Enabling SQL Audit
Scenarios
If you enable the SQL audit function, all SQL operations will be logged for your download and query. By default, SQL audit is disabled. Enabling this function may affect database performance. The performance impact depends on the audit log throughput.
This section describes how to enable, modify, and disable SQL audit.
Supported Kernel Versions
The kernel version must be 2.0.60.241200 or later. If your DB engine version is too early, upgrade it to the latest version by referring to Upgrading the Minor Version of a DB Instance. For details about how to check the kernel version, see How Can I Check the Version of a TaurusDB Instance?
Constraints
|
Audit Log Type |
Constraint |
|---|---|
|
SQL audit logs |
|
|
Audit logs reported to LTS |
|
Configuring Audit Logs
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose SQL Audits. On the displayed page, click Set SQL Audit above the list. In the displayed dialog box, configure information as required and click OK.
- Enabling or setting SQL audit
- To enable SQL audit, toggle
 (disabled) to
(disabled) to  (enabled).
(enabled). - Audit logs can be retained from 1 to 732 days and are retained for 7 days by default.
Figure 1 Setting SQL audit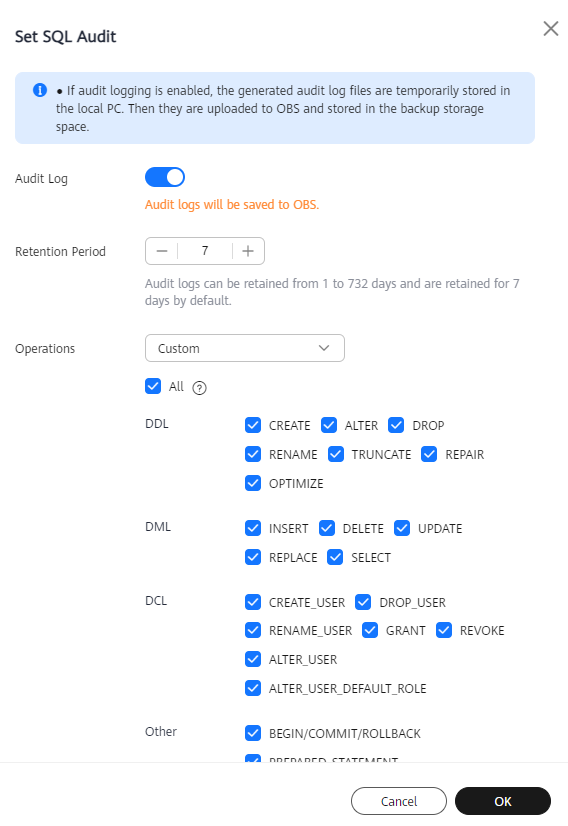
The SQL statements executed by PreparedStatement and scheduled tasks through a MySQL client will be treated as PREPARED_STATEMENT and CREATE, respectively. However, the SQL statements executed by PreparedStatement through JDBC will not be recorded.
You can change the value of the audit_log_buffer_size parameter on the console to adjust the size of the audit log buffer. For details, see Modifying Parameters of a DB Instance.
Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Level
Description
audit_log_buffer_size
GLOBAL
Size of the audit log buffer, in bytes.
