After you upload a file to a bucket, OBS generates an access address for the file that includes the bucket's default domain name. Accessing this address using a browser will automatically download the file. To avoid exposing the default domain name of a bucket or to preview files online through a browser, you can bind a user-defined domain name to the bucket and use it to access the files in the bucket.
Scenarios
- File preview: To avoid automatic file downloads, you can bind a user-defined domain name to a bucket for online file preview.
- Keeping the access address unchanged: To keep website or file access addresses unchanged after a migration or storage location change, you can upload the files to a bucket and bind a user-defined domain name to the bucket. This will establish a mapping between the website domain name and the default bucket domain name. In this way, you can still access the files using the original address.
- Improved brand image: Having a fixed and personalized domain name for accessing an enterprise website can make the enterprise appear more professional and reliable. This enhances enterprise image and improves customer experience.
- Easy access: You can use a user-defined domain name that is easy to remember to access a bucket and files in the bucket.
- Accessing .apk or .ipa files: For security and compliance purposes, OBS blocks downloads of .apk or .ipa files via a bucket's default domain name. However, these files can still be accessed through a user-defined domain name bound to the bucket.

When you download an .apk or .ipa file using a bucket's default domain name, OBS returns error code 400 and InsecureDownloadForbidden.
Principles
The following describes the process of accessing objects in a bucket using a user-defined domain name and the process of accessing objects in a bucket using the default bucket domain name.
Figure 1 shows the process of using a user-defined domain name to access objects in a bucket.
Figure 1 Using a user-defined domain name to access objects in a bucket
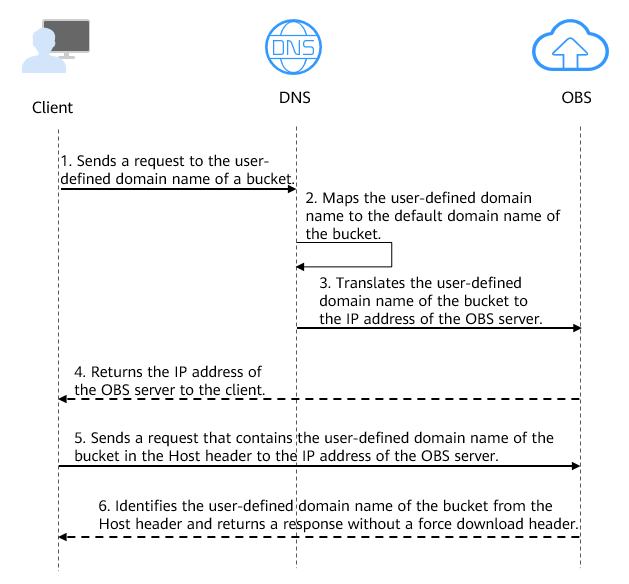
- A user enters a file access address (that includes a user-defined domain name) in a browser to initiate an access request.
- DNS maps the user-defined domain name to the default domain name of the bucket.
- DNS translates the default domain name of the bucket to the IP address of the OBS server.
- OBS returns the IP address of the server to the client.
- The client sends a request with the user-defined domain name specified in the Host header to the IP address of the OBS server.
- OBS identifies the user-defined domain name in the Host header and returns a response with Content-Disposition set to inline to the client, which indicates that the file is expected to be displayed in the browser.
Figure 2 shows the process of using a bucket's default domain name (bucketName.obs.endpoint.myhuaweicloud.com) to access objects in the bucket.
