Collecting Details of Self-built Oracle Databases
Scenarios
MgC enables you to discover self-built Oracle databases and collect their details. The operation procedure also applies to service-based Oracle databases.
Collection Process
- You install the MgC Agent (formerly Edge) on a Windows or Linux server that can communicate with your self-built Oracle databases.
- The MgC Agent accesses your Oracle databases using the connection credentials you provided. The provided account must have the SELECT ANY DICTIONARY permission. Otherwise, not all details can be collected.
- MgC delivers a collection command to the MgC Agent through IoTDA. After receiving the commands, the MgC Agent creates an Oracle database collection task.
- The MgC Agent invokes the Oracle database collector through RPC. Then the collector queries data by invoking database commands and concatenating SQL statements.
- The collector reports the collected data to the MgC Agent through RPC. The MgC Agent processes RPC messages and reports the collected data to MgC through IoTDA.
- MgC processes and stores the collected data.
Figure 1 Collection flowchart

Required Inputs
|
Parameter |
Mandatory |
Description |
|
ip |
Yes |
The IP address of the database instance. |
|
port |
Yes |
The port used by the Oracle database instance. |
|
user |
Yes |
The username for accessing the Oracle database instance. The account must have the SELECT ANY DICTIONARY permission. |
|
password |
Yes |
The password of the Oracle database instance account. |
|
sid |
No |
The unique identifier of the Oracle database instance. You only need to provide the ID or the service name of the database instance. |
|
serviceName |
No |
The service name of the Oracle database instance. You only need to provide the ID or the service name of the database instance. |
Collected Data
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
name |
The database instance name. |
|
connectAddress |
The access IP address. |
|
useSsl |
Whether SSL is enabled. |
|
instanceId |
The instance ID. |
|
vpcId |
vpcId |
|
subnetId |
The subnet ID. |
|
privateAddress |
The private access address. |
|
publicAddress |
The public access address. |
|
type |
The cluster type. |
|
dbType |
The database type. |
|
nodes |
The cluster nodes. For details, see Collected node data. |
|
dbVersion |
The database engine version. |
|
oracleDatabases |
The database list. For details, see Description of the oracleDatabases field. |
|
serverCharset |
The server character set. |
|
fileStorageMode |
The file storage mode. |
|
backupMode |
The backup mode. |
|
deployMode |
The deployment mode. |
|
racNodesNum |
The number of RAC nodes. |
|
redundancyType |
Whether DR is configured. |
|
dbRelational |
Whether the database instance is connected with other instances. |
|
oracleInstances |
The details of database nodes. For details, see Description of the oracleInstances field. |
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
instanceName |
The database instance name. |
|
archive |
Whether archive is enabled |
|
patches |
The database patches. |
|
controlFiles |
The control file location. |
|
redologFiles |
The location of the redo files. |
|
archiveFreq |
The archive frequency. |
|
dataBaseRole |
The database role. |
Constraints
- Only username/password pairs are supported.
- The provided Oracle account must have the SELECT ANY DICTIONARY permission.
- Due to network restrictions, the collection may fail. In this case, you can restart the collector to solve the problem.

SELECT ANY DICTIONARY is a system permission that allows users to query all data dictionaries of a database. A data dictionary is a central repository for storing database structure information, including tables, columns, data types, and constraints.
- Only online collection is supported.
Preparations
- You have obtained the IP address, port, service name or SID, username, and password of the source Oracle database. In Oracle databases, the default service name is often set to ORCL. You need to specify the service name of the Oracle database to be collected.
You can log in to the Oracle database instance and run the following command to view the names of all registered services:
SELECT instance_name from v$instance
- Prepare a Windows server that can communicate with the Oracle database instance. Perform the following operations:
- Install the MgC Agent and log in. For details, see Installing the MgC Agent.
- Connect the MgC Agent to MgC.
Collecting Details of Oracle Databases
- Sign in to the MgC console. In the navigation pane, under Project, select your application migration project from the drop-down list.
- In the navigation pane, choose Source Resources.
- Click the Databases tab.
- Click Add above the list.
Figure 2 Adding a database
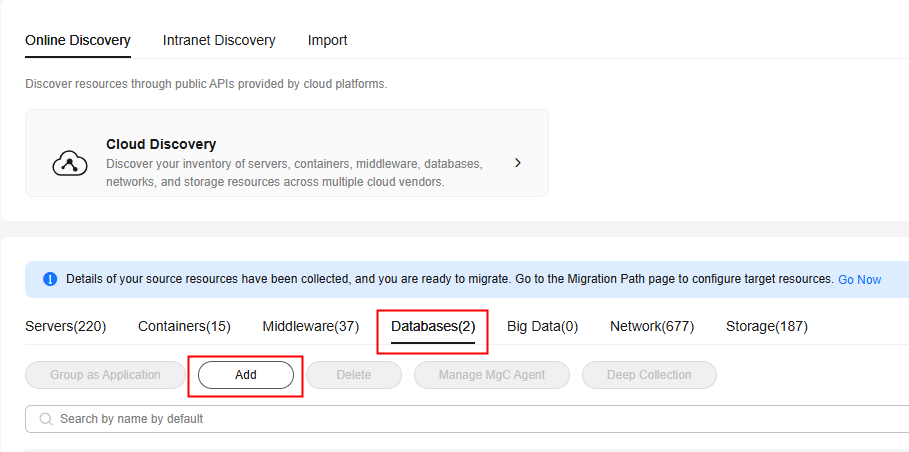
- Set the parameters based on Table 5.
