Elastically Adding or Deleting a Logical Cluster
Context
You can add or delete VWs manually or automatically. Computing logical clusters can be created and deleted during the scheduled period of time to dynamically scale computing resources.
- A custom scheduled scaling plan creates a logical cluster that provides computing power. Once such logical cluster is associated, user's queries are handled by it, while table creation statements are still managed by the original logical cluster. For instructions on how to configure a custom scheduled scaling plan, see Configuring a Custom Scheduled Scaling Plan. This method is suitable if you have an understanding of your service workloads that fluctuate periodically and mainly involve query requests, such as periodic batch jobs.
- An auto scaling plan creates a logical cluster that facilitates parallel expansion. Once such logical cluster is associated with the primary logical cluster, specific queries from the primary logical cluster are routed to the logical cluster, but table creation statements are still executed in the original logical cluster. For how to configure an auto scaling plan, see Configuring an Auto Scaling Plan. This method is suitable if you are a beginner. It does not require knowledge of service workloads or manual intervention. It applies to workloads that mainly involve complex queries and jobs that may last for dozens of minutes to a few hours.
To reduce statement queuing time, use parallel expansion. When the primary cluster is overwhelmed by high-concurrency tasks and lacks resources like memory, DWS will automatically add extra cluster capacity to process the increased read and write statements. The performance and data consistency are consistent for users, regardless of whether the statement is executed on the primary cluster or the parallel extended cluster. You can set up a resource pool to control which statements are directed to a parallel extended cluster. When parallel expansion is enabled, qualifying statements are directed to the concurrent expansion cluster instead of being queued.

- VWs can be added and deleted only in storage-compute decoupled clusters. VWs can be automatically added and deleted only in storage-compute decoupled clusters using ECSs of version 9.1.0.200 or later.
- The fine-grained snapshot feature is automatically enabled in the cluster. An error will be reported when you create or delete a plan. You need to manually disable this feature.
- In a yearly/monthly storage-compute decoupled cluster, nodes are automatically added when logical clusters are added as scheduled. Nodes are billed on a pay-per-use basis.
Notes and Constraints
Constraints for custom scheduled scaling plans:
- A user can be bound to only one computing logical cluster.
- If a user associated with the read-only logical cluster has workloads in progress when the cluster is deleted, an error may be reported.
- To avoid affecting services and ensure resources are available at the scheduled time, the plan may be skipped if it conflict with O&M operations, and may be executed about 20 minutes earlier than planned if the cluster creation is time-consuming.
- You are advised to manually add nodes to a logical cluster based on the following rules:
- Optimal configuration for parallel workloads: The number of nodes in an elastic logical cluster is determined based on the historical memory usage of services routed to the cluster. If n jobs are to be routed to the elastic logical cluster, the peak memory usage of the i job is mi, the number of nodes in the logical cluster is N, and the available memory of a single node is S. In this case, you are advised to set the number of nodes in the elastic logical cluster to
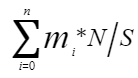 . You can query the max_peak_memory field of GS_WLM_SESSION_INFO to view the peak memory usage and query the max_dynamic_memory field of PGXC_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL to view the available memory of a single node.
. You can query the max_peak_memory field of GS_WLM_SESSION_INFO to view the peak memory usage and query the max_dynamic_memory field of PGXC_TOTAL_MEMORY_DETAIL to view the available memory of a single node. - Optimal configuration for serial workloads: The number of nodes in an elastic logical cluster is determined by the job with the highest memory usage in the serial workloads. If the maximum memory usage of a serial job is M, the number of nodes in a logical cluster is N, and the available memory of a single node is S, you are advised to set the number of elastic logical clusters to
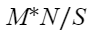 . You can check the peak memory usage of a job and the available memory of a single node by referring to the preceding method.
. You can check the peak memory usage of a job and the available memory of a single node by referring to the preceding method.
- Optimal configuration for parallel workloads: The number of nodes in an elastic logical cluster is determined based on the historical memory usage of services routed to the cluster. If n jobs are to be routed to the elastic logical cluster, the peak memory usage of the i job is mi, the number of nodes in the logical cluster is N, and the available memory of a single node is S. In this case, you are advised to set the number of nodes in the elastic logical cluster to
Constraints for auto scaling plans:
You are advised to enable and use the concurrent extension feature based on the following rules:
- Only V3 tables and foreign tables are supported. If the table is a replication table, only SELECT is supported.
- Only SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements are supported.
- COPY cannot be used to import data.
