CREATE FUNCTION
Function
A function is a reusable code block that accepts input parameters, performs specific operations, and returns a value or result set. CREATE FUNCTION is used to create a user-defined function (UDF) in a database, enabling other computing functions that are not supported by the built-in system functions of GaussDB(DWS) and covering complex computing scenarios specific to users.
The functions have the following features:
- They support input parameters and return results depending on specific conditions.
- You must declare the return value's data type. It outputs either a single value (scalar function) or a table (table-valued function).
- By wrapping complex logic into one function, you can call it like a built-in SQL function, enhancing code reuse.
Precautions
- The precision values (if any) of the parameters or return values of a function are not checked.
- Always define a clear schema for table operations in your functions. For instance, use hr.table1 to point to a table in the hr schema. Without this, the function might not run correctly.
- current_schema and search_path specified by SET during function creation are invalid. The values of search_path and current_schema after function execution are the same as those before function execution.
- If a function has output parameters, the SELECT statement uses the default values of the output parameters when calling the function. When the CALL statement calls the function, it requires that the output parameter values are adapted to Oracle. When the CALL statement calls an overloaded PACKAGE function, it can use the default values of the output parameters. For details, see examples in CALL.
- Only the functions compatible with PostgreSQL or those with the PACKAGE attribute can be overloaded. After REPLACE is specified, a new function is created instead of replacing a function if the number of parameters, parameter type, or return value is different.
- You can use the SELECT statement to specify different parameters using identical functions, but cannot use the CALL statement to call identical functions without the PACKAGE attribute because CALL aligns with Oracle syntax.
- When you create a function, you cannot insert other agg functions out of the avg function or other functions.
- In non-logical cluster mode, return values, parameters, and variables cannot be set to the tables of the Node Groups that are not installed in the system by default. The internal statements of SQL functions cannot be executed on such tables.
- In logical cluster mode, if return values and parameters of the function are user tables, all the tables must be in the same logical cluster. If the function body involves operations on multiple logical cluster tables, the function cannot be set to IMMUTABLE or SHIPPABLE, preventing the function from being pushed down to a DN.
- In logical cluster mode, the parameters and return values of the function cannot use the %type to reference a table column type. Otherwise, the function will fail to be created.
- By default, the permissions to execute new functions are granted to PUBLIC. For details, see GRANT. You can revoke the default execution permissions from PUBLIC and grant them to other users as needed. To avoid the time window during which new functions can be accessed by all users, create functions in transactions and set function execution permissions.
- In a cluster with multiple CNs, the input or output parameters of a function cannot be set to the temporary table type. This is because the correct temporary schema cannot be obtained based on the table name when the function is created on a non-current CN. As a result, the accurate table type cannot be obtained.
Syntax
- Syntax (compatible with PostgreSQL) for creating a user-defined function:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] FUNCTION function_name ( [ { argname [ argmode ] argtype [ { DEFAULT | := | = } expression ]} [, ...] ] ) [ RETURNS rettype [ DETERMINISTIC ] | RETURNS TABLE ( { column_name column_type } [, ...] )] LANGUAGE lang_name [ {IMMUTABLE | STABLE | VOLATILE } | {SHIPPABLE | NOT SHIPPABLE} | WINDOW | [ NOT ] LEAKPROOF | {CALLED ON NULL INPUT | RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT | STRICT } | {[ EXTERNAL ] SECURITY INVOKER | [ EXTERNAL ] SECURITY DEFINER | AUTHID DEFINER | AUTHID CURRENT_USER} | {FENCED | NOT FENCED} | {PACKAGE} | COST execution_cost | ROWS result_rows | SET configuration_parameter { {TO | =} value | FROM CURRENT }} ][...] { AS 'definition' | AS 'obj_file', 'link_symbol' }
- Oracle syntax of creating a customized function:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] FUNCTION function_name ( [ { argname [ argmode ] argtype [ { DEFAULT | := | = } expression ] } [, ...] ] ) RETURN rettype [ DETERMINISTIC ] [ {IMMUTABLE | STABLE | VOLATILE } | {SHIPPABLE | NOT SHIPPABLE} | {PACKAGE} | {FENCED | NOT FENCED} | [ NOT ] LEAKPROOF | {CALLED ON NULL INPUT | RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT | STRICT } | {[ EXTERNAL ] SECURITY INVOKER | [ EXTERNAL ] SECURITY DEFINER | AUTHID DEFINER | AUTHID CURRENT_USER } | COST execution_cost | ROWS result_rows | SET configuration_parameter { {TO | =} value | FROM CURRENT ][...] { IS | AS } plsql_body /
Parameter Description
|
Parameter |
Description |
Value Range |
|---|---|---|
|
function_name |
Specifies the name of the function to be created (optionally schema-qualified).
