Viewing Monitored Playbook Instances
Scenarios
After a playbook is executed, a playbook instance is generated in the playbook instance management list for monitoring. Each record in the instance monitoring list is an instance. You can view the historical instance task list and the statuses of historical instance tasks.
View instance monitoring information.
Limitations and Constraints
The maximum number of retries within a day in a workspace of an account is as follows:
- Manual retries: 100. After a retry, the playbook cannot be retried until the current execution is complete.
- API retries: 100. After a retry, the playbook cannot be retried until the current execution is complete.
Viewing Monitored Playbook Instances
- Log in to the SecMaster console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Security & Compliance > SecMaster.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Security & Compliance > SecMaster. - In the navigation pane on the left, choose Workspaces > Management. In the workspace list, click the name of the target workspace.
Figure 1 Workspace management page

- In the navigation pane on the left, choose . On the displayed page, click the Instance Management tab.
Figure 2 Instance Management page
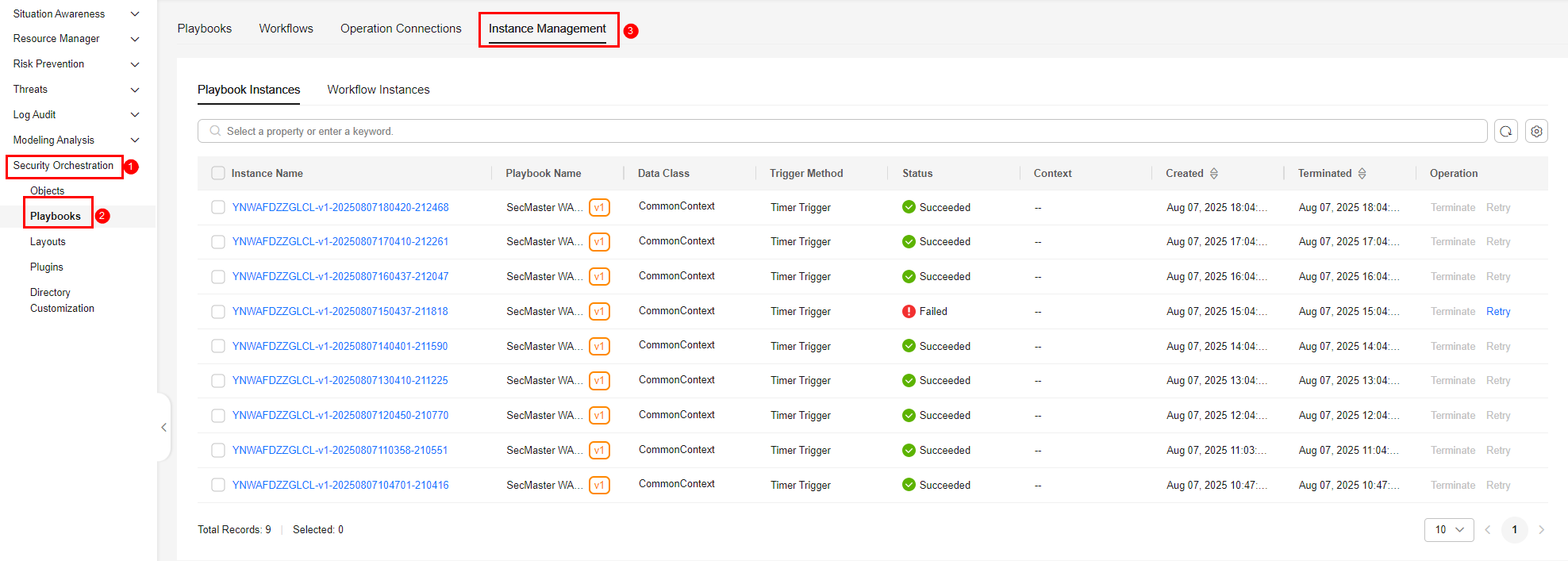
- On the Instance Management tab, click the Playbook Instances or Workflow Instances tab, and view the instance information. For details about the parameters, see Table 1.
Figure 3 Instances

- You can view the total number of instances below the instance list. You can view a maximum of 10,000 instance records page by page. To view more than 10,000 records, optimize the filter criteria.
- An instance can be stored for a maximum of 180 days.
- To view details about an instance, click the instance name. On the displayed page, you can view the instance workflow, workflow nodes, start time, and end time.
Table 1 Parameters in the instance list Parameter
Description
Instance Name
Name of the instance generated by the system.
Playbook/Instance Name
Name of the corresponding playbook/instance.
Data Class
Operation object of a playbook
Trigger Method
Triggering mode of an instance
- Timer Trigger
- Event Trigger
Status
Status of an instance
- Succeeded: The playbook instance is successfully executed.
- Failed: The playbook instance fails to be executed. You can click Retry in the Operation column to execute the playbook again.
- Running: The playbook instance is running. You can click Terminate in the Operation column to terminate the playbook.
- Retrying: The playbook instance is being retried.
- Terminating: The playbook instance is being terminated.
- Stopped: The playbook instance has been terminated.
Context
Context information of an instance
Instance Creation Time
Time when an instance is created.
Instance Ended
Time when an instance ends.
Operation
You can terminate or retry an instance.
Related Operations
- To stop a running instance, click Terminate in the Operation column of the target instance. After an instance is terminated, no operations are supported.
- To start a failed instance, click Retry in the Operation column.
You can retry instances up to 100 times a day in a workspace. After a retry, the playbook cannot be retried until the current execution is complete.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






