How Can We Use CBH to Locate Incident Causes?
As cloud services develop, the number of cloud O&M engineers increases. In this case, security incidents may occur due to negligence. Tradition servers do not provide functions such as command monitoring and operation playback, resulting in incomplete traceability of security events.
CBH can manage and control all operations and log all operations in detail. Audit logs of sessions can be viewed online, recorded and played online, and played offline after being downloaded. CBH allows you to audit operations performed over character protocols (SSH and TELNET), graphics protocol (RDP and VNC), file transfer protocols (FTP, SFTP, and SCP), and database protocols (DB2, MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server), as well as application publishing. For operations over character and database protocols, their operation instructions can be parsed so that you can know what actions have been done. For file transfer actions, the name and destination path of a transferred file can be logged.
Overview
This topic describes how to use CBH session audit function to trace and investigate security events and determine responsibilities.
Prerequisites
You have purchased a CBH instance and logged in to it using an account that has the audit module permission.
Auditing Historical Sessions
- Log in to CBH console. Go to the History Session page. For details, see Viewing History Sessions.
- Enter the related information in the advanced search box based on your security issues.
Figure 1 Advanced search
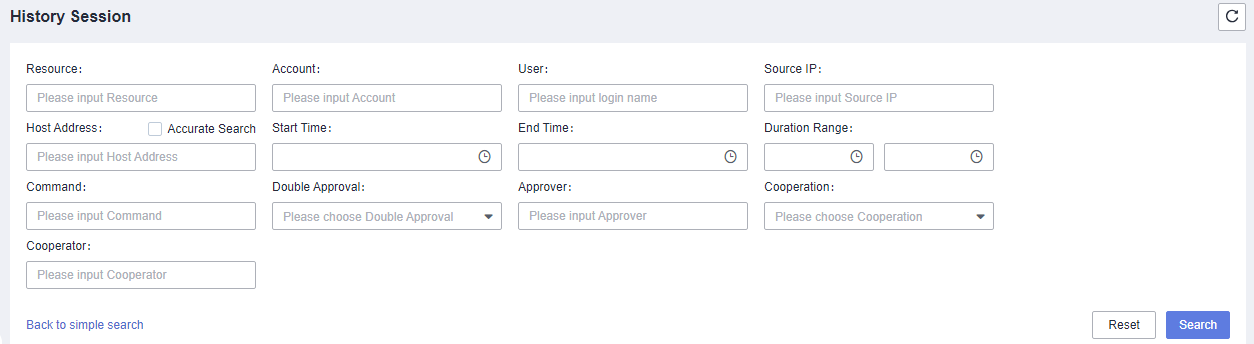
- Locate the target security issue, click Detail in the Operation column to view the historical commands and file transfers.
You can locate the fault based on the commands, ensuring event traceability. You can also use the session playback function to view the specific operations by playing the corresponding O&M video. For details, see Managing Session Videos.

CBH also provides real-time session monitoring. This means you can view the O&M page of high-risk operations in real time. If an alarm is reported for an on-going risky command, the corresponding operations can be immediately terminated to ensure service security.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





