Enabling Logs
After you authorize Anti-DDoS to access Log Tank Service (LTS), you can use the Anti-DDoS logs recorded by LTS for quick and efficient real-time analysis, device O&M management, and analysis of service trends.
Prerequisites
You have created an LTS log group and log stream. For details, see Managing Log Groups and Managing Log Streams.
Enabling LTS
- Log in to the Anti-DDoS console.
- Click the Configure Logs tab, enable LTS (
 ), and select a log group and log stream. Table 1 describes the parameters.
Figure 1 Configuring logs
), and select a log group and log stream. Table 1 describes the parameters.
Figure 1 Configuring logs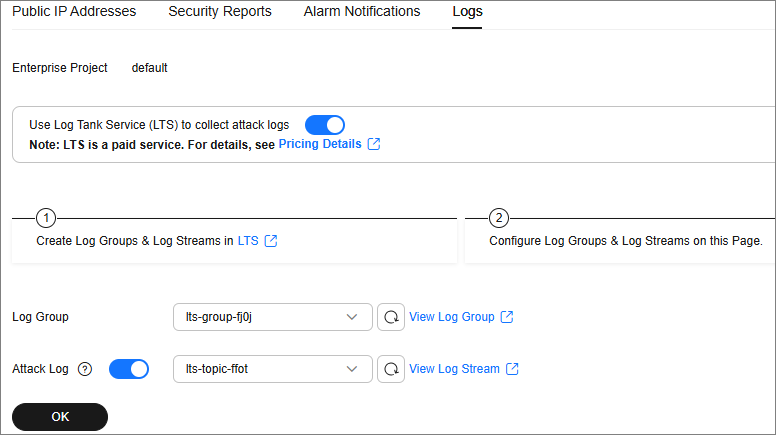
Table 1 Log configuration Parameter
Description
Log Group
Select a log group or click View Log Group to go to the LTS console and create a log group.
Attack Log
Select a log stream or click View Log Stream to go to the LTS console and create a log stream.
Attack logs record alarm information about each attack, including the attack type and protected IP address.
- Click OK.
You can view Anti-DDoS protection event logs on the LTS console.
Log Fields in LTS
The following table describes the log fields.
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
logType |
Log type. The default value is ip_attack_sum, indicating attack logs. |
|
deviceType |
Type of the device that reports logs. The default value is CLEAN, indicating the scrubbing device. |
|
inKbps |
Inbound traffic, in kbit/s. |
|
maxPps |
Peak incoming traffic, in pps. |
|
dropPps |
Average number of discarded packets, in pps. |
|
maxAttackInBps |
Indicates the incoming traffic at the peak time of attack traffic, in bit/s. |
|
currentConn |
Current connections |
|
zoneIP |
Protected IP address. |
|
logTime |
Time when a log is generated. |
|
attackType |
Attack type. For details about the corresponding attack types, see Table 3. |
|
inPps |
Inbound traffic, in pps. |
|
maxKbps |
Peak inbound traffic, in kbit/s. |
|
dropKbps |
Average discarded traffic, in kbit/s. |
|
startTime |
Time when the attack starts. |
|
endTime |
End time of the attack. If this parameter is left blank, the attack has not ended yet. |
|
maxAttackInConn |
Number of connections at the peak time of attack traffic. |
|
newConn |
New connections. |
|
Value |
Attack Type |
|---|---|
|
0-9 |
User-defined attack type |
|
10 |
SYN flood attack |
|
11 |
Ack flood attack |
|
12 |
SynAck flood attack |
|
13 |
Fin/Rst flood attack |
|
14 |
Concurrent connections exceed the threshold. |
|
15 |
The number of new connections exceeds the threshold. |
|
16 |
TCP fragment attack |
|
17 |
TCP fragment bandwidth limit attack |
|
18 |
TCP bandwidth limit attack |
|
19 |
UDP flood attack |
|
20 |
UDP fragment attack |
|
21 |
UDP fragment bandwidth limit attack |
|
22 |
UDP bandwidth limit attack |
|
23 |
ICMP bandwidth limit attack |
|
24 |
Other bandwidth limit attack |
|
25 |
Traffic limiting attack |
|
26 |
HTTPS flood attack |
|
27 |
HTTP flood attack |
|
28 |
Reserved |
|
29 |
DNS query flood attack |
|
30 |
DNS reply flood attack |
|
31 |
SIP flood attack |
|
32 |
Blacklist dropping |
|
33 |
Abnormal HTTP URL behavior |
|
34 |
TCP fragment abnormal dropping traffic attack |
|
35 |
TCP abnormal dropping traffic attack |
|
36 |
UDP fragment abnormal dropping traffic attack |
|
37 |
UDP abnormal dropping traffic attack |
|
38 |
ICMP abnormal attack |
|
39 |
Other abnormal attacks |
|
40 |
Connection flood attack |
|
41 |
Domain name hijacking attack |
|
42 |
DNS poisoning packet attack |
|
43 |
DNS reflection attack |
|
44 |
Oversize DNS packet attack |
|
45 |
Abnormal rate of DNS source requests |
|
46 |
Abnormal rate of DNS source replies |
|
47 |
Abnormal rate of DNS domain name requests |
|
48 |
Abnormal rate of DNS domain name replies |
|
49 |
DNS request packet TTL anomaly |
|
50 |
DNS packet format anomaly |
|
51 |
DNS cache matching and dropping attack |
|
52 |
Port scan attacks |
|
53 |
Abnormal TCP packet flag bit |
|
54 |
BGP attack |
|
55 |
UDP association defense anomaly |
|
56 |
DNS NO such Name |
|
57 |
Other fingerprint attacks |
|
58 |
Zone traffic limit attack |
|
59 |
HTTP slow attacks |
|
60 |
Malware prevention |
|
61 |
Domain name blocking |
|
62 |
Filtering |
|
63 |
Web attack packet capture |
|
64 |
SIP source rate limiting |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






