Application Scenarios
IoTDA allows you to connect your physical devices to the cloud, where you can collect device data and deliver commands to devices.
IoV
Requirements: For better management, automotive vendors connect vehicles to the cloud platform. The platform needs to support data transmission using protocols such as JT/T808 and MQTT and can clean data for big data analysis and data mining.
Solutions: IoTDA provides secure and reliable connections at a low latency and supports multiple standard protocols. It uploads road, vehicle, and driving behavior data collected by vehicles to the cloud and processes the data with rules and FunctionGraph. In addition, IoTDA stores data in InfluxDB and DWS for big data analysis and uses ModelArts to perform machine learning to mine valuable data.
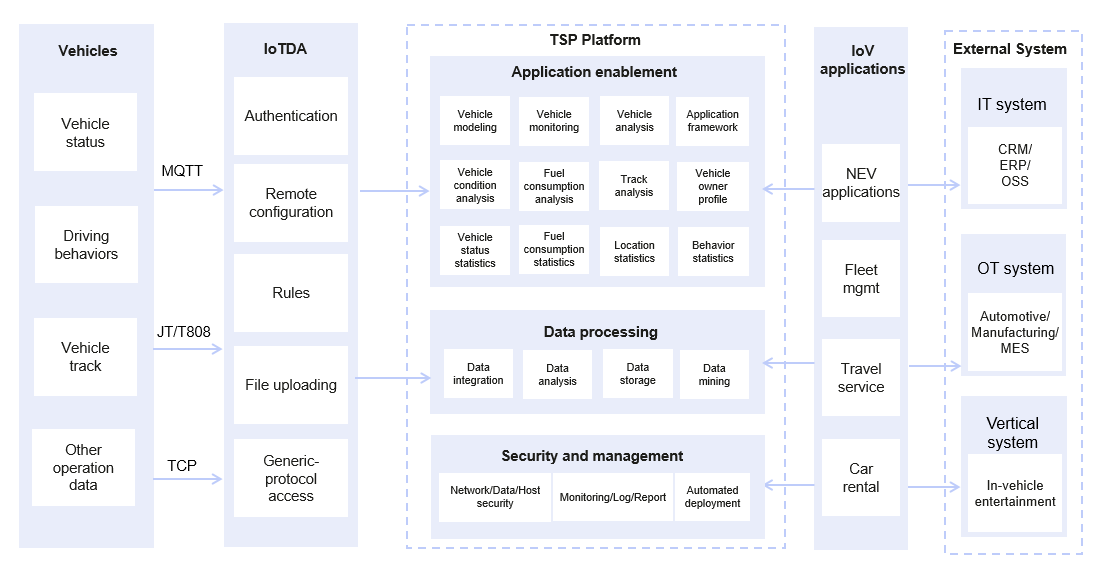
Reference architecture of the IoV scenario:
- The T-Box on the device side reports data such as vehicle status, driving behavior, and vehicle track to the cloud through MQTT or JT/T808.
- IoTDA transfers data to different cloud services for data cleaning, storage, and analysis, building multiple IoV data applications.
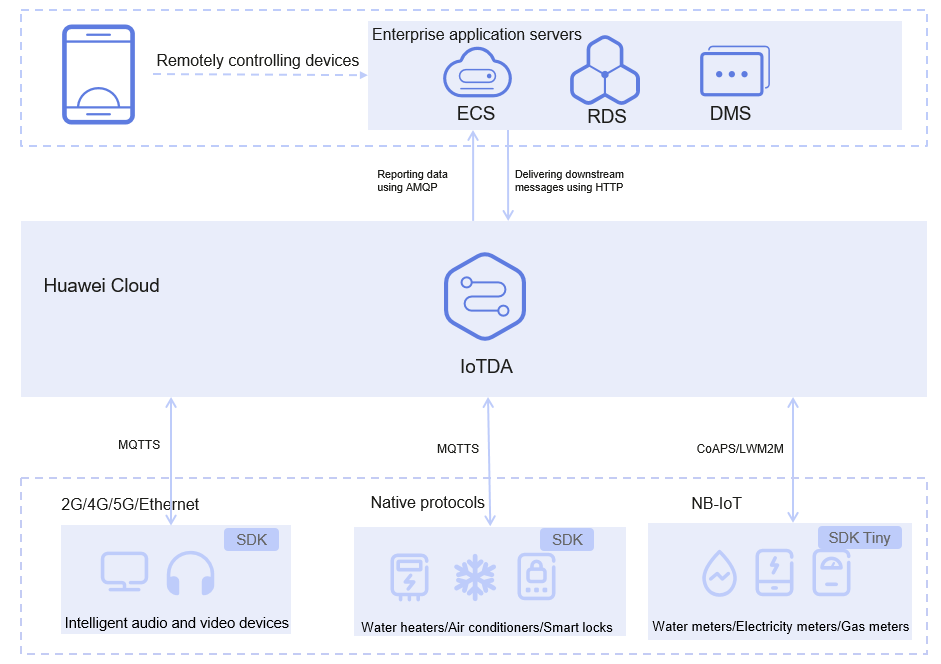
Smart Home
Requirements: Home appliances, such as refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, sockets, TVs, and lighting devices, need to be connected to the cloud for data reporting and running status detection. Users can also send commands through applications provided by device vendors to remotely control devices.
