This section describes where CFW is deployed in the network architecture for inbound cloud traffic protection and how to configure CFW when it is used with other Huawei Cloud services.
Overview
Web Application Firewall (WAF), Advanced Anti-DDoS (AAD), and Content Delivery Network (CDN) work as reverse proxies. If these services are deployed, the source IP addresses received by CFW is the back-to-origin IP addresses returned by these services.
If other Huawei Cloud products are configured, traffic will be protected by multiple services. For inbound traffic protection, if a reverse proxy service, such as Content Delivery Network (CDN), Anti-DDoS Service (AAD), or cloud Web Application Firewall (cloud WAF), is deployed before CFW, you need to configure a policy that allows back-to-source IP addresses to avoid misblocking. If a dedicated or load-balancing WAF instance is purchased, configure it as needed.
AAD/CDN
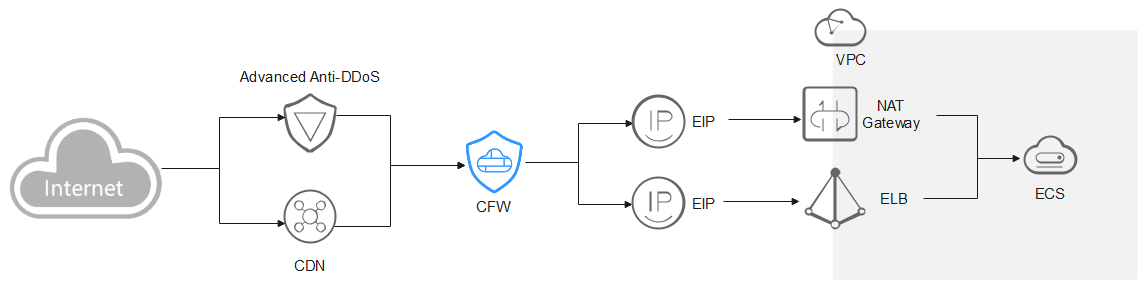
You are advised to create a protection rule to allow access from back-to-source IP addresses, or add these IP addresses to the whitelist.
- Creating a rule: Create a policy with the highest priority to allow all back-to-origin IP addresses. In this way, traffic still goes to CFW for check.
- Adding to whitelist: After back-to-source IP addresses are added to the whitelist, the traffic will be directly allowed to pass through, and CFW does not perform any protection.
After traffic passes through the reverse proxy, a source IP address is translated into a back-to-source IP address. If an external attack occurs, CFW cannot obtain the real IP address of an attacker. In this case, you can obtain the real IP address based on the X-Forwarded-For field. For details, see How Do I Obtain the Real IP Address of an Attacker?

Do not block back-to-origin IP addresses or add them to a blacklist. Otherwise, all traffic from the IP addresses will be blocked and your services may be affected.
Cloud WAF
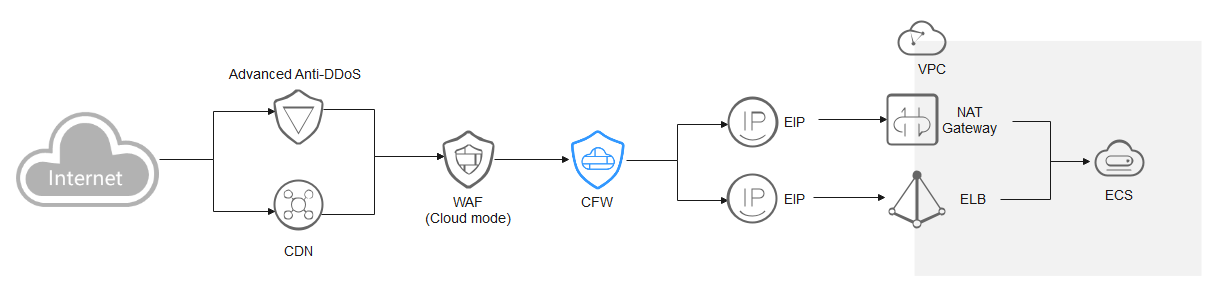
You are advised to create a protection rule to allow access from back-to-source IP addresses, or add these IP addresses to the whitelist.
