Managing Configuration Items
Configuration items (ConfigMaps) are user-defined resources that store application configurations. They can be used as files or environment variables in applications.
Configuration items allow you to decouple configuration files from images to enhance the portability of applications.
Benefits of configuration items:
- Manage configurations for different environments and services.
- Deploy an application in different environments using the same configuration. You can maintain configuration files in multiple versions, which makes it easy to update and roll back applications.
- Quickly import configurations in the form of files to containers.
This section describes how to create, view, update, and delete configuration items for the cluster bound to a Kubernetes or VM + Kubernetes environment.
Restrictions
Configuration items must be associated with namespaces. CCE cluster 1.11.7-r2 and later support Kubernetes RBAC authorization and namespace permission configuration. You can regulate users' or user groups' access to Kubernetes resources in a single namespace based on their Kubernetes RBAC roles. For details, see Namespace Permissions.
If a CCE cluster 1.11.7-r2 or later is bound in the environment and namespace permissions are configured, you must have the administrator permission (cluster-admin) for all namespaces in the cluster or the development permission (admin) for a single namespace to be operated to manage namespaces.
Prerequisites
A cluster has been bound to the environment. For details, see Binding a Cluster.
Creating a Configuration Item
- Log in to ServiceStage.
- Choose Environment Management. The Environment Management page is displayed.
- Click the target environment. The Overview page is displayed.
- Choose Clusters from Compute.
- Go to the ConfigMap page.
- For a non-HA environment, click the ConfigMap tab.
- For an HA environment, click the bound cluster and click the ConfigMap tab.
- Click Create Configuration Item.
ServiceStage allows you to create configuration items in Visualization or YAML mode.
- Method 1: Visualization
Configure the configuration item by referring to Table 1. Parameters marked with an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
Table 1 Parameters for creating a configuration item in visualization mode Parameter
Description
*Configuration Name
Configuration item name, which must be unique in a namespace.
Enter 4 to 24 characters. Start with a lowercase letter and end with a lowercase letter or digit. Only use lowercase letters, digits, or hyphens (-).
*Cluster
Select the cluster bound to the environment.
*Namespace
Namespace to which the configuration item belongs.
- Select an existing namespace: Select the cluster-created namespace default or a user-created namespace. For details about namespace types, see Managing Namespaces.
- Use a new namespace: Click Create Namespace and create a namespace by referring to Creating a Namespace.
Description
Configuration item description. Enter 0 to 255 characters.
Configuration Data
Configuration data to be used in applications or used to store configuration data. Key indicates a file name, and Value indicates the content in the file.
- Click Add Data.
- Enter the key and value.
- The key contains 1 to 63 characters. Only use digits, letters, dots (.), hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
- The value contains 0 to 1,048,576 characters.
Configuration Labels
Labels are attached to objects such as applications, nodes, and services in key-value pairs. Labels define the identifiable attributes of these objects and are used to manage and select the objects.
- Click Add Label.
- Enter the key and value.
- The key contains 1 to 63 characters. Start and end with a letter or digit. Only use digits, letters, dots (.), hyphens (-), underscores (_), and slashes (/).
- The value contains 1 to 63 characters. Start and end with a letter or digit. Only use digits, letters, dots (.), hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
- Method 2: YAML
To create a configuration item by uploading a file, ensure that a configuration item resource file in YAML format has been created and the file size is less than 1 MB. For details, see Requirements for the Configuration Item Resource File.
- Select a cluster from the Cluster drop-down list.
- Use either of the following methods to set the configuration item resource file:
- Click Upload File, select the configuration item resource file created locally, click Open, and wait until the file is uploaded.
- Write or modify the ConfigMap resource file in Orchestration Content.
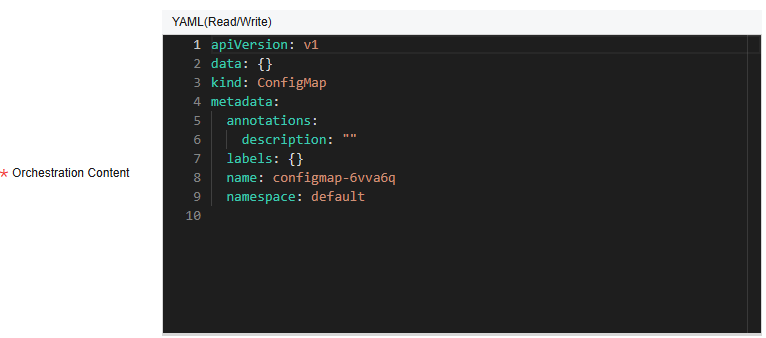
- Method 1: Visualization
- Click Create ConfigMap.
After the configuration item is created, it is displayed in the configuration item list.
Follow-up Operations
After a configuration item is created, you can search for, view, update, and delete the configuration item by referring to Table 2.
- After a configuration item is deleted, the component to which the configuration item is mounted or referenced in environment variables may fail to be started after being upgraded.
- System configuration items can only be viewed.
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Searching for a configuration item |
|
|
Viewing a configuration item |
Click Show YAML in the Operation column of the target configuration item to view the content of the YAML file of the configuration item. |
|
Editing a configuration item |
To update data, labels, and description in a configuration item in YAML mode, perform the following operations:
|
|
Modifying a configuration item |
|
|
Deleting a configuration item |
|
Requirements for the Configuration Item Resource File
A configuration item resource file should be in YAML format, and the file size cannot exceed 1 MB.
Example:
apiVersion: v1
data: {}
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
annotations:
description: ''
labels: {}
name: configmap-ww8qkl
namespace: cse
For details about key parameters, see Table 3.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
apiVersion |
Fixed value: v1. |
|
kind |
Fixed value: ConfigMap. |
|
metadata.name |
Configuration item name, which can be customized. The configuration item name must be unique in a namespace. Enter 4 to 24 characters. Start with a lowercase letter and end with a lowercase letter or digit. Only use lowercase letters, digits, or hyphens (-). |
|
data |
Configuration item data in key-value pair format.
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