Figure 2 Using a bucket's default domain name to access objects in the bucket
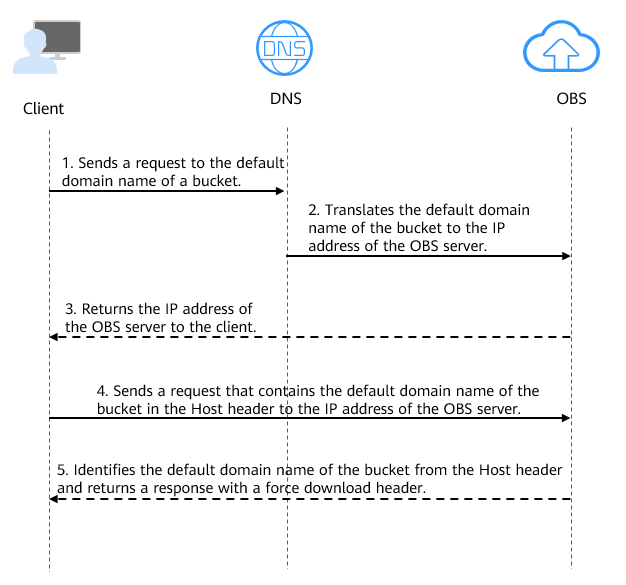
- A user enters a file access address (that includes the default domain name of the bucket) in the browser to initiate an access request.
- DNS translates the default domain name of the bucket to the IP address of the OBS server.
- OBS returns the IP address of the server to the client.
- The client sends a request with the default domain name specified in the Host header to the IP address of the OBS server.
- OBS identifies the default domain name in the Host header and returns a response with Content-Disposition set to attachment to the client, which indicates that the file is expected to be downloaded and saved locally.
Constraints
Table 1 Constraints
|
Item |
Description |
|
Bucket version |
Only buckets whose version is 3.0 or later support user-defined domain names. To check the version of a bucket, go to OBS Console, click the bucket name to go to the Overview page, and find the version in the Basic Information area. |
|
Number of domain names |
By default, a bucket can have up to 20 user-defined domain names bound. |
|
Functions |
- A user-defined domain name can be bound to only one bucket.
- Chinese domain names are not supported.
- The suffix of a user-defined domain name can contain 2 to 6 uppercase or lowercase letters.
- As required by the MIIT, if the bucket which a user-defined domain name is bound to is in a Chinese mainland region, you must complete the ICP filing.
- To access an OBS bucket over the Internet, typically use a user-defined domain name. For intranet access, it is recommended to use the bucket's default domain name (bucketName.obs.endpoint.myhuaweicloud.com).
|
Prerequisites
- There is a bucket with objects. For details, see Creating a Bucket.
- There is a second-level domain.
- As required by the MIIT, if the bucket which a user-defined domain name is bound to is in a Chinese mainland region, you must complete the ICP filing.
Configuring a User-Defined Domain Name
You can use OBS Console, APIs, or SDKs to configure user-defined domain names.
Specifically, perform the following steps:
- Bind a user-defined domain name to the bucket.
- Add a CNAME record set to map the user-defined domain name to the default domain name of the bucket.
- (Optional) Configure HTTPS to secure access through the user-defined domain name.
Using OBS Console
Step 1: Bind a User-Defined Domain Name
- In the navigation pane of OBS Console, choose Object Storage.
- In the bucket list, click the bucket you want to operate. The Objects page is displayed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Basic Configurations > Domain Name Mgmt.
Figure 3 Domain name management page

- Click Configure User Domain Name in the upper part of the page.
If no user-defined domain names are bound, you also can click Configure User Domain Name in the lower part of the page.