- The UPSERT statement is not supported.
- Transaction blocks are not supported.
- Stored procedures are not supported.
- Recursive statements with the RETURNING clause and WITH RECURSIVE are not supported.
- Lightweight update is not supported.
- INSERT statements generated by a single VALUES or generate_series are not supported.
Configuring a Custom Scheduled Scaling Plan
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The Cluster Information page is displayed.
- Once storage-compute decoupled clusters are set up, they operate in logical cluster mode. You can only have up to two active plans at a time.
- For storage-compute decoupled clusters: In the navigation pane, choose Logical Clusters. On the displayed page, click Add Plan to configure a proper scheduling plan.
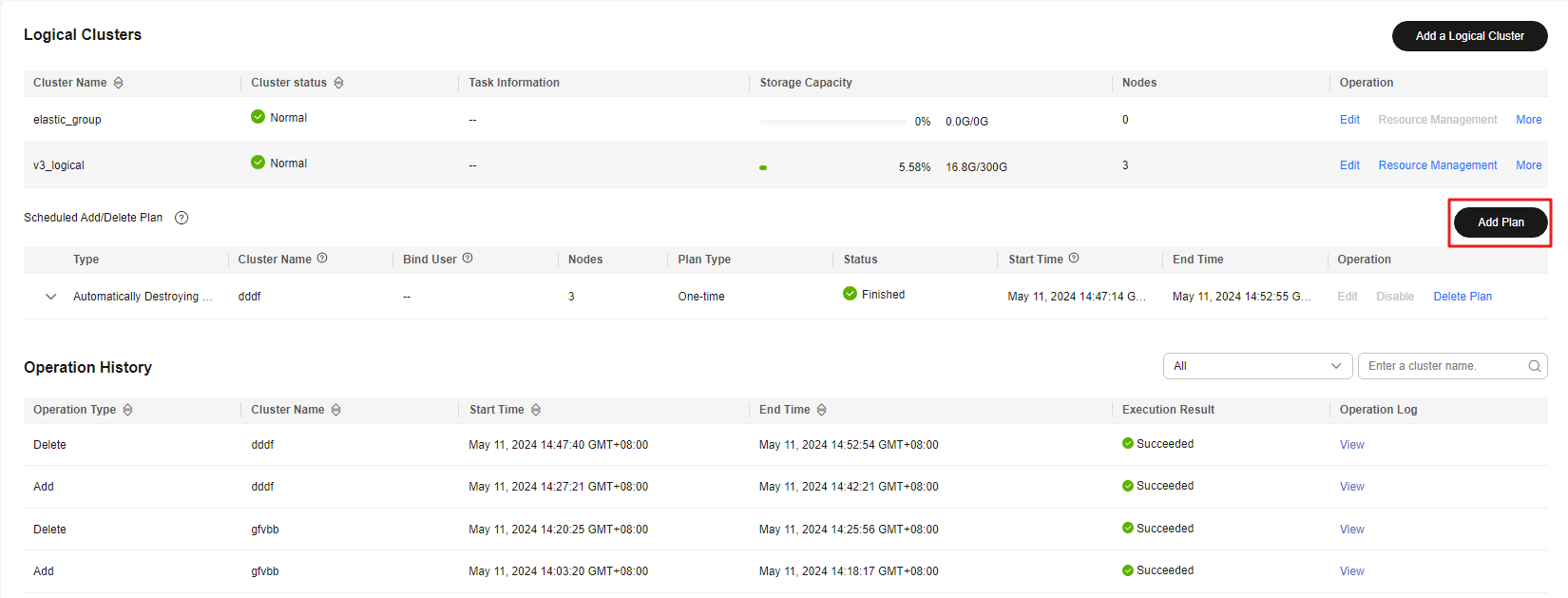
- For storage-compute decoupled clusters: In the navigation pane, choose Logical Clusters. On the displayed page, click Add Plan to configure a proper scheduling plan.
- Select a plan type. It can be:
- Periodicity: The plan is executed once in every specified period (week or month). A logical cluster is created or deleted as scheduled as long as it does not conflict with other O&M operations. You can set the weekly time intervals for creating or deleting logical clusters.
