Scenario
The yearly/monthly CU adjustment for elastic resource pools allows you to modify resource configurations and billing modes based on actual usage needs. This ensures efficient resource utilization and cost optimization.
For a yearly/monthly elastic resource pool, CUs within the range defined by yearly/monthly CUs (specifications) are billed under the yearly/monthly mode. Any excess CUs beyond this range are billed by CUH. By adjusting the specification according to your actual CU usage, you can achieve more favorable billing terms.
For example, if the current yearly/monthly CUs (specifications) for the elastic resource pool are 64, but most of the time your usage exceeds 128 CUs, without adjustment, only the first 64 CUs will be billed on a yearly/monthly basis, while the additional 64 CUs will be billed by CUH. To optimize costs, you can adjust the specification limit to 128. Once updated, all 128 CUs will fall under the yearly/monthly billing mode, resulting in overall savings.
In summary, adjusting the yearly/monthly CUs (specifications) converts the billing mode for excess resources from pay-per-use to yearly/monthly, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
Precautions
- Only yearly/monthly elastic resource pools support CU (specifications) adjustments.
- Adjustments to a queue's CU range, changes to the pool's yearly/monthly CUs (specifications), or modifications to the pool's CU settings take effect at the next full hour.
- Increasing the number of queues to adjust the pool's actual CUs takes immediate effect.
Basic Concepts of Elastic Resource Pools
This section explains the meanings of actual CUs, used CUs, CU range, and yearly/monthly CUs (specifications) in elastic resource pools.
Relationship Diagram and Constraints
- Actual CUs dynamically scale within the CU range defined by [Minimum CUs, Maximum CUs] based on the queue load.
- If actual CUs ≤ yearly/monthly CUs, billing is entirely based on the yearly/monthly rate with no additional pay-per-use charges.
- If actual CUs > yearly/monthly CUs, the difference is billed hourly at the pay-per-use rate.
Figure 1 Relationship between the actual CUs, used CUs, CU range, and yearly/monthly CUs of DLI

Constraints for setting elastic resource pool CUs:
- The minimum CUs (minCU) of an elastic resource pool must be less than or equal to the actual CUs. If expanding minCU exceeds the current actual CUs, you must first increase the actual CUs. Otherwise, the modification will fail.
- The sum of all queues' minimum CUs in an elastic resource pool must not exceed the pool's minCU.
- Any single queue's maxCU cannot exceed the pool's maxCU.
- Adjustments to a queue's CU range, changes to the pool's yearly/monthly CUs, or modifications to the pool's CU settings take effect at the next full hour.
- Increasing the number of queues to adjust the pool's actual CUs takes immediate effect.
Actual CUs
- Actual CUs are the total amount of compute resources currently allocated in an elastic resource pool for running jobs (measured in CUs). They also serve as the direct basis for billing.
- Calculation rules for actual CUs:
- When no queues exist in the resource pool: The actual CUs equal the minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool.
- When there are queues in the resource pool, the formula to calculate actual CUs is:
- Actual CUs = max{(min[sum(maximum CUs of queues), maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool]), minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool}.

- The result must be a multiple of 16 CUs. If not divisible by 16, round up to the nearest multiple.
- Billing modes:
Table 1 Billing modes
|
Billing Mode |
Billing Object |
Description |
|
Pay-per-use |
Based on actual CUs |
For details, see Billing Modes. |
|
Yearly/Monthly |
Divided into two parts: within specifications and beyond specifications |
- Within specifications: billed on a yearly/monthly basis.
- Beyond specifications: excess CUs (actual CUs – specifications) are billed on a pay-per-use basis. Cost optimization tip: To achieve more favorable pricing, adjust the elastic resource pool's specifications to match the actual CUs. This ensures all CUs are billed on a yearly/monthly basis, resulting in overall cost savings.
|
- Relationship between actual CUs and elastic resource pool scaling
Scaling out or in an elastic resource pool means adjusting its actual CUs.
Refer to Scaling Out or In an Elastic Resource Pool and Actual CUs Calculation Formula.
- Example of actual CU allocation:
Consider Table 2 below, which illustrates the process of calculating actual CUs for an elastic resource pool:
- Calculate the sum of maximum CUs of the queues: sum(maximum CUs) = 32 + 56 = 88 CUs.
- Compare the sum of maximum CUs of the queues with the maximum CUs of the elastic resource pool and take the smaller value: min{88 CUs, 112 CUs} = 88 CUs.
- Compare the value with the minimum CUs of the elastic resource pool and take the larger value: max(88 CUs, 64 CUs) = 88 CUs.
- Check if 88 CUs is a multiple of 16 CUs. Since 88 is not divisible by 16, round up to 96 CUs.
Table 2 Example of actual CU allocation of an elastic resource pool
|
Scenario |
Resource Type |
CU Range |
|
New elastic resource pool: 64–112 CUs
Queues A and B are created within the elastic resource pool. The CU ranges of the two queues are:
- CU range of queue A: 16–32 CUs
- CU range of queue B: 16–56 CUs
|
Elastic resource pool |
64–112 CUs |
|
Queue A |
16–32 CUs |
|
Queue B |
16–56 CUs |
Used CUs
Figure 2 Used CUs