Default value: 1048576
After SQL audit is enabled, Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Control Language (DCL), and other operation types are supported. The details are as follows:
Table 3 DDL types and operations Type
Operation
CREATE
create_db, create_event, create_function, create_index, create_procedure, create_table, create_trigger, create_udf, create_view
ALTER
alter_db, alter_db_upgrade, alter_event, alter_function, alter_instance, alter_procedure, alter_table, alter_tablespace
DROP
drop_db, drop_event, drop_function, drop_index, drop_procedure, drop_table, drop_trigger, drop_view
RENAME
rename_table
TRUNCATE
truncate
REPAIR
repair
OPTIMIZE
optimize
Table 4 DML types and operations Type
Operation
INSERT
insert, insert_select
DELETE
delete, delete_multi
UPDATE
update, update_multi
REPLACE
replace, replace_select
SELECT
select
Table 5 DCL types and operations Type
Operation
CREATE_USER
create_user
DROP_USER
drop_user
RENAME_USER
rename_user
GRANT
grant_roles, grant
REVOKE
revoke, revoke_all, revoke_roles
ALTER_USER
alter_user
ALTER_USER_DEFAULT_ROLE
alter_user_default_role
Table 6 Other types and operations Type
Operation
BEGIN/COMMIT/ROLLBACK
begin, commit, release_savepoint, rollback, rollback_to_savepoint, savepoint
PREPARED_STATEMENT
execute_sql, prepare_sql, dealloc_sql
CALL_PROCEDURE
call_procedure
KILL
kill
SET_OPTION
set_option
CHANGE_DB
change_db
UNINSTALL_PLUGIN
uninstall_plugin
INSTALL_PLUGIN
install_plugin
SHUTDOWN
shutdown
SLAVE_START
slave_start
SLAVE_STOP
slave_stop
LOCK_TABLES
lock_tables
UNLOCK_TABLES
unlock_tables
FLUSH
flush
XA
xa_commit, xa_end, xa_prepare, xa_recover, xa_rollback, xa_start
- To enable SQL audit, toggle
- Disabling SQL audit
To disable SQL audit, toggle
 (enabled) to
(enabled) to  (disabled).If you select the check box "I acknowledge that after audit log is disabled, all audit logs are deleted." and click OK, all audit logs will be deleted.
(disabled).If you select the check box "I acknowledge that after audit log is disabled, all audit logs are deleted." and click OK, all audit logs will be deleted.
Deleted audit logs cannot be recovered. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- Enabling or setting SQL audit
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose SQL Audits.
- Click
 next to Report Audit Logs to LTS.
next to Report Audit Logs to LTS. - In the displayed dialog box, select a log group and log stream, and click OK.
Figure 2 Reporting audit logs to LTS
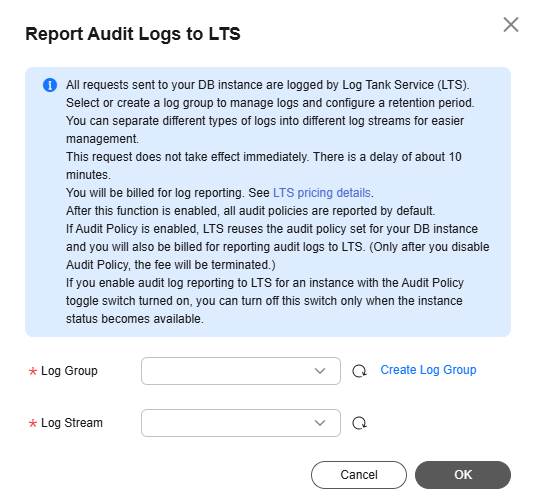
- To change the log group and log stream, click Edit.
Figure 3 Changing the log group and log stream

- In the displayed dialog box, click OK.
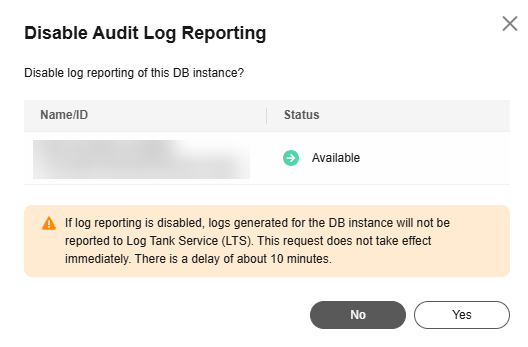
Disabling Audit Log Reporting
- Log in to the TaurusDB console.
- On the Instances page, click the instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose SQL Audits.
- Click
 next to Report Audit Logs to LTS.
next to Report Audit Logs to LTS. - In the displayed dialog box, click Yes.
Figure 4 Disabling audit log reporting
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