Solutions: IoTDA provides a secure and reliable system to support large-scale device connections. It supports many protocols like MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, LwM2M, and WebSocket. You can send messages and commands from the cloud to control devices quickly.
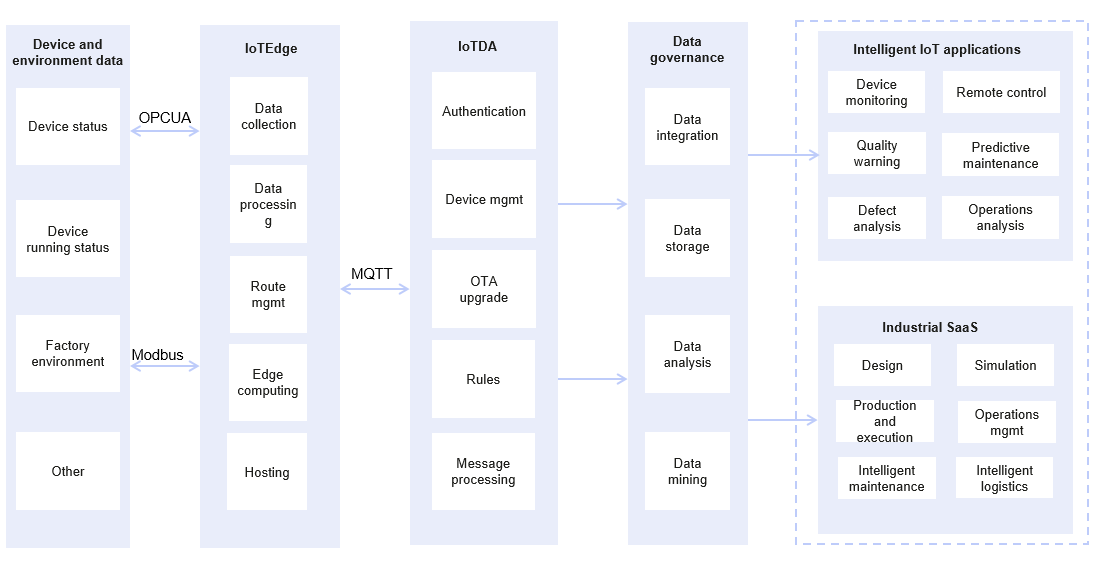
Smart Manufacturing
Requirements: To manage mechanical devices of various brands and types on the assembly lines, factories need to collect device running and environment monitoring data with a cloud platform. The platform should calculate and analyze device running status in real time, provide device exception or fault prediction and alarm, and allow users to perform remote maintenance and upgrade.
Solutions: Factories can use IoT Edge to collect OT data such as device and environment data, report them to IoTDA through industrial gateways, and transfer them to other cloud services for data conversion and analysis. With this data, factories can monitor devices, receive alarms for abnormal devices, and upgrade and maintain devices remotely.