Figure 1 Setting Plan Type to Periodicity
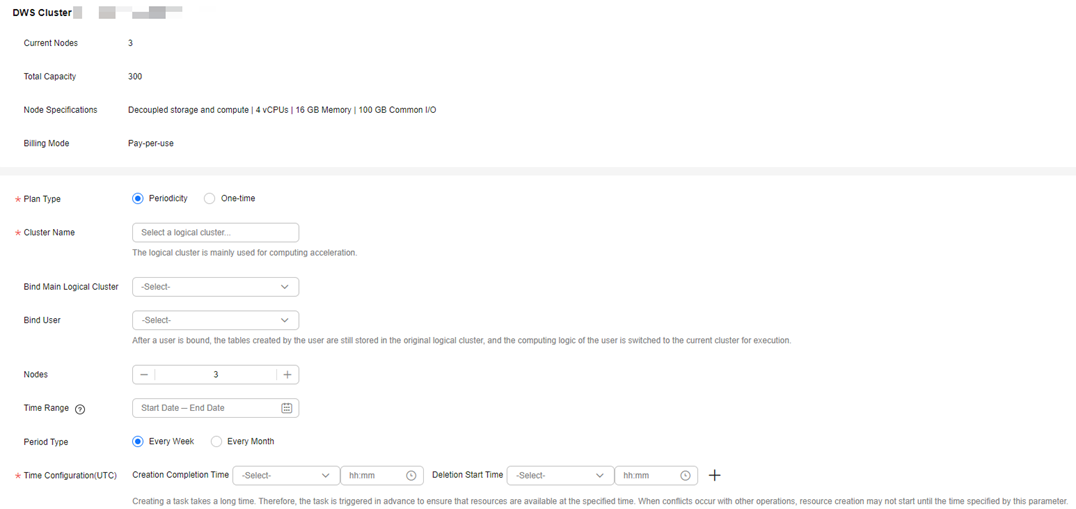
- One-time: The plan is executed only once in the specified period.
Figure 2 Selecting One-time
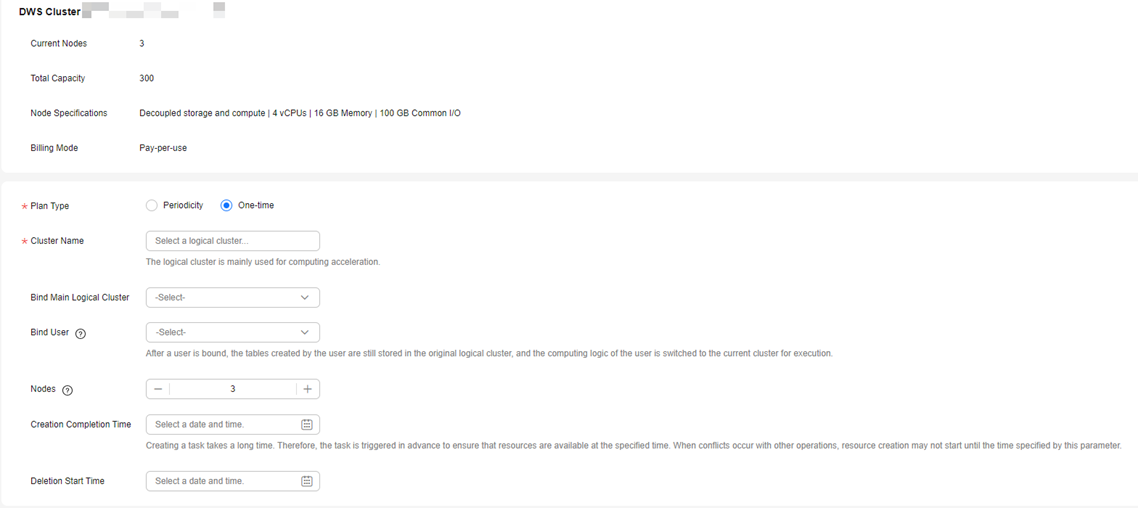
- Periodicity: The plan is executed once in every specified period (week or month). A logical cluster is created or deleted as scheduled as long as it does not conflict with other O&M operations. You can set the weekly time intervals for creating or deleting logical clusters.
- Click OK. In the scheduled plan list, you can view the plan details and next execution time.
Configuring an Auto Scaling Plan
- Log in to the DWS console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Dedicated Clusters > Clusters.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The Cluster Information page is displayed.
- In the navigation pane, choose Logical Clusters to access the page for cluster management. Because once you have created a storage-compute decoupled cluster, it will be in logical cluster mode.
- Click Auto Resiliency Switch to enable the auto scaling function for logical clusters.
Enabling this function allows the system to efficiently manage node resources by detecting service demand and creating or deleting read-only elastic logical clusters as needed. This means that unused nodes are free of charge and the system can adapt to peak and off-peak hours seamlessly.