CAUTION:
If the name of the function to be created is the same as that of a system function, you are advised to specify a schema. When invoking a user-defined function, you need to specify a schema. Otherwise, the system preferentially invokes the system function. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. For details, see Identifier Naming Conventions. |
|
argname |
Specifies the name of a function parameter. |
A string, which must comply with the naming convention. |
|
argmode |
Specifies the mode of a function parameter. |
IN, OUT, INOUT, or VARIADIC.
CAUTION:
The parameters of OUT and INOUT cannot be used in function definition of RETURNS TABLE. |
|
argtype |
Data types of function parameters. |
For details about common data types, see Data Types. |
|
expression |
Indicates the default expression of a parameter. |
- |
|
rettype |
Indicates the return data type. |
When there is OUT or IN OUT parameter, the RETURNS clause can be omitted. When this clause is present, the result type matches the specified output parameter. For multiple outputs, the result type becomes RECORD. With only one output, the result type aligns with that single parameter. The SETOF modifier indicates that the function will return a set of items, rather than a single item. |
|
DETERMINISTIC |
Adapted to Oracle SQL syntax. You are not advised to use it. |
- |
|
column_name |
Specifies the column name. |
- |
|
column_type |
Specifies the column type. |
- |
|
definition |
Specifies a string constant defining the function; the meaning depends on the language. It can be an internal function name, a path pointing to a target file, a SQL query, or text in a procedural language. |
- |
|
LANGUAGE lang_name |
Indicates the name of the language that is used to implement the function. It can be SQL, internal, or the name of user-defined process language. To ensure downward compatibility, the name can use single quotation marks. Contents in single quotation marks must be capitalized. |
- |
|
WINDOW |
Indicates that the function is a window function. The WINDOW attribute cannot be changed when the function definition is replaced.
CAUTION:
For a user-defined window function, the value of LANGUAGE can only be internal, and the referenced internal function must be a window function. |
- |
|
IMMUTABLE |
Indicates that the function always returns the same result if the parameter values are the same. |
If the input argument of the function is a constant, the function value is calculated at the optimizer stage. The advantage is that the expression value can be obtained as early as possible, so the cost estimation is more accurate and the execution plan generated is better. A user-defined IMMUTABLE function is automatically pushed down to DNs for execution, which may cause potential risks. If a function is defined as IMMUTABLE but the function execution process is in fact not IMMUTABLE, serious problems such as result errors may occur. Therefore, exercise caution when defining the IMMUTABLE attribute for a function. Examples:
To prevent possible problems, you can set behavior_compat_options to check_function_conflicts in the database to check definition conflicts. This method can identify the 1 and 2 scenarios described above. |
|
STABLE |
Indicates that the function cannot modify the database, and that within a single table scan it will consistently return the same result for the same parameter values, but that its result varies by SQL statements. |
- |
|
VOLATILE |
Indicates that the function value can change even within a single table scan, so no optimizations can be made. |
- |
|
SHIPPABLE NOT SHIPPABLE |
Indicates whether the function can be pushed down to DNs for execution. |
|
|
PACKAGE |
Indicates whether the function can be overloaded. PostgreSQL-style functions can be overloaded, and this parameter is designed for Oracle-style functions. |
|
|
LEAKPROOF |
Indicates that the function has no side effects. LEAKPROOF can be set only by the system administrator. |
- |
|
CALLED ON NULL INPUT |
Declares that some parameters of the function can be invoked in normal mode if the parameter values are NULL. This parameter can be omitted. |
- |
|
RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT STRICT |
Indicates that the function always returns NULL whenever any of its parameters are NULL. If this parameter is specified, the function is not executed when there are NULL parameters; instead a NULL result is returned automatically. The usage of RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT is the same as that of STRICT. |
- |
|