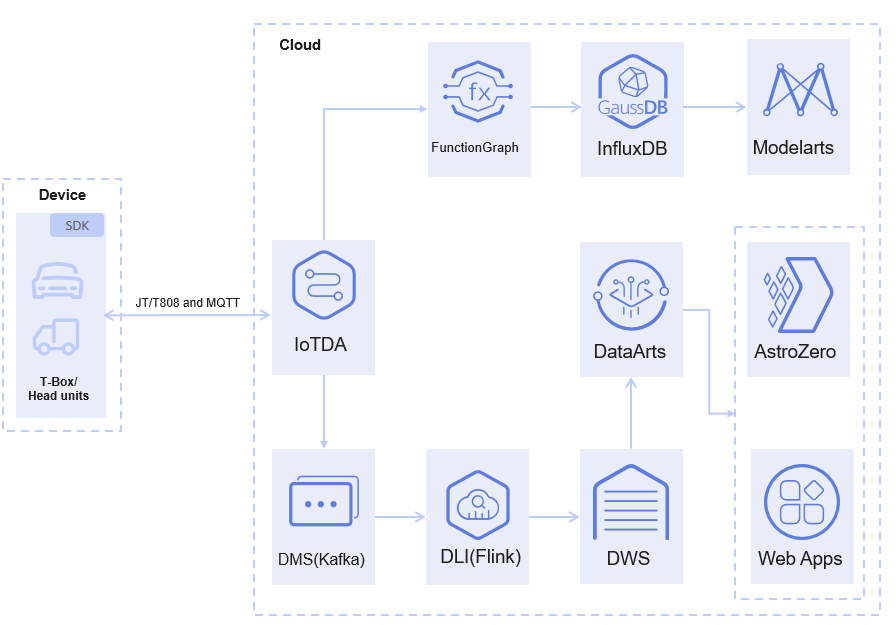
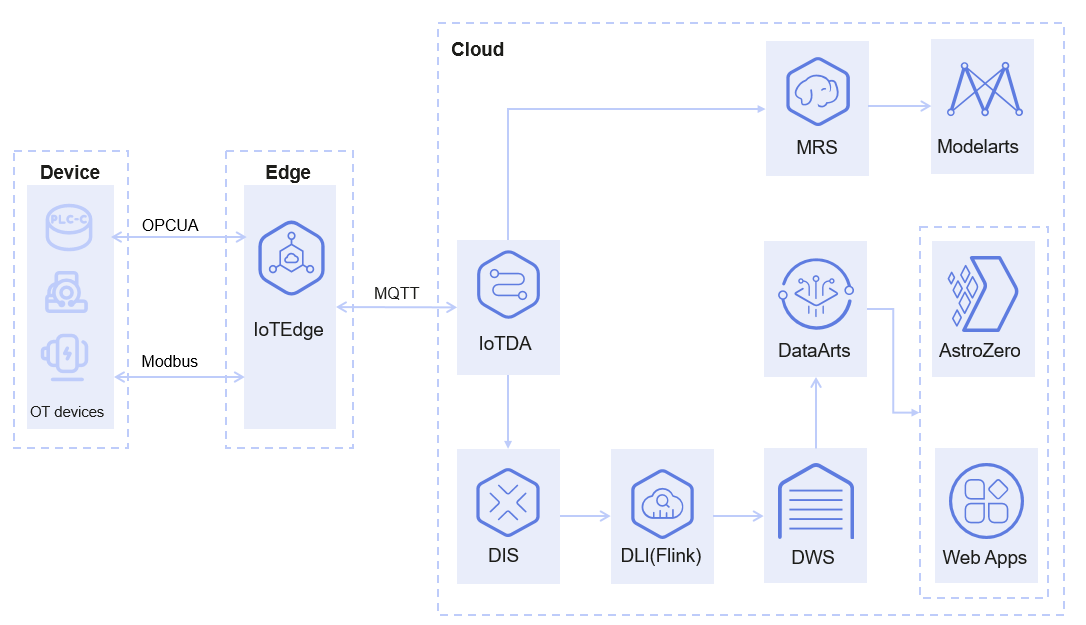
Reference architecture of the smart manufacturing scenario:
- Edge nodes deployed on devices support protocols such as OPC UA and Modbus, collect running data, status data, and environment monitoring data of various OT devices, and report data from edge gateways to IoTDA.
- IoTDA uses rules to transfer data to DIS. After being processed by DLI-Flink, the data is written to DWS for subsequent data governance. Data can also be transferred to MapReduce Service (MRS) for big data cleaning and processing, facilitating subsequent AI analysis and data mining.
