still exists. The user data, indexes, and statistics of a session are isolated from those of another session. Each session can only view and modify the data committed by itself. Global temporary tables can be created using ON COMMIT PRESERVE ROWS or ON COMMIT DELETE ROWS. The former one creates a session-level table, where user data is automatically cleared when a session ends; the latter creates a transaction-level table, where user data is automatically cleared when a commit or rollback operation is performed. If the ON COMMIT option is not specified during table creation, the session level is used by default. Different from local temporary tables, you can specify a schema that does not start with pg_temp_ when creating a global temporary table.
A local temporary table is visible only in the current session and is automatically dropped at the end of the session. Therefore, you can create and use temporary tables in the current session as long as the connected database node in the session is normal. Temporary tables are created only in the current session. If a DDL statement involves operations on temporary tables, a DDL error will be generated. Therefore, you are advised not to perform operations on temporary tables in DDL statements. TEMP is equivalent to TEMPORARY.

- Local temporary tables are visible to the current session through the schema starting with pg_temp_. You are advised not to manually delete the schema starting with pg_temp_ or pg_toast_temp_.
- If TEMPORARY or TEMP is not specified when you create a table and its schema is set to that starting with pg_temp_ in the current session, the table will be created as a temporary table.
- If another session is using a global temporary table or index, the ALTER or DROP operation cannot be performed on it.
- The DDL of a global temporary table affects only the user data and indexes of the current session. For example, TRUNCATE, REINDEX, and ANALYZE are valid only for the current session.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
-- Create a table and insert data into the table. gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE tbl_person ( id integer, name varchar(20), gender varchar(5) CHECK(gender = 'Male' or gender = 'Female') ); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO tbl_person VALUES (1, 'Bob', 'Male'),(2, 'Anne', 'Female'),(3, 'Jack', 'Male'),(4, 'Danny', 'Male'),(5, 'Alice', 'Female'),(6, 'Susan', 'Female'); -- Add information about all persons whose gender is male in the person table to the new table. gaussdb=#SELECT * INTO tbl_man FROM tbl_person WHERE gender =' Male' -- Query data in the tbl_man table. gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM tbl_man; id | name | gender ----+-------+----- 1 | Bob | Male 3 | Jack | Male 4 | Danny | Male (3 rows) -- Drop the table. gaussdb=#DROP TABLE tbl_person, tbl_man; |
Helpful Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