Figure 3 Enabling auto scaling for logical clusters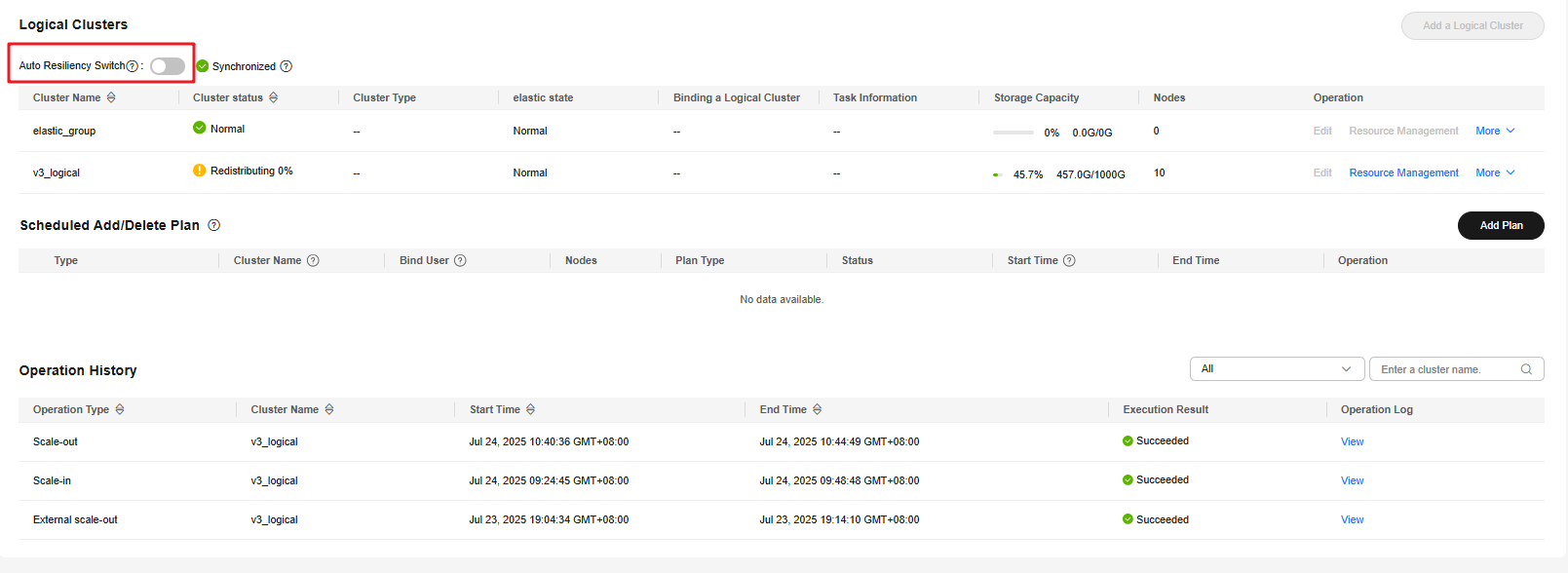
- After auto scaling is enabled, run SQL statements after completing the operation described in Using the SQL Editor to Connect to a Cluster to create and set a resource pool, and bind a user to the resource pool to enable auto scaling for the specified resource pool. In the command, poolg indicates the resource pool name, which can be customized.
1 2 3
create resource pool "poolg" with(nodegroup = 'v3_logical'); alter user "write_user" with resource pool "poolg"; alter resource pool "poolg" with (enable_concurrency_scaling=true);
Figure 4 Setting a resource pool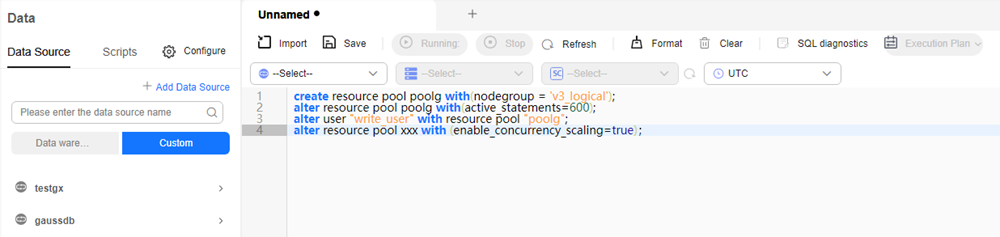
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