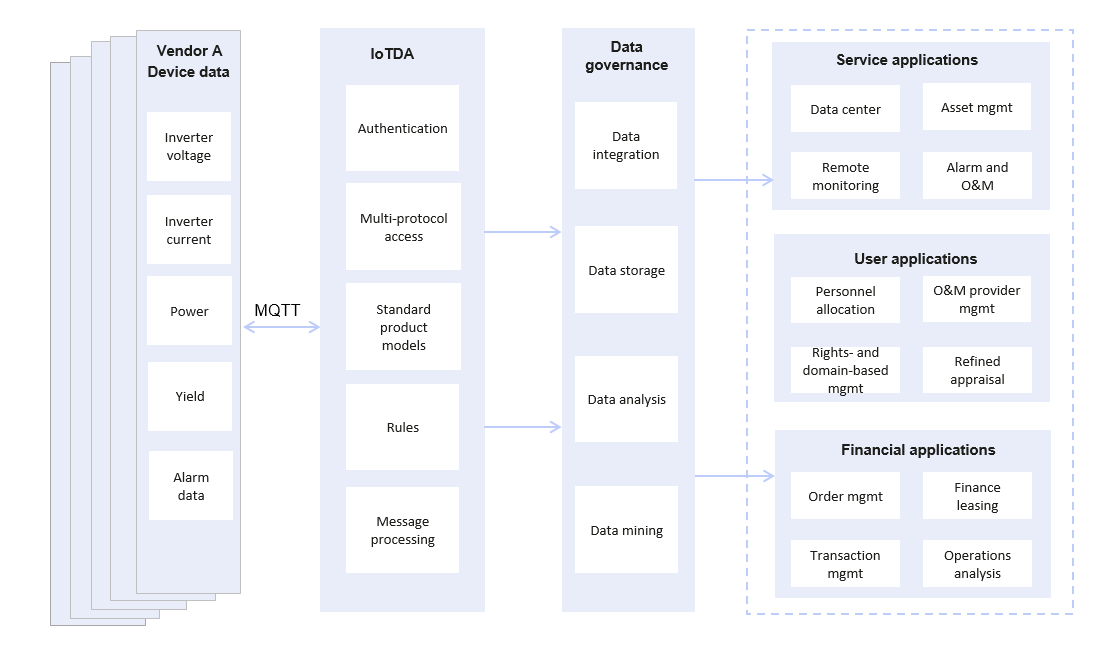
Distributed Photovoltaics (PV)
Requirements: New energy companies need to collect the voltage, current, power, yield, and alarm data of inverters produced by various vendors to the cloud for further data processing and analysis, facilitating data center development, alarm O&M, and operation analysis.
Solutions: IoTDA provides standard object models and supports multi-protocol access. Shielding the format and protocol differences of data reported by devices from multiple PV device vendors, IoTDA uses rules to transfer data to OBS for storage and MRS for further data processing.
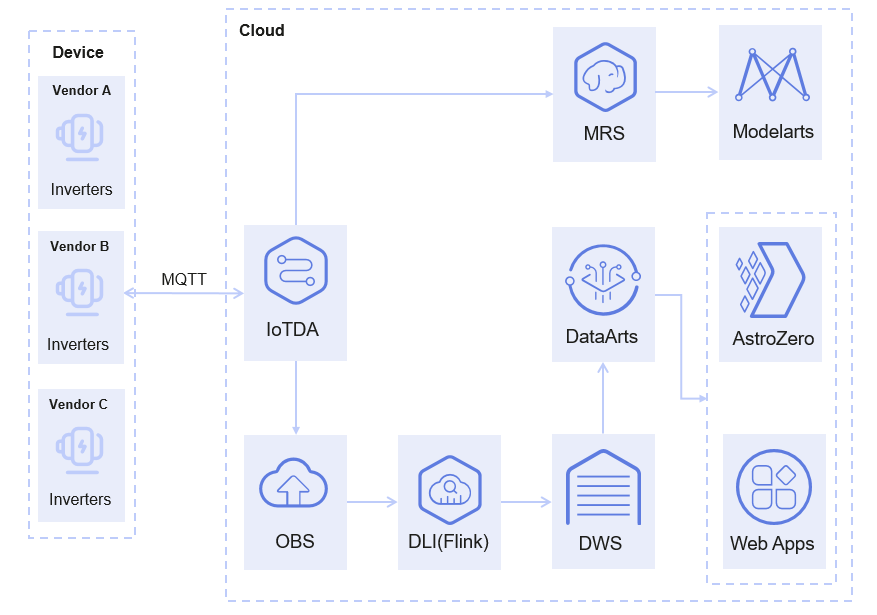
Reference architecture of the distributed PV scenario:
- Inverters from different vendors report data such as voltage, current, power, and yield to the cloud through MQTT.
- IoTDA uses rules to transfer data to OBS for storage. After being processed by DLI-Flink, the data is written to DWS for subsequent data governance. Data can also be transferred to MRS for big data cleaning and processing, facilitating subsequent AI analysis and data mining.