EXTERNAL |
The keyword EXTERNAL is allowed for SQL conformance, but it is optional since, unlike in SQL, this feature applies to all functions not only external ones. |
- |
|
SECURITY INVOKER AUTHID CURRENT_USER |
Indicates that the function is to be executed with the permissions of the user that calls it. This parameter can be omitted. SECURITY INVOKER and AUTHID CURRENT_USER have the same functions. |
- |
|
SECURITY DEFINER AUTHID DEFINER |
Specifies that the function is to be executed with the permissions of the user that created it. The usage of AUTHID DEFINER is the same as that of SECURITY DEFINER. |
- |
|
FENCED NOT FENCED |
(Effective only for C functions) Specifies whether functions are executed in fenced mode. In NOT FENCED mode, a function is executed in a CN or DN process. In FENCED mode, a function is executed in a new fork process, which does not affect CN or DN processes. |
Application scenarios:
|
|
COST execution_cost |
A positive number giving the estimated execution cost for the function. The unit of execution_cost is cpu_operator_cost. |
Positive |
|
ROWS result_rows |
Estimates the number of rows returned by the function. This is only allowed when the function is declared to return a set. |
Its value is a positive number. The default value is 1000. |
|
configuration_parameter |
Specifies the parameter value configured for the function. |
|
|
plsql_body |
Indicates the PL/SQL stored procedure body. When the function is creating users, the log will record unencrypted passwords. You are not advised to do it. |
- |
Example: Calculate the Sum of Two Integers Using an SQL Function
Syntax:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION func_add_sql( integer, --The first integer parameter is not named and is referenced by the location parameter $1. integer --The second integer parameter is not named and is referenced by the location parameter $2. ) RETURNS integer --The return type of the function is integer. AS 'select $1 + $2;' --The function body adds the location parameters $1 and $2. LANGUAGE SQL --The SQL language is used to implement this function. IMMUTABLE --The function type is IMMUTABLE, which indicates that the same result is returned for the same input. RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT; --It is same as STRICT. If any parameter is NULL, the function returns NULL. |
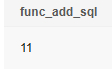
Return the sum of the two input parameters.
1
|
SELECT func_add_sql(8,3); |
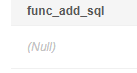
Return null because the input parameter is null.
1
|
SELECT func_add_sql(Null,3); |
Example: Increment an Integer, in PL/pgSQL
Syntax:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION func_increment_plsql( i integer -The input parameter is of the integer type. ) RETURNS integer -The return value of the function is of the integer type. AS $$ BEGIN --The function body begins. RETURN i + 1; --The return result is the sum of 1 and the input parameter. END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; --The function is written in PL/pgSQL. |
Return the integer auto-increment result.
1
|
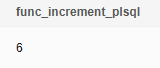
SELECT func_increment_plsql(5); |
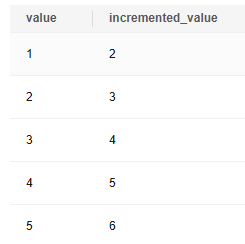
The input parameter is specified by the first column of the numbers table. After the function is used for calculation, the calculation result is returned to the second column.
1 2 3 4 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS numbers; CREATE TABLE numbers (value integer); INSERT INTO numbers VALUES (1), (2), (3), (4), (5); SELECT value, func_increment_plsql(value) AS incremented_value FROM numbers ORDER BY 1; |
Example: Return a Record in PL/pgSQL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION compute( i int, ---The input parameter is of the integer type. out result_1 bigint, --The output result is 1 and the data type is large integer. out result_2 bigint --The output result is 2 and the data type is large integer. ) RETURNS SETOF RECORD --A record containing more than one output parameter is returned. AS $$ BEGIN result_1 = i + 1; -- It is used to calculate the first result value. The input value is increased by 1. result_2 = i * 10; -- It is used to calculate the second result value. The input value is multiplied by 10. RETURN next; --It returns the current calculation result and then continue to execution (multiple rows can be returned). END; $$LANGUAGE plpgsql; --The function is written in PL/pgSQL. |
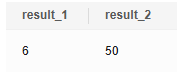
Return the following information when the function is called once.
