Configuring the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring Add-on in a Large-Scale Cluster
In a large-scale cluster, the collection configurations of the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on greatly affect the collection performance. In the data collection phase, appropriate configurations can significantly improve the efficiency and stability of the monitoring system.
This section describes how to configure and manage the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on in a large-scale cluster to ensure stable services and efficient O&M. The following configurations are involved:
- Adjusting the Collection Interval
- Adjusting the Number of Shards for Prometheus-based Data Collection
- Adjusting the Number of Shards of kube-state-metrics
- Adjusting the Specifications of kube-state-metrics
- Adjusting Remote Write Parameters
Prerequisites
- The local storage has been disabled for the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on in the large-scale cluster.
- Master nodes in the large-scale cluster have low memory usage (less than 40% in normal cases and less than 45% in peak hours). You can view the memory usage of each master node on the cluster overview page. If the memory usage is high, modify the cluster specifications. For details, see Changing a Cluster Scale.
Adjusting the Collection Interval
For a cluster with at least 200 nodes or 10,000 pods, adjust the collection interval to 60 or 30 seconds to prevent system overload caused by frequent data collection.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons. On the displayed page, locate the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on and click Edit. In Parameters, change the value of Collection Interval.
- Click OK and wait until the add-on update is complete.
Adjusting the Number of Shards for Prometheus-based Data Collection

Adjusting the number of shards will increase the memory usages of the master nodes in the cluster, especially the memory usage of kube-apiserver. Do not adjust the number of shards in peak hours.
To meet the performance requirements of Prometheus in large-scale cluster monitoring, you can adjust the number of shards to allocate collection tasks to multiple Prometheus instances. This reduces the AOM load and improves the overall performance. You are advised to create one shard for every 75 nodes (or every 50 nodes if there is a large number of custom metrics or pods). A maximum of 32 shards can be created.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons. On the displayed page, locate the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on and click Edit. In Specifications, change the number of shards.
- Click OK and wait until the add-on update is complete.
Adjusting the Number of Shards of kube-state-metrics

- The Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on version must be 3.12.1 or later.
- Adjusting the number of shards will increase the memory usages of the master nodes in the cluster, especially the memory usage of kube-apiserver. Do not adjust the number of shards in peak hours.
kube-state-metrics is an open-source monitoring component in Kubernetes. It monitors Kubernetes APIs to expose the metrics of resources (such as pods, Deployments, and nodes) in a cluster. As the cluster scale increases, kube-state-metrics needs to process more API calls and generate more metrics, which may cause performance problems. You can shard kube-state-metrics to distribute workloads to multiple kube-state-metrics instances, improving overall performance and availability.
The following are some policies for sharding kube-state-metrics:
- If the cluster has up to 50 nodes, do not change the number of shards. By default, kube-state-metrics has one shard.
- If the cluster has 50 to 200 nodes, change the number of shards to 3.
- If the cluster has over 200 nodes, change the number of shards to 5. If the number of shards is greater than 5, the cluster will be overloaded. To prevent this, the maximum number of shards is kept at 5.
Take the following steps:
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons. On the displayed page, locate the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on and click Edit. Then, click Edit YAML above the add-on name.
- Set operator_manage_ksm to true and ksm_shards to the recommended value.
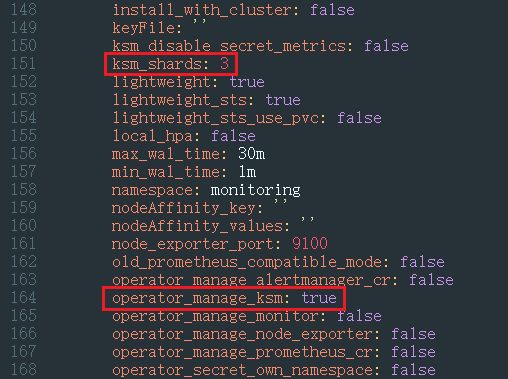
- Click OK and wait until the add-on update is complete. You can view the workload of each sharded kube-state-metrics on the Pods tab.
Adjusting the Specifications of kube-state-metrics
When the cluster scale is large, the amount of data to be processed by kube-state-metrics increases significantly. As a result, kube-state-metrics becomes overloaded. If you do not adjust the resource configurations in a timely manner, the kube-state-metrics performance may be affected or even kube-state-metrics may be unavailable.
If there are 10,000 pods in a cluster, set the CPU limit of kube-state-metrics to 500m, the memory limit to 1.5 GiB, and the CPU and memory requests to 30% to 40% of their limits. If the pod YAML files in the cluster are large, increase the request-to-limit ratios by 50%.
For example, if a cluster has 40,000 pods, set the CPU limit of kube-state-metrics to 2,000m (the request is 1,000m) and the memory limit to 6 GiB (the request is 1 GiB to 2 GiB).
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Add-ons. On the displayed page, locate the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on and click Edit. In Specifications, set Add-on Specifications to Custom and modify the resource quotas of kube-state-metrics.
- Click OK and wait until the add-on update is complete.
Adjusting Remote Write Parameters

The Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on version must be 3.12.1 or later.
When Prometheus is interconnected with AOM, the data transmission efficiency and stability may be affected if a large amount of data is processed. You can adjust the remote write parameters to control the batch size of uploaded data. This improves the data transmission efficiency and system performance. You are advised to test and monitor in the actual environment, and adjust the remote write parameters based on the application scenario and system load for the optimal performance.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose ConfigMaps and Secrets. Then, select the monitoring namespace. On the ConfigMaps tab, locate persistent-user-config.
- Click Edit YAML to edit the configuration data and add two parameters to operatorConfigOverride. If there is a square bracket ([]) after operatorConfigOverride, the array is empty. In this case, delete the square bracket ([]). The following are the two parameters to be added:
... operatorConfigOverride: - lightweight.agent.max-block-size=31457280 - lightweight.agent.max-rows-per-block=30000 ... - Click OK.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