Table 5 Parameters for adding a database Parameter
Description
Name
User-defined
MgC Agent
Select the MgC Agent connected to MgC.
Type
Select Oracle.
IP Address
Enter the IP address for connecting to the source Oracle database server.
Port
Enter the listening port of the source Oracle database. The default value is 1521.
Service Name/SID
Enter the service name of the source database. The default value is ORCL.
You can log in to the Oracle database server and run the following command to view the service name of the database you want to add to MgC:SELECT instance_name FROM v$instance;
Credential
Select the database credential. If the credential is not displayed in the drop-down list, go to the MgC Agent console, add the credential, and synchronize it to MgC. When you add the credential to the MgC Agent, set Resource Type to Database and Authentication to Username/Password.
- Click Confirm. The system automatically starts collecting details about the database. When Collected shows up in the Deep Collection column, the collection is complete. Click the database name. On the displayed database details page, you can view the collected information.
Generating Target Recommendations
- In the navigation pane, choose Migration Path.
- On the Target Recommendations tab, click Generate Target Recommendations.
- Enter a report name, set Scope to Select Resource, and select the Oracle databases to be assessed.
- Configure an assessment policy based on Table 6.
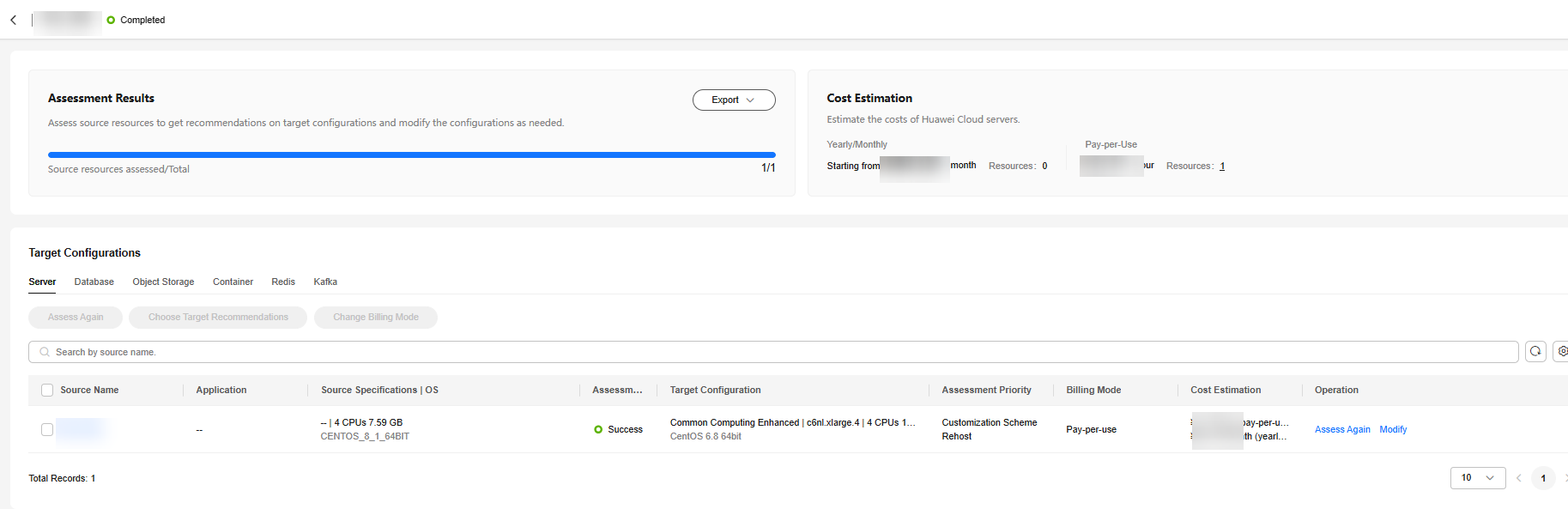
- Click Create Assessment. After the assessment task is complete, you can view target recommendations which include the recommended configurations of target resources.
Viewing Target Recommendations
On the Target Recommendations page, click the corresponding assessment report to view the assessment details.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