- Creating a rule: Create a policy with the highest priority to allow all back-to-origin IP addresses. In this way, traffic still goes to CFW for checks.
- Adding to whitelist: After back-to-source IP addresses are added to the whitelist, the traffic will be directly allowed to pass through, and CFW does not perform any protection.
After traffic passes through the reverse proxy, a source IP address is translated into a back-to-source IP address. If an external attack occurs, CFW cannot obtain the real IP address of the attacker. In this case, you can obtain the real IP address based on the X-Forwarded-For field. For details, see How Do I Obtain the Real IP Address of an Attacker?

Do not block back-to-origin IP addresses or add them to a blacklist. Otherwise, all traffic from the IP addresses will be blocked and your services may be affected.
Dedicated WAF
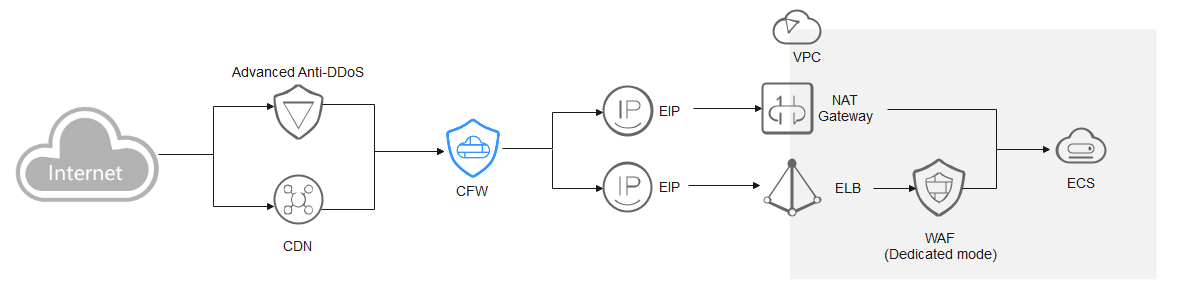
Traffic passes through CFW and then WAF. The log viewing method varies depending on the protection scenario.
- You have enabled CFW protection for the EIPs bound to public network ELB load balancers.
If there is an attack from the client, CFW prints the attack event on the Internet Border Firewall tab under Attack Event Logs.
The destination IP address of the event is the EIP bound to the public ELB load balancer, and the source IP address is the IP address of the client.
- You have enabled VPC border firewall and associated with the VPC where the origin server resides. No protection is enabled for EIPs bound to the ELB load balancer.
If there is an attack from the client, CFW prints the attack event on the VPC Border Firewall tab under Attack Event Logs.
The destination IP address of the event is the private IP address of the origin server, and the source IP address is the private IP address of the traffic ingress (such as the Nginx server).
ELB-mode WAF
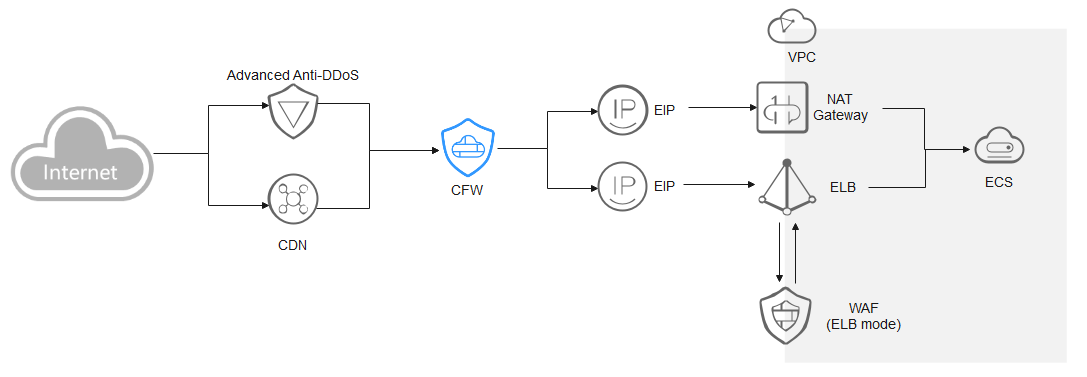
The traffic passes through CFW and then WAF. Configure services as needed.