Figure 4 Configuring a user domain name
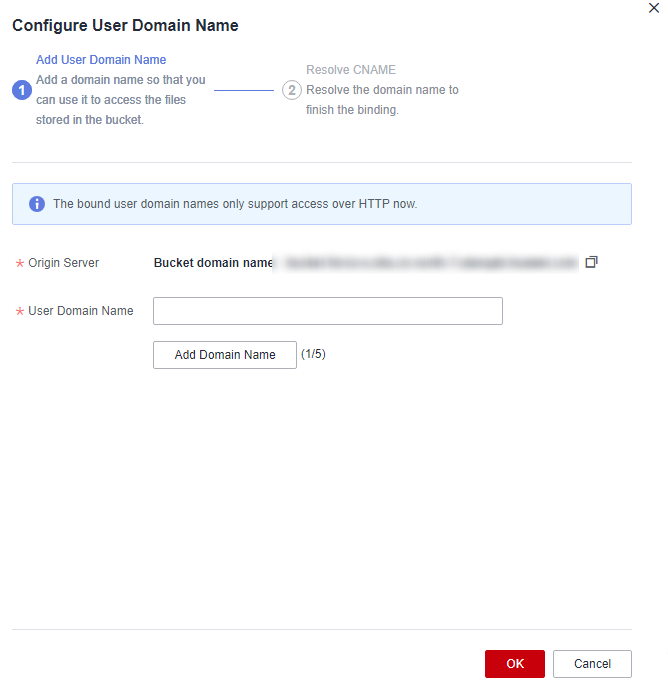
- Specify a user-defined domain name for User Domain Name.
The domain name:
- Must start with an asterisk (*), a letter, or a digit.
- Can contain letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.).
- Can have a suffix of 2 to 6 uppercase or lowercase letters, for example, .com and .cn.
By default, a bucket can have up to 20 user-defined domain names bound.

If you want to choose one of the existing Huawei Cloud domain names from the drop-down list on OBS Console, you must have the Domains:domains:getDetails permission. You can contact the administrator to use IAM to grant you this permission. For details, see Assigning Permissions to an IAM User.
- Click OK.
Step 2: Add a CNAME Record Set
Add a CNAME record set to map the user-defined domain name to the default domain name of the bucket.
- Click Resolve to automatically add a CNAME record set.
- If you specified a Huawei Cloud domain name, click Resolve for DNS to add a CNAME record set.
- If you specified a domain name that is not registered with Huawei Cloud, skip this step and go to 2.
- Manually add a CNAME record set.
- If you are not using a Huawei Cloud domain name, follow the CNAME resolution guide provided by your DNS provider.
- If you are using a Huawei Cloud domain name, do as follows:
- Log in to the DNS console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Public Zones.
- (Optional) Create a public zone. If you have already created one, skip this step.
- On the Public Zones page, click Create Public Zone in the upper right corner.
- Configure parameters by referring to the following table. Retain the default settings for other parameters.
Table 2 Parameters for creating a public zone
|
Parameter |
Example Value |
Description |
|
Domain Name |
example.com |
The domain name purchased from a domain name registrar
Enter the user-defined domain name bound to the bucket here. |
|
Enterprise Project |
default |
The enterprise project to be associated with the public zone. You can manage public zones by enterprise project.
This parameter is available and mandatory only when you are using an enterprise account.
Notes:
|
- Click OK.
- Locate the row that contains the domain name to which you want to add a record set and click the domain name.
- On the Record Sets tab, click Add Record Set.
- Configure parameters by referring to Table 3. Keep the default settings for the parameters that are not listed in the following table.
For details, see
Adding a CNAME Record Set.
Table 3 Parameters for adding a CNAME record set
|
Parameter |
Example Value |
Description |
|
Type |
CNAME – Map one domain to another |
Choose a record set type depending on the purpose of the domain name.
Select CNAME – Map one domain to another here.
A message may be displayed, indicating that the record set you are trying to add conflicts with an existing record set of the zone.
For details, see Why Is a Message Indicating Conflict with an Existing Record Set Displayed When I Add a Record Set? |
|
Name |
Leave it blank. |
The prefix of the domain name to be resolved
For example, if the domain name is example.com, its prefix can be:
|
|
Line |
Default |
Resolution line. The DNS server will return the IP address of the specified line, depending on where the visitor comes from.
The default value is Default.
This parameter can only be configured for public zone record sets.
- Default: returns the default resolution result irrespective of where the visitors come from.
- ISP: returns the resolution result based on visitors' carrier networks. For details, see Configuring ISP Lines.
