Scenarios
More and more companies in various industries use OBS to store static resource files such as images, videos, and software packages, and use OBS as the storage source for websites, forums, apps, and games. These static resources can be obtained by accessing OBS through URLs. Generally, files are stored in only one region. If you access OBS far away from the region where files are stored, the response speed may be slow. In scenarios where frequent access is required, accessing OBS to obtain files consumes a large amount of traffic.
To improve the speed and stability for accessing static resource files, you can use CDN acceleration. If you have configured a user-defined domain name for a bucket, you can directly enable CDN acceleration for the domain name. If you have not configured a user-defined domain name for the bucket, you can configure a CDN acceleration domain name.
CDN acceleration applies to the following scenarios:
- Website acceleration
When static resources (such as images and files) on portals, e-commerce platforms, or user-generated content (UGC) apps are accessed by large or globally distributed user bases, CDN acceleration can make the responses faster.
- Download acceleration
CDN acceleration enables higher bandwidth and faster transmission, which reduces the time required for downloading files from websites, game clients, or app stores.
- On-demand service acceleration
In scenarios, such as online education and video sharing, that offer video on demand (VOD) and audio on demand (AOD) services, CDN acceleration can minimize playback buffering.
For details, see Application Scenarios.
Video Tutorial
This video shows how to configure a CDN acceleration domain name for an OBS bucket:
- On OBS Console, bind an acceleration domain name to the OBS bucket.
- On the DNS console, add a CNAME record set.
Billing for CDN-Accelerated Access to OBS
If you use Huawei Cloud CDN to accelerate access to the data stored in OBS, you will be billed for using both OBS and CDN.
Figure 1 shows how and what costs are generated.
Figure 1 Using CDN to access OBS
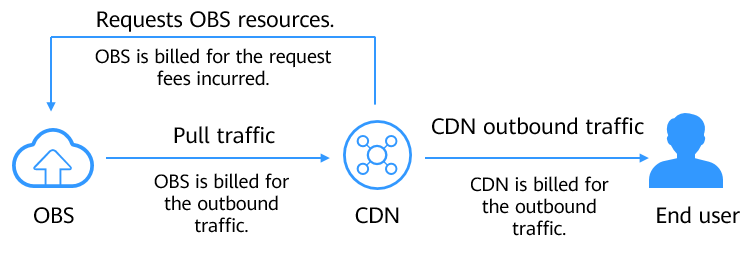
Table 1 describes the billing items in detail.
Table 1 Billing items for accessing OBS via CDN acceleration
|
Billing Item |
Billing Party |
Description |
Billing Mode |
|
Requests |
OBS |
When you attempt to access data the first time, a CDN edge PoP will send requests to pull data from the origin server (OBS). OBS bills you for the requests, also the number of API calls. |
Pay-per-Use |
|
CDN pull traffic |
OBS |
Pull traffic generated when the origin server (OBS 3.0 bucket) returns data and caches it on the CDN edge PoP. If Direct Connect is used, the price will be different. For details, see Product Pricing Details.
Such traffic is only generated for OBS 3.0 buckets. If data is pulled from OBS 2.0 buckets, the data is directly transferred out over the Internet. |
Pay-per-Use |
|
CDN traffic |
CDN |
Outbound traffic generated when you access a CDN edge PoP. For details, see Billing by Traffic. |
Pay-per-Use
Resource packages (prepaid CDN traffic packages)
|
Principles
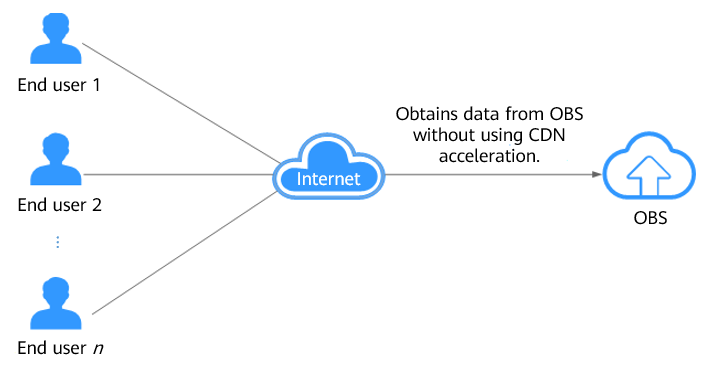
Accessing OBS without CDN acceleration: Files are stored in only one region. Therefore, when a client accesses OBS far away from the region, the response speed may be slow.