CU Range
The CU range acts as a safety fence for scaling elastic resource pools, defined by two boundaries: minimum CUs (minCU) and maximum CUs (maxCU). The actual CUs of the elastic resource pool automatically scale within this range, preventing unlimited expansion risks.
When calculating actual CUs: If the result is below minCU, actual CUs default to minCU. If the result exceeds maxCU, actual CUs cap at maxCU. Thus, actual CUs always remain within the CU range.
- Minimum CUs (minCU)
In yearly/monthly mode, the minCU set during purchase is the yearly/monthly CUs (specifications) for the elastic resource pool. This can be increased on the Modify Yearly/Monthly CU page.
During resource pool expansion, the minCU is linked to and changes accordingly to match the yearly/monthly CUs (specifications), while maxCU remains unchanged.
During resource pool scale-in, actual CUs never fall below minCU, ensuring immediate availability for job takeover.
The sum of all queues' minimum CUs in an elastic resource pool must not exceed the pool's minCU.
- Maximum CUs (maxCU)
Any single queue's maxCU cannot exceed the pool's maxCU.
The resource pool ensures it meets the minCU requirements across all queues while striving to accommodate their maxCU demands.
Yearly/Monthly CUs (Specifications)
This refers to the CU quantity purchased under the yearly/monthly mode. At purchase, the minCU of the CU range serves as the yearly/monthly CUs (specifications).
The chosen minimum CU value during purchase defines the elastic resource pool's specifications, which is unique to yearly/monthly resource pools. Resources within the specifications are billed on a yearly/monthly basis, and excess usage incurs pay-per-use charges.
The queue's maximum CUs directly impact actual CU allocation. If actual CUs exceed the specifications, the excess portion is billed at the pay-per-use rate. To optimize costs in such scenarios, you can increase the elastic resource pool's yearly/monthly CUs (specifications). Once updated, all resources within the new yearly/monthly CUs (specifications) will be billed under the more cost-effective yearly/monthly mode, eliminating partial pay-per-use charges.
Figure 3 Elastic resource pool – yearly/monthly + pay-per-use billing | cost optimization example

Checking Before Yearly/Monthly CUs (Specifications) Change (Scale-Out)
Before changing the yearly/monthly CUs (specifications) (scale-out), check whether the actual CUs are greater than or equal to the target CUs of the new specifications.
If the actual CUs are fewer than the target CUs, you need to increase the maximum CUs of queues or add more queues to adjust the actual CUs.
Example: A yearly/monthly elastic resource pool has 64 actual CUs, a CU range of 64–96, and specifications of 64 CUs. The planned target specification is 80 CUs.
Procedure
- Increase the actual CUs of the elastic resource pool to 80 by adjusting the maximum CUs of existing queues or adding new queues within the current elastic resource pool.
When the total maximum CUs of all queues exceeds the actual CUs of the elastic resource pool, the actual CUs will increase. The adjusted actual CUs = min(total maximum CUs of queues, maximum CU limit of the elastic resource pool). (Changes to the CU range of a queue take effect at the next full hour.)
- Once the actual CUs have been increased to 80, proceed with the specification change operation to update the elastic resource pool's specifications to 80 CUs. (Elastic resource pool specification changes take effect at the next full hour.)
After the specification change, the minimum CU in the CU range of the elastic resource pool will also align with the actual CUs.
Scaling Out
- In the navigation pane on the left of the console, choose Resources > Resource Pool.
- Locate the elastic resource pool you want to scale out, click More in the Operation column, and select Modify Yearly/Monthly CU.
- On the Modify Yearly/Monthly CU page, set Operation to Scale-out and specify the number of CUs you want to add.
Figure 4 Scaling out
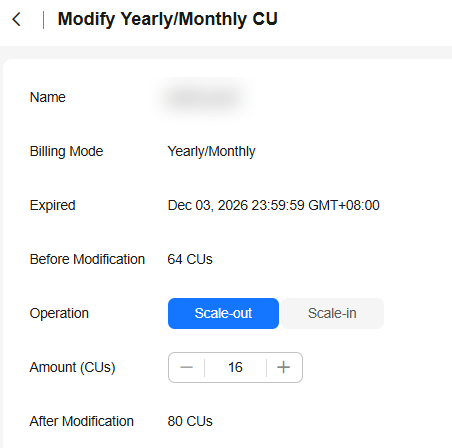
- Confirm the changes and click OK.
- Choose Job Management > SQL Jobs to view the status of the SCALE_POOL SQL job.
If the job status is Scaling, the elastic resource pool is scaling out. Wait until the job status changes to Finished.
Scaling In
By default, the minimum number of CUs is 16. That is, when the specifications of an elastic resource pool are 16 CUs, you cannot scale the pool down.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Resource Pool.
- Locate the elastic resource pool you want to scale in, click More in the Operation column, and select Modify Yearly/Monthly CU.
- On the Modify Yearly/Monthly CU page, set Operation to Scale-in and specify the number of CUs you want to decrease.
Figure 5 Scaling in
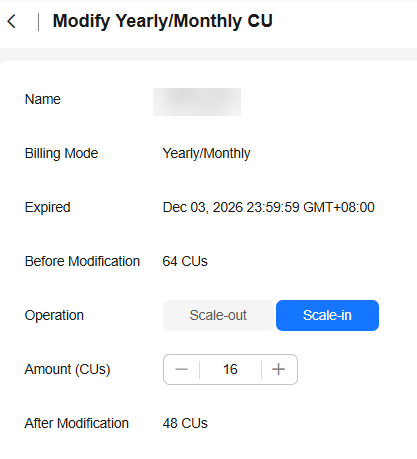
- Confirm the changes and click OK.
- Choose Job Management > SQL Jobs to view the status of the SCALE_POOL SQL job.
If the job status is Scaling, the elastic resource pool is scaling in. Wait until the job status changes to Finished.