- Region: returns the resolution result based on visitors' geographical locations. For details, see Configuring Region Lines.
- Custom line: returns a specific IP address based on the IP address range of visitors. For details, see Configuring Custom Lines.
|
|
TTL (s) |
300 |
The length of time (in seconds) for which a local DNS server caches a record set
The default value is 300, which is 5 minutes. (value range: 1 to 2147483647).
If your service address changes frequently, set TTL to a smaller value. Otherwise, set TTL to a larger value.
For more information about TTL, see What Is TTL? |
|
Value |
example-bucket.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com |
Domain name alias. You can enter only one domain name.
- If CDN acceleration is not used, set this parameter to the bucket domain name.
- If CDN acceleration is used, set this parameter to the domain name specified in the CNAME record allocated by CDN.
|
- Click OK.
- Verify that the added CNAME record set is in effect.
Open the Windows command line interface and run the following command:
nslookup -qt=cname example.name
In this command, example.name indicates the user-defined domain name or CDN acceleration domain name specified for the bucket. Replace it with your actual domain name.
- Without CDN acceleration: If the output is the bucket domain name, the CNAME record set is in effect.
- With CDN acceleration: If the output is the CNAME domain name allocated by CDN, the CNAME record set is in effect.
Step 3: (Optional) Configure HTTPS
- On OBS Console, open the Configure User Domain Name dialog box and click Next under the Resolve CNAME step.
- (Optional) On the (Recommended) Configure HTTPS page, if you do not need to configure HTTPS, click OK in the lower right corner.
- (Optional) If you need to configure HTTPS, set the parameters according to Table 4.
Table 4 Configuring HTTPS for a user-defined domain name
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Custom domain name |
Select the custom domain name for which you want to configure an HTTPS certificate. |
|
Certificate |
Select an SCM certificate, a server digital certificate provided by Cloud Certificate & Manager (CCM).
Each certificate has an expiration time. Ensure that the certificate you chose has not expired.
Replace the certificate before it expires, or services may be affected. |
- Click Configure in the lower right corner.
Using SDKs
|
Java: not supported |
Python |
C |
Go |
BrowserJS: not supported |
.NET: not supported |
Android: not supported |
iOS: not supported |
PHP: not supported |
Node.js: not supported |
Using a User-Defined Domain Name to Access Objects
After a user-defined domain name is bound to a bucket and the domain name resolution is successful, verify that you can use the domain name to access objects. You can use SDKs to access objects via the user-defined domain name, but you cannot use OBS console, APIs, OBS Browser+, or obsutil.
Using SDKs
- Obtain a pre-signed URL.
The following are example codes in common programming languages:
- Java
import com.obs.services.ObsClient;
import com.obs.services.ObsConfiguration;
import com.obs.services.model.HttpMethodEnum;
import com.obs.services.model.TemporarySignatureRequest;
import com.obs.services.model.TemporarySignatureResponse;
public class GetObject001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Obtain an AK/SK pair using environment variables or import it in other ways. Using hard coding may result in leakage.
// Obtain an AK/SK pair on the management console.
String ak = System.getenv("ACCESS_KEY_ID");
String sk = System.getenv("SECRET_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
// (Optional) If you are using a temporary AK/SK pair and a security token to access OBS, you are advised not to use hard coding, which may result in information leakage.
// Obtain an AK/SK pair and a security token using environment variables or import them in other ways. If you use a temporary AK/SK pair and a security token to make an API call, uncomment the following line.
// String securityToken = System.getenv("SECURITY_TOKEN");
// Set the endpoint to the bucket's user-defined domain name. If the user-defined domain name has a certificate configured, you can use https.
String endPoint = "http://example.domain";
// Obtain an endpoint using environment variables or import it in other ways.
//String endPoint = System.getenv("ENDPOINT");
ObsConfiguration obsConfiguration = new ObsConfiguration();
obsConfiguration.setCname(true);
obsConfiguration.setEndPoint(endPoint);
try {
// Create an ObsClient instance.
