Configuring the Target Server
Scenarios
Before starting the migration, you need to configure the target server, which will receive data from the source server. You can clone the target server for service testing and launch it once you've confirmed that your services can run properly.
Prerequisites
You can configure the target server when:
- The source server is Connected to SMS.
- The migration task is in the Migration Feasibility Check stage.
- The migration task is in the Pending target configuration status.
Procedure
- Sign in to the SMS console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Servers.
Figure 1 Server list
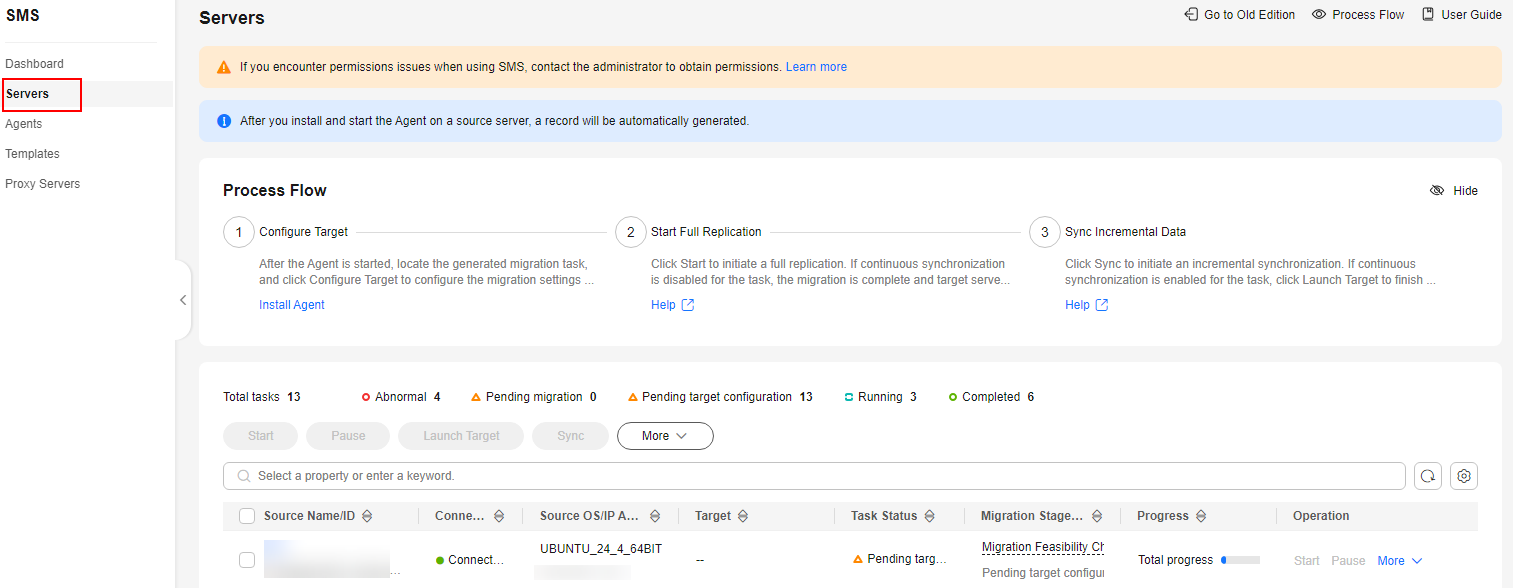
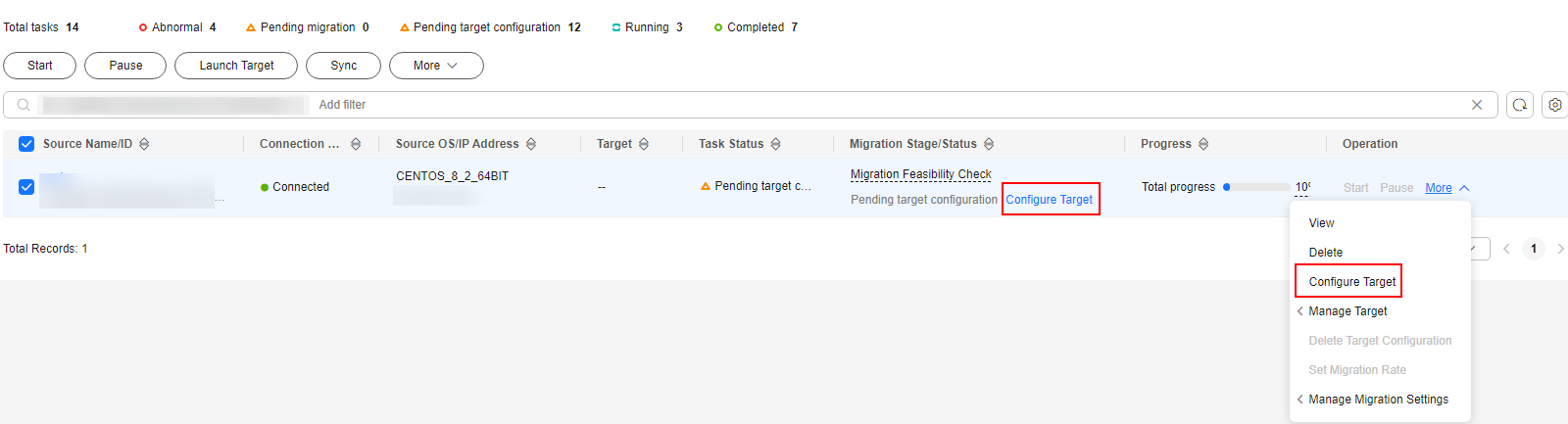
- In the server list, locate the source server and click Configure Target in the Migration Stage/Status column.
You can also choose More > Configure Target in the Operation column.

If you do not find the record for your source server, check that the account you are currently using is the migration account.
- On the Configure Basic Settings page, configure parameters by referring to Table 1.
Table 1 Basic parameter settings Area
Parameter
Option
Description
Migration Template
Migration Template
-
You can use the default migration template provided by the system. You can also create a migration template. After you choose a migration template, the system will populate Network Type, Migration Rate Limit, Migration Method, Enable Continuous Synchronization, Resize Disks and Partitions, Region, and Project based on the template.
Network Settings
Network Type
Public
An EIP must be bound to the target server.
Public is the default value of Network Type.
Private
A Direct Connect connection, VPN connection, VPC peering connection, VPC subnet, or Cloud Connect connection must be provisioned. The private IP address of the target server will be used for migration.
IP Version
IPv4
IPv4 can be used for data migration.
IPv6
On a dual-stack network, IPv6 can be used for migration. For details about the preparations and precautions for migration over IPv6, see Migrating Servers over an IPv6 Network.
Migration Rate Limit
-
You can limit the migration rate based on the source bandwidth and service requirements.
If you do not want to limit the migration rate, set this parameter to 0.
Traffic limiting is unavailable if:
- The migration uses an IPv6 network.
- Traffic Control (TC) is missing from the source server.
Overrate Threshold (%)
-
You can regulate how much the migration rate can exceed the configured limit. If the migration rate exceeds the threshold for multiple consecutive times, the migration task is automatically paused.
For example, if the migration rate limit is set to 10 Mbit/s and the overrate threshold is set to 10%, the task is automatically paused when the migration rate exceeds 11 Mbit/s (110% of the limit) multiple times consecutively.
CAUTION:This option is only available for Linux migration. It will