Accessing OBS with CDN acceleration: When a client initiates a request, CDN searches for the CDN PoP that responds the fastest to the domain name and checks whether the CDN PoP has already cached the data requested by the client.
- If cached, the CDN PoP returns the data to the client.
- If not, the CDN PoP pulls the data from OBS, returns the data to the client, and caches the data on itself.
The CDN acceleration service can speed up response and improve user experience at low costs.
The following explains how a client accesses OBS without and with CDN acceleration.
Figure 2 shows the process of accessing OBS directly from clients without CDN acceleration.
Figure 2 Process of obtaining data from OBS
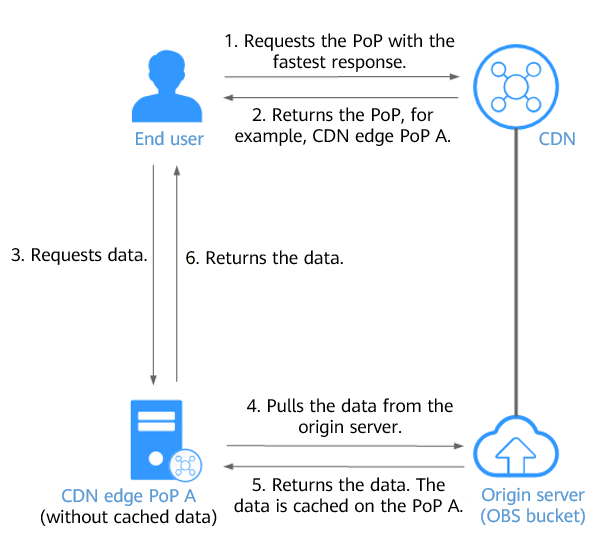
When a client initiates a request, CDN searches for the CDN PoP that responds the fastest to the domain name and detects that the requested data is not cached on the PoP. Then, the CDN PoP pulls the data from OBS, returns the data to the client, and caches the data on itself. Figure 3 shows the request process.
Figure 3 Accessing OBS with CDN acceleration (without cached data on the CDN PoP)
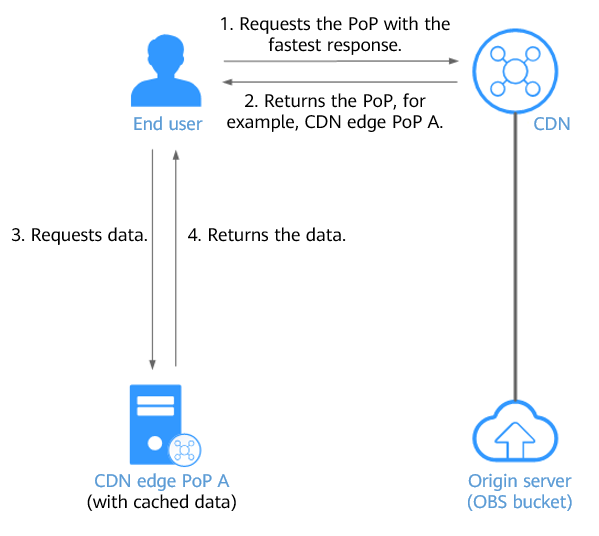
When a client initiates a request, CDN searches for the CDN PoP that responds the fastest to the domain name and detects that the requested data is cached on the PoP. Then, the CDN PoP returns the data to the client, without pulling data from OBS. Figure 4 shows the request process.