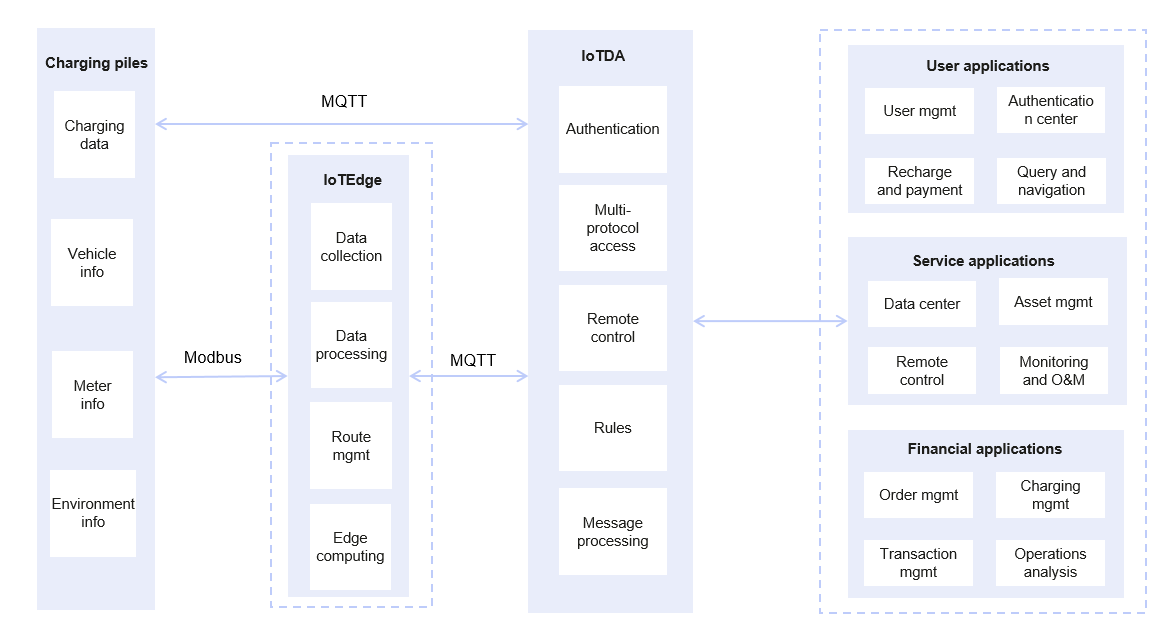
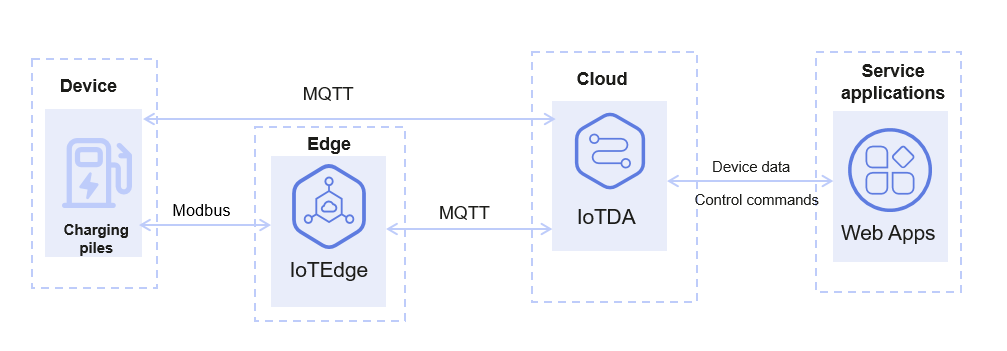
Smart Charging Pile
Requirements: Charging pile operators need to collect charging data, meter information, and charging vehicle information of charging piles produced by different vendors to the cloud, so cloud applications can detect the status of user vehicles and charging piles in real time for fee calculation. Applications need to deliver commands to start and stop the charging.
- Solution 1: Charging pile devices from multiple vendors are directly connected to the IoTDA through MQTT. Generic-protocol plug-ins are deployed on the cloud for parsing and multi-protocol access. IoTDA can directly push data to customers' applications and allow applications to deliver commands to control the start and stop of the charging. This solution applies to urban areas or outdoor areas with good network environments.
- Solution 2: IoT Edge is used to collect charging pile data from multiple vendors. Protocol plug-ins can be deployed on edge nodes to shield proprietary protocols of multiple vendors. Some simple computing applications can also be deployed on edge nodes to reduce interaction with the cloud. The edge gateway reports data to the IoTDA through MQTT. IoTDA can directly push data to customers' applications and allow applications to deliver commands to control the start and stop of the charging. This solution applies to areas with poor network environments, such as highway service areas and underground parking lots.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





