Creating a Dimension
If the data you need to analyze cannot be directly obtained from the data table and requires processing based on raw data, you can create a dimension. By creating a dimension, you can transform raw data into more meaningful information. For example, you can create a dimension called profit based on the original data of sales prices and costs. This section describes how to create a dimension.
Prerequisites
- A project has been created by referring to Creating a Project.
- A data source has been connected by referring to Connecting to a Data Source.
- A dataset has been created by referring to Creating a Dataset.
Procedure
- Log in to the DataArts Insight console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console to select a region. Then, select an enterprise project in the upper right corner.
in the upper left corner of the management console to select a region. Then, select an enterprise project in the upper right corner. - On the top menu of the console, click Project. On the displayed My Projects page, click the name of the desired project.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Data Management > Datasets.
- On the displayed page, click the name of the dataset you created.
- On the displayed page, click Create Dimension.
Figure 1 Creating a dimension
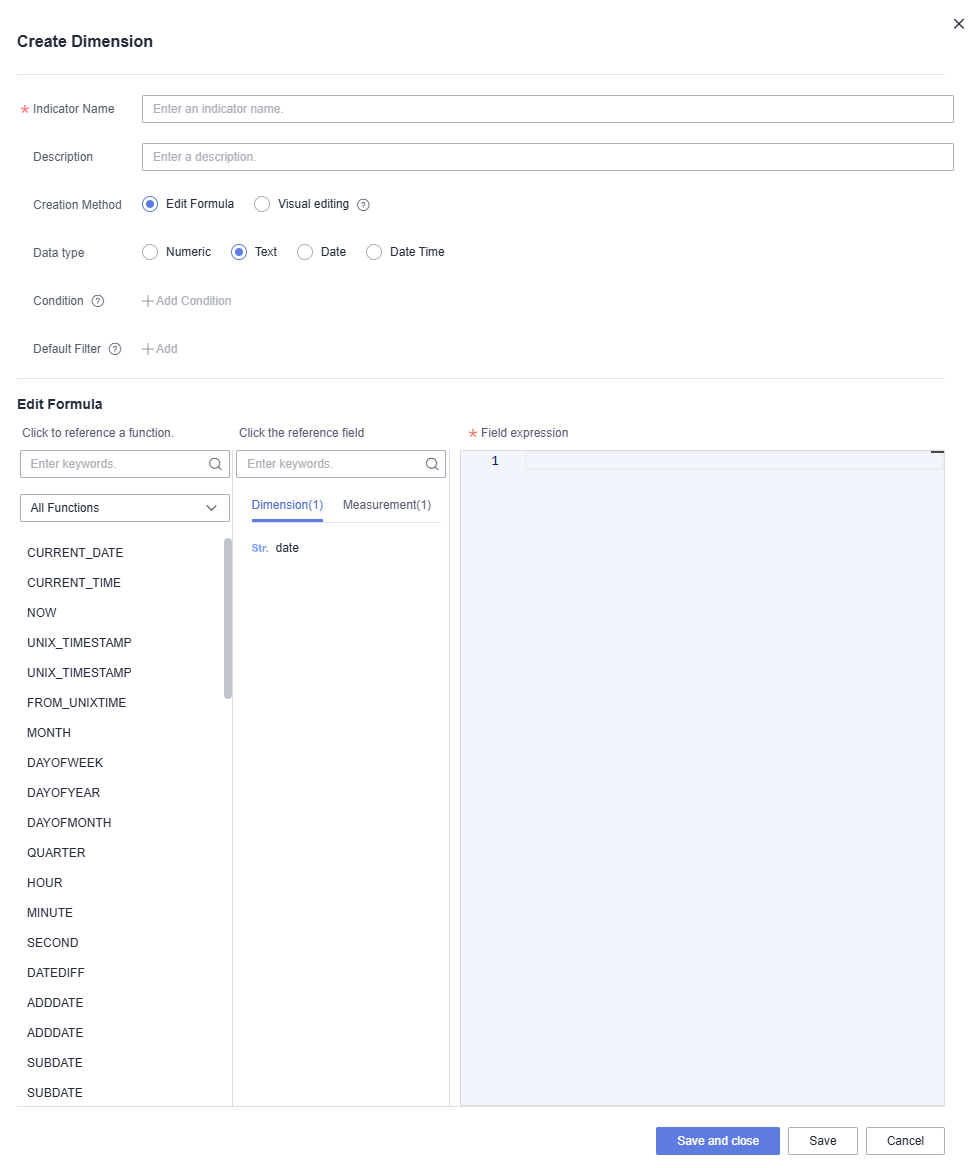
- After setting the parameters, click Confirm.