Figure 4 Accessing OBS with CDN acceleration (with cached data on the CDN PoP)
Constraints
Only buckets whose version is 3.0 or later support CDN acceleration. To check the version of a bucket, go to OBS Console, click the bucket name to go to the Overview page, and find the version in the Basic Information area.
Configuring an Acceleration Domain Name
You can use OBS Console to configure acceleration domain names.
To configure an acceleration domain name on OBS Console, perform the following steps:
- Bind an acceleration domain name to the bucket.
- Add a CNAME record set to map the acceleration domain name to the default domain name of the bucket.
Step 1: Bind an Acceleration Domain Name
- In the navigation pane of OBS Console, choose Object Storage.
- In the bucket list, click the bucket you want to operate. The Objects page is displayed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Basic Configurations > Domain Name Mgmt.
Figure 5 Domain name management page
- In the upper part of the page, click Configure Acceleration Domain Name.
If no user-defined domain names are bound, you also can click
Configure Acceleration Domain Name in the lower part of the page.

If CDN has not been enabled, a dialog box is displayed after you click Configure Acceleration Domain Name. Enable CDN as prompted.
Figure 6 Configuring an acceleration domain name
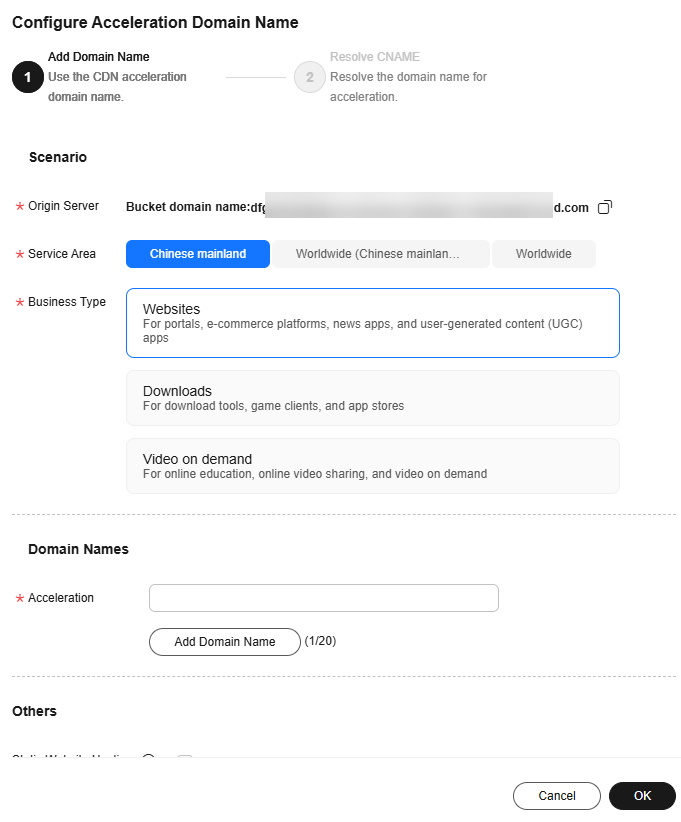
- Configure parameters by referring to Table 2.