1
|
SELECT * FROM compute(5); |
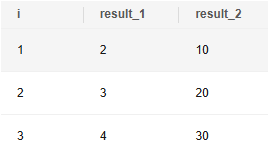
Generate a sequence of 1, 2, and 3, and call the compute function for each value in the sequence.
1 2 3 |
SELECT i, (compute(i)).* --Call the compute function first, and then expand all columns returned by the function. FROM generate_series(1, 3) --Generate a temporary sequence containing 1, 2, and 3 to assign values to i. AS t(i); --Assign the result to temporary table t, in which i is the column name. |
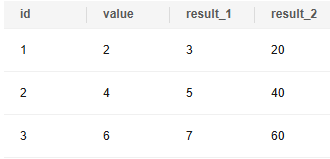
The data in table test_data is used. The value column in the table is used as the input parameter of the compute function. The calculation result is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_data; CREATE TABLE test_data (id serial, value int); INSERT INTO test_data (value) VALUES (2), (4), (6); SELECT id, value, (compute(value)).* FROM test_data ORDER BY 1; |
Example: Create an SQL Function that Returns Multiple Output Parameters
Syntax:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
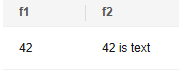
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION func_dup_sql( in int, --The input parameter is of the integer type. out f1 int, --The first output parameter is of the integer type. out f2 text) --The second output parameter is of the text type. AS $$ SELECT $1, CAST($1 AS text) || 's text' -- Function body. The query returns two columns. The first column is the input parameter $1, and the second column is the parameter converted to text and concatenated with is text. $$ LANGUAGE SQL; |
Execute the function.
1
|
SELECT * FROM func_dup_sql(42); |
Example: Create an Overloaded Function with the PACKAGE Attribute
Define two overloaded functions named package_func_overload in package. The two functions have different meanings depending on the parameter type.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION package_func_overload( col int, --The first input parameter is of the integer type. col2 int --The second input parameter is of the integer type. ) RETURN integer PACKAGE AS DECLARE col_type text; -- Declare a local variable. BEGIN col := 122; --Set the first parameter to 122. dbms_output.put_line('two int parameters ' || col2); RETURN 0; --Return the integer 0. END; / CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION package_func_overload( col int, col2 smallint ) RETURN integer PACKAGE AS DECLARE col_type text; BEGIN col := 122; dbms_output.put_line('two smallint parameters ' || col2); RETURN 0; END; / |
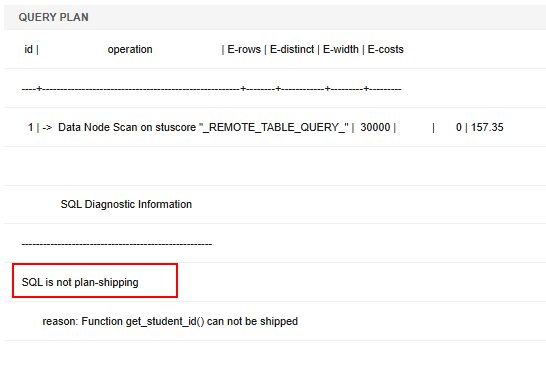
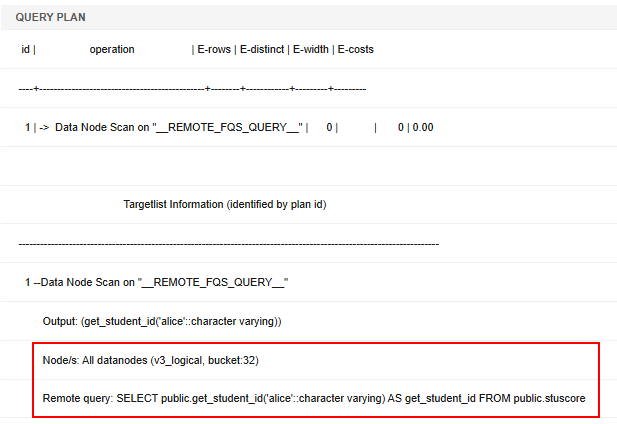
Function Pushdown Logic and Example
Pushdown logic for functions has two main aspects:
- The system checks if the entire function can be pushed down based on its SHIPPABLE attribute.
- If the full function is not pushed down, the optimizer automatically determines which individual SQL statements within the function can be executed separately.
Helpful Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.