- Creation Method: Select Edit Formula. The options for Data type are Numeric, Text, Date, and Date Time. For details about the parameters, see Table 1.
- When using expressions, make sure to use parentheses in the English input method.
- Use functions supported by each data source.
Table 1 Parameter descriptions Parameter
Description
Data type
Options: Numeric, Text, Date, and Date Time.
Condition
This parameter is available only when Data type is set to Numeric or Text.
- If you create or change a data type, you need to save the settings before setting this parameter.
- This parameter is a field-level configuration item. It only takes effect for the field.
Default Filter
Default filters can be added only for numeric and text dimensions.
- If you create or change a data type, you need to save the settings before setting this parameter.
- After a default filter is added, the dataset applies the filter. If no other filter criteria are added in the intelligent Q&A and dashboard scenarios, the data filtered by the default filter is automatically returned.
Click to reference a function.
Functions used to process data. You can select date, text, and numeric functions.
Click the reference field
Dimensions and metrics of a dataset.
Field expression
Field expression that helps you understand the data processing process.
Table 2 Date functions Function
Usage
Description
CURRENT_DATE
CURRENT_DATE()
Returns the current date.
CURRENT_TIME
CURRENT_TIME()
Returns the current time.
NOW
NOW()
Return system's current date and time.
UNIX_TIMESTAMP
UNIX_TIMESTAMP()
Returns the current time as a UNIX timestamp.
UNIX_TIMESTAMP
UNIX_TIMESTAMP(d)
Returns the time d as a UNIX timestamp.
FROM_UNIXTIME
FROM_UNIXTIME(d)
Converts the time in the UNIX timestamp format to the time in the common format.
MONTH
MONTH(d)
Returns the month value in the date d, ranging from 1 to 12.
DAYOFWEEK
DAYOFWEEK(d)
Calculates the day of the week corresponding to date d.
DAYOFYEAR
DAYOFYEAR(d)
Calculates the day of the year corresponding to date d.
DAYOFMONTH
DAYOFMONTH(d)
Calculates the day of the month corresponding to date d.
QUARTER
QUARTER(d)
Returns the season of date d as a value between 1 and 4.
HOUR
HOUR(t)
Returns the hour value in t.
MINUTE
MINUTE(t)
Returns the minute value in t.
SECOND
SECOND(t)
Returns the second value in t.
DATEDIFF
DATEDIFF(d1,d2)
Calculates the number of days between d1 and d2.
ADDDATE
ADDDATE(d,n)
Calculates the date that is n days after the start date d.
ADDDATE
ADDDATE(d, INTERVAL expr type)
Calculates the date that is the result of adding a time segment to the start date d.
SUBDATE
SUBDATE(d,n)
The date n days before date d.
SUBDATE
SUBDATE(d,INTERVAL expr type)
The date resulting from subtracting a time segment from date d.
DATE_FORMAT
DATE_FORMAT(d,f)
Displays the date d as required by expression f.
TIME_FORMAT
TIME_FORMAT(t,f)
Displays the time t as required by expression f.
Table 3 Text functions Function
Usage
Description
CHAR_LENGTH
CHAR_LENGTH(s)
Returns the number of characters in string s.
LENGTH
LENGTH(s)
Returns the length of string s.
CONCAT
CONCAT(s1,s2,...)
Combines multiple strings such as s1 and s2 into one string.
CONCAT_WS
CONCAT_WS(x,s1,s2,...)
Uses the first parameter as the separator, which is associated with all following parameters.
UPPER
UPPER(s)
Converts letters in string s into uppercase letters.
LOWER
LOWER(s)
Converts letters in string s into lowercase letters.
LEFT
LEFT(s,n)
Returns the first n characters of string s.
RIGHT
RIGHT(s,n)
Returns the last n characters of string s.
LPAD
LPAD(s1,len,s2)
Uses string s2 to fill the beginning of s1 so that the string length reaches len.
RPAD
RPAD(s1,len,s2)
Uses string s2 to fill the end of s1 so that the string length reaches len.
LTRIM
LTRIM(s)
Deletes the space at the beginning of the string s.
RTRIM
RTRIM(s)
Deletes the space at the end of the string s.
TRIM
TRIM(s1 FROM s)
Removes the string s and the string s1 at the end.
REPEAT
REPEAT(s,n)
Repeats the string s for n times.
REPLACE
REPLACE(s,s1,s2)
Replaces the string s1 in the string s with the string s2.
SUBSTRING
SUBSTRING(s,n,len)
Obtains a string whose length is len from the nth position in the string s.
LOCATE
LOCATE(s1,s)
Obtains the start position of s1 from the string s.
INSTR
INSTR(s,s1)
Obtains the start position of s1 from the string s.
REVERSE
REVERSE(s)
Reverses the sequence of the string s.
MD5
MD5(str)
You can hash the string str to encrypt data that does not require decryption.
Table 4 Numeric functions Function
Usage
Description
ABS
ABS(x)
Returns the absolute value of x.
CEIL
CEIL(x)
Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to x.
FLOOR
FLOOR(x)
Returns the largest integer less than or equal to x.
RANDOM
RANDOM()
Returns a random number ranging from 0.0 to 1.0.
SIGN
SIGN(x)
Returns the sign of x, which is either -1, 0, or 1 depending on whether x is negative, zero, or positive.
PI
PI()
Returns pi.
TRUNC
TRUNC(x, y)
Returns the value of x rounded to y decimal places.
ROUND
ROUND(x)
Returns the integer closest to x.
ROUND
ROUND(x, y)
Returns the value of x rounded to y decimal places, with any truncated part being rounded off.
POWER
POWER(x,y)
Returns the value of x raised to the power of y.
SQRT
SQRT(x)
Returns the square root of x.
EXP
EXP(x)
Returns the value of e raised to the power of x.
MOD
MOD(x,y)
Returns the remainder when x is divided by y.
LOG
LOG(x)
In the ORA- or TD-compatible mode, this operator means the logarithm with 10 as the base. In the MySQL-compatible mode, this operator means the natural logarithm.
RADIANS
RADIANS(x)
Converts the angle to a radian.
DEGREES
DEGREES(x)
Converts the radian to an angle.
SIN
SIN(x)
Calculates the sine value given in radians.
ASIN
ASIN(x)
Calculates the arc sine value given in radians.
COS
COS(x)
Calculates the cosine value given in radians.
ACOS
ACOS(x)
Calculates the arc cosine value given in radians.
TAN
TAN(x)
Calculates the tangent value given in radians.
ATAN
ATAN(x)
Calculates the arc tangent value given in radians.
COT
COT(x)
Calculates the cotangent value given in radians.
- Visual editing: You can only derive grouping dimensions based on a single dimension. If you need to derive more complex new dimensions based on multiple dimensions, use the formula editor.
- Select a grouping field.
- Set the group and select the group field value.
- Click Refresh Preview and then Confirm.
- Creation Method: Select Edit Formula. The options for Data type are Numeric, Text, Date, and Date Time. For details about the parameters, see Table 1.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