Table 2 Parameters for adding an acceleration domain name
|
Parameter |
Value |
Description |
Example Value |
|
Origin Server |
- |
The origin server (the default domain name of the OBS bucket that stores the requested resources) that is accessed by the client using the acceleration domain name
This parameter is displayed by default and requires no configuration. |
- |
|
Service Area |
Chinese mainland |
If you select Chinese mainland, all requests are scheduled to CDN PoPs in the Chinese mainland. The acceleration domain name must be licensed by the MIIT. For details, see ICP Filing Process. |
Worldwide |
|
Outside of Chinese mainland |
If you select Outside of Chinese mainland, all requests are scheduled to CDN PoPs outside the Chinese mainland. You do not need to apply for a license for the acceleration domain name from the MIIT. |
|
Worldwide |
If you select Worldwide, worldwide requests are scheduled to the nearest, optimal CDN PoP. The acceleration domain name must be licensed by the MIIT. For details, see ICP Filing Process. |
|
Business Type |
Websites |
When static resources (such as images and files) on portals, e-commerce platforms, or user-generated content (UGC) apps are accessed by large or globally distributed user bases, CDN acceleration can make the responses faster. |
Websites |
|
Downloads |
CDN acceleration enables higher bandwidth and faster transmission, which reduces the time required for downloading files from websites, game clients, or app stores. |
|
Video on demand |
In scenarios, such as online education and video sharing, that offer video on demand (VOD) and audio on demand (AOD) services, CDN acceleration can minimize playback buffering. |
|
Acceleration |
- |
The user-defined domain name to be accelerated
- The domain name:
- Must start with an asterisk (*), a letter, or a digit.
- Can contain letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.).
- Can have a suffix of 2 to 6 uppercase or lowercase letters, for example, .com and .cn.
- The ownership of the domain name must be verified.
To prevent domain names from being maliciously added, you need to verify the ownership of the domain name the first time you connect a domain name to CDN. For details, see Verifying the Domain Name Ownership.
- You can add up to five domain names at a time.
NOTE:
If you want to choose one of the existing Huawei Cloud domain names from the drop-down list on OBS Console, you must have the Domains:domains:getDetails permission. You can contact the administrator to use IAM to grant you this permission. For details, see Assigning Permissions to an IAM User.
|
static.example.com |
|
Static Website Hosting |
- |
You can upload static website files to your OBS bucket and grant anonymous users the read permission for these files, and then configure static website hosting for the bucket, so that OBS can host your static website. For details, see Static Website Hosting.
|
- |
- Click OK.
Step 2: Add a CNAME Record Set
Add a CNAME record set to map the user-defined domain name to the default domain name of the bucket.
- Click Resolve to automatically add a CNAME record set.
- If you specified a Huawei Cloud domain name, click Resolve for DNS to add a CNAME record set.
- If you specified a domain name that is not registered with Huawei Cloud, skip this step and go to 2.
- Manually add a CNAME record set.
- If you are not using a Huawei Cloud domain name, follow the CNAME resolution guide provided by your DNS provider.
- If you are using a Huawei Cloud domain name, do as follows:
- Log in to the DNS console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Public Zones.
- (Optional) Create a public zone. If you have already created one, skip this step.
- On the Public Zones page, click Create Public Zone in the upper right corner.
- Configure parameters by referring to the following table. Retain the default settings for other parameters.
Table 3 Parameters for creating a public zone
|
Parameter |
Example Value |
Description |
|
Domain Name |
example.com |
The domain name purchased from a domain name registrar
Enter the user-defined domain name bound to the bucket here. |
|
Enterprise Project |
default |
The enterprise project to be associated with the public zone. You can manage public zones by enterprise project.
This parameter is available and mandatory only when you are using an enterprise account.
Notes:
|
- Click OK.
- Locate the row that contains the domain name to which you want to add a record set and click the domain name.
- On the Record Sets tab, click Add Record Set.
- Configure parameters by referring to Table 4. Keep the default settings for the parameters that are not listed in the following table.
For details, see
Adding a CNAME Record Set.
Table 4 Parameters for adding a CNAME record set
|
Parameter |
Example Value |
Description |
|
Type |
CNAME – Map one domain to another |
Choose a record set type depending on the purpose of the domain name.
Select CNAME – Map one domain to another here.
A message may be displayed, indicating that the record set you are trying to add conflicts with an existing record set of the zone.
For details, see Why Is a Message Indicating Conflict with an Existing Record Set Displayed When I Add a Record Set? |
|
Name |
Leave it blank. |
The prefix of the domain name to be resolved
For example, if the domain name is example.com, its prefix can be:
|
|
Line |
Default |
Resolution line. The DNS server will return the IP address of the specified line, depending on where the visitor comes from.
The default value is Default.
This parameter can only be configured for public zone record sets.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on visitors' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on visitors' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom line: returns a specific IP address based on the IP address range of visitors. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
|
|
TTL (s) |
300 |
The length of time (in seconds) for which a local DNS server caches a record set
The default value is 300, which is 5 minutes. (value range: 1 to 2147483647).
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
For more information about TTL, see What Is TTL? |
|
Value |
example-bucket.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com |
Domain name alias. You can enter only one domain name.
- If CDN acceleration is not used, set this parameter to the bucket domain name.
- If CDN acceleration is used, set this parameter to the domain name specified in the CNAME record allocated by CDN.
|
- Click OK.
- Verify that the added CNAME record set is in effect.
Open the Windows command line interface and run the following command:
nslookup -qt=cname example.name
In this command, example.name indicates the user-defined domain name or CDN acceleration domain name specified for the bucket. Replace it with your actual domain name.
- Without CDN acceleration: If the output is the bucket domain name, the CNAME record set is in effect.
- With CDN acceleration: If the output is the CNAME domain name allocated by CDN, the CNAME record set is in effect.

After the domain name is configured, CDN acceleration is not applied immediately. Refresh the domain name list to check the status. CDN acceleration is in effect only when the CNAME status is Enabled.
Enabling Acceleration for a User-Defined Domain Name
You can use OBS Console to enable acceleration for a user-defined domain name that has been configured for the bucket.
To enable acceleration on OBS Console, perform the following steps:
- Enable acceleration for the bound user-defined domain name.
- Add a CNAME record set to map the acceleration domain name to the default domain name of the bucket.
Step 1: Enable Acceleration
- In the domain name list, locate the card of the bound domain name and click Enable next to Acceleration disabled.
- Configure parameters by referring to Table 5.
Table 5 Acceleration domain name parameters
|
Parameter |
Value |
Description |
Example Value |
|
Origin Server |
- |
The origin server (the default domain name of the OBS bucket that stores the requested resources) that is accessed by the client using the acceleration domain name
This parameter is displayed by default and requires no configuration. |
- |
|
Service Area |
Chinese mainland |
If you select Chinese mainland, all requests are scheduled to CDN PoPs in the Chinese mainland. The acceleration domain name must be licensed by the MIIT. For details, see ICP Filing Process. |
Worldwide |
|
Outside of Chinese mainland |
If you select Outside of Chinese mainland, all requests are scheduled to CDN PoPs outside the Chinese mainland. You do not need to apply for a license for the acceleration domain name from the MIIT. |
|
Worldwide |
If you select Worldwide, worldwide requests are scheduled to the nearest, optimal CDN PoP. The acceleration domain name must be licensed by the MIIT. For details, see ICP Filing Process. |
|
Business Type |
Websites |
When static resources (such as images and files) on portals, e-commerce platforms, or user-generated content (UGC) apps are accessed by large or globally distributed user bases, CDN acceleration can make the responses faster. |
Websites |
|
Downloads |
CDN acceleration enables higher bandwidth and faster transmission, which reduces the time required for downloading files from websites, game clients, or app stores. |
|
Video on demand |
In scenarios, such as online education and video sharing, that offer video on demand (VOD) and audio on demand (AOD) services, CDN acceleration can minimize playback buffering. |
|
Acceleration |
- |
The user-defined domain name to be accelerated
This parameter is displayed by default and requires no configuration.
To prevent domain names from being maliciously added, you need to verify the ownership of the domain name the first time you connect a domain name to CDN. For details, see Verifying the Domain Name Ownership. |
static.example.com |
|
Static Website Hosting |
- |
You can upload static website files to your OBS bucket and grant anonymous users the read permission for these files, and then configure static website hosting for the bucket, so that OBS can host your static website. For details, see Static Website Hosting.
|
- |
- Click OK.
Step 2: Add a CNAME Record Set
Add a CNAME record set to map the user-defined domain name to the default domain name of the bucket.
- Click Resolve to automatically add a CNAME record set.
- If you specified a Huawei Cloud domain name, click Resolve for DNS to add a CNAME record set.
- If you specified a domain name that is not registered with Huawei Cloud, skip this step and go to 2.
- Manually add a CNAME record set.
- If you are not using a Huawei Cloud domain name, follow the CNAME resolution guide provided by your DNS provider.
- If you are using a Huawei Cloud domain name, do as follows:
- Log in to the DNS console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Public Zones.
- (Optional) Create a public zone. If you have already created one, skip this step.
- On the Public Zones page, click Create Public Zone in the upper right corner.
- Configure parameters by referring to the following table. Retain the default settings for other parameters.
Table 6 Parameters for creating a public zone
|
Parameter |
Example Value |
Description |
|
Domain Name |
example.com |
The domain name purchased from a domain name registrar
Enter the user-defined domain name bound to the bucket here. |
|
Enterprise Project |
default |
The enterprise project to be associated with the public zone. You can manage public zones by enterprise project.
This parameter is available and mandatory only when you are using an enterprise account.
Notes:
|
- Click OK.
- Locate the row that contains the domain name to which you want to add a record set and click the domain name.
- On the Record Sets tab, click Add Record Set.
- Configure parameters by referring to Table 7. Keep the default settings for the parameters that are not listed in the following table.
For details, see
Adding a CNAME Record Set.
Table 7 Parameters for adding a CNAME record set
|
Parameter |
Example Value |
Description |
|
Type |
CNAME – Map one domain to another |
Choose a record set type depending on the purpose of the domain name.
Select CNAME – Map one domain to another here.
A message may be displayed, indicating that the record set you are trying to add conflicts with an existing record set of the zone.
For details, see Why Is a Message Indicating Conflict with an Existing Record Set Displayed When I Add a Record Set? |
|
Name |
Leave it blank. |
The prefix of the domain name to be resolved
For example, if the domain name is example.com, its prefix can be:
|
|
Line |
Default |
Resolution line. The DNS server will return the IP address of the specified line, depending on where the visitor comes from.
The default value is Default.
This parameter can only be configured for public zone record sets.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on visitors' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on visitors' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom line: returns a specific IP address based on the IP address range of visitors. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
|
|
TTL (s) |
300 |
The length of time (in seconds) for which a local DNS server caches a record set
The default value is 300, which is 5 minutes. (value range: 1 to 2147483647).
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
For more information about TTL, see What Is TTL? |
|
Value |
example-bucket.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com |
Domain name alias. You can enter only one domain name.
- If CDN acceleration is not used, set this parameter to the bucket domain name.
- If CDN acceleration is used, set this parameter to the domain name specified in the CNAME record allocated by CDN.
|
- Click OK.
- Verify that the added CNAME record set is in effect.
Open the Windows command line interface and run the following command:
nslookup -qt=cname example.name
In this command, example.name indicates the user-defined domain name or CDN acceleration domain name specified for the bucket. Replace it with your actual domain name.
- Without CDN acceleration: If the output is the bucket domain name, the CNAME record set is in effect.
- With CDN acceleration: If the output is the CNAME domain name allocated by CDN, the CNAME record set is in effect.

After the domain name is configured, CDN acceleration is not applied immediately. Refresh the domain name list to check the status. CDN acceleration is in effect only when the CNAME status is Enabled.
Accessing an Acceleration Domain Name over HTTPS
CDN supports HTTPS acceleration. You can configure an HTTPS certificate for an acceleration domain name on the CDN console. After the certificate is configured, clients can access CDN PoPs over HTTPS. For details, see Configuring an HTTPS Certificate.