// Use the permanent AK/SK pair to initialize the client.
ObsClient obsClient = new ObsClient(ak, sk, obsConfiguration);
// Use a temporary AK/SK pair and security token to initialize the client.
// ObsClient obsClient = new ObsClient(ak, sk, securityToken, obsConfiguration);
// Set the validity period of the URL to 3600 seconds.
long expireSeconds = 3600L;
TemporarySignatureRequest request = new TemporarySignatureRequest(HttpMethodEnum.GET, expireSeconds);
request.setBucketName("examplebucket");
request.setObjectKey("objectname");
TemporarySignatureResponse response = obsClient.createTemporarySignature(request);
System.out.println("Getting object using temporary signature url:");
System.out.println("SignedUrl:" + response.getSignedUrl());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("create temporary signature failed");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- Python
from obs import ObsClient
import os
import traceback
# Obtain an AK and SK pair using environment variables (recommended) or import it in other ways. Using hard coding may result in leakage.
# Obtain an AK/SK pair on OBS Console by referring to https://support.huaweicloud.com/en-us/usermanual-ca/ca_01_0003.html.
ak = os.getenv("AccessKeyID")
sk = os.getenv("SecretAccessKey")
# (Optional) If you use a temporary AK/SK pair and a security token to access OBS, obtain them using environment variables.
# security_token = os.getenv("SecurityToken")
# Set the server to the bucket's user-defined domain name. If the user-defined domain name has a certificate configured, you can use https.
server = "http://example.domain"
# Create an ObsClient instance.
obsClient = ObsClient(access_key_id=ak, secret_access_key=sk, server=server, is_cname=True)
# If you use a temporary AK/SK pair and a security token to access OBS, you must specify security_token when creating an instance.
#obsClient = ObsClient(access_key_id=ak, secret_access_key=sk, security_token=security_token, server=server, is_cname=True)
try:
# Create a signed URL for downloading an object.
res = obsClient.createSignedUrl(method='GET', bucketName='bucketname', objectKey='objectkey', expires=3600)
print('signedUrl:', res.signedUrl)
except:
print(traceback.format_exc())
- Access the pre-signed URL in a browser.
References
Using CDN Acceleration to Accelerate Access
To improve the speed and stability for accessing static resource files, you can use CDN acceleration. If you have configured a user-defined domain name for a bucket, you can directly enable CDN acceleration for the domain name. If you have not configured a user-defined domain name for the bucket, you can configure a CDN acceleration domain name. For details, see Accessing a Bucket Using a CDN Acceleration Domain Name.
You can also manage HTTPS certificates on the CDN console to allow access over HTTPS. For details, see Configuring an HTTPS Certificate.
Using a Permanent, Unsigned URL to Access an Object

- To obtain a permanent, unsigned URL (http://DomainName/ObjectName) for accessing a file, you must set the file to be publicly readable. Once the file is publicly accessible, anyone can access it, which may lead to data leakage and soaring costs from frequent requests. Therefore, it is recommended to use signed URLs with an expiration time to access files.
- If you allow your file to be accessed by a permanent, unsigned URL, you should configure URL validation to prevent the file from being stolen.
You can set an object to be publicly readable in either of the following ways:
Preventing Data Theft
Some rogue websites may steal links from other websites to enrich their content without any costs. Link stealing hurts the interests of the original websites and it is also a strain on their servers. URL validation is designed to address this issue.
To prevent data stored in buckets from being theft, you can specify Referer (a whitelisted, blacklisted, or empty Referer) in the HTTP header to allow access only from specific sources. For details, see Configuring URL Validation to Prevent Unauthorized Access to Your Data.
Configuring Static Website Hosting
If you want to host your static website on OBS and use a user-defined domain name to access the website, you need to configure static website hosting for the storage space. For details, see Static Website Hosting.












