Pay-per-Use Billing
Pay-per-use billing is a postpaid mode, ideal for users who do not want to pay upfront or make long-term commitments. This section walks you through pay-per-use billing policies and examples.
Scenarios
Pay-per-use billing is ideal for uninterruptible applications or services with temporary, bursty, or unpredictable traffic.
Billing Items
Pay-per-use billing items for KVS are as follows:
|
Billing Item |
Unit Price |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Storage |
Standard storage |
$0.00045861 USD/GB-hour |
You pay for the storage space used by all KV items and indexes you store in KVS. The billing is on an hourly basis. |
|
Requests |
Standard write request units (WRUs) |
$1.667 USD/million WRUs |
put-kv (adding a single KV item), update-kv (updating a single KV item), delete-kv (deleting a single KV item), batch-write-kv (batch writing KV items), and others |
|
Standard read request units (RRUs) |
$0.3302 USD/million RRUs |
get-kv (querying a single KV item), scan-kv (scanning all the KV items in a table), scan-skey-kv (scanning part of the items by shard key), and others |
|
Billing Cycle
Resource use in KVS is billed on an hourly basis. There are no charges for creating stores or creating, listing, or querying tables. You are billed based on the standard storage and write and read request units in each billing cycle. There are no minimum charges.
A duration of less than an hour is billed as a full hour. For example, assume you store data in KVS at a certain time between 10:00:00 and 11:00:00 on a day, you are billed for the whole hour of this billing cycle for storage.
Billing Formulas
Storage price = Used capacity (GB-hour) × List unit price
Request price = Request units × List unit price
KVS charges one WRU for 1 KB of KV items and one RRU for 4 KB of KV items. Table 2 shows how to convert the size of KV items into WRUs or RRUs.
|
Billing Item |
Conversion Formula |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard WRUs |
1 WRU = 1 KB of KV items |
If you call a put-kv API to write 5 KB of KV items at a time, you are charged for: 5 KB/1 KB = 5 WRUs |
|
Standard RRUs |
1 RRU = 4 KB of KV items |
If you call a get-kv API to read 8 KB of KV items at a time, you are charged for: 8 KB/4 KB = 2 RRUs |

In an API call, a standard write of less than 1 KB is billed as 1 KB, and a standard read of less than 4 KB is billed as 4 KB.
Billing Examples
The estimated prices in the following example are only for reference.
Assume that from 8:00:00 to 9:00:00 on a certain day, your table occupied 10 GB of storage and processed 1 million RRUs. From 9:00:00 to 10:00:00 on the same day, it occupied 10.1 GB and processed 2 million WRUs. The billing details for the cycle from 8:00:00 to 10:00:00 are as follows:
|
Billing Cycle |
Operation |
Billing Item |
Unit Price |
Usage |
Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
8:00:00–9:00:00 |
Storage |
Standard storage |
$0.00045861 USD/GB-hour |
10 GB |
10 GB × $0.00045861 USD/GB = $0.0045861 USD |
|
Read |
Standard RRUs |
$0.3302 USD/million RRUs |
1 million RRUs |
1 million RRUs × $0.3302 USD/million RRUs = $0.3302 USD |
|
|
9:00:00–10:00:00 |
Storage |
Standard storage |
$0.00045861 USD/GB-hour |
10.1 GB |
10.1 GB × $0.00045861 USD/GB = $0.004631961 USD |
|
Write |
Standard WRUs |
$1.667 USD/million WRUs |
2 million WRUs |
2 million WRUs × $1.667 USD/million WRUs = $3.334 USD |
|
|
Total |
/ |
/ |
/ |
/ |
$3.673418061 USD |
The table usage from 8:00:00 to 10:00:00 costed $3.673418061 USD.
Impact of Arrears
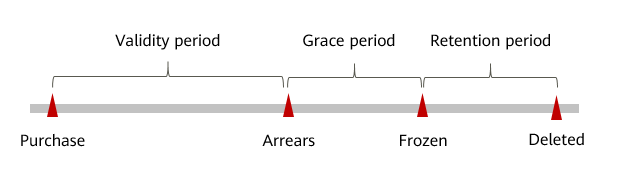
Figure 1 shows the statuses of pay-per-use KVS resources in different periods. The first period your resources in KVS enter is a validity period, when you can normally use them. If your account goes into arrears, your resources enter a grace period and if no payments are made within the specific time, they enter a retention period.
Impact of Arrears
KVS bills pay-per-use resources in each cycle based on the billing items. If bills are not paid when the usage of your expenditure quota reaches or exceeds 100%, your pay-per-use resources enter a grace period.
If bills are not paid during the grace period, your pay-per-use resources enter a retention period and get frozen, meaning you cannot do any operations on them.
If bills are not paid during the retention period, your pay-per-use resources will be deleted, and data cannot be restored.
- For details about how to add a credit card for automatic payment, see Adding a Payment Method.
- For details about how to manually make payments, see Making Payments (Postpaid Direct Customers).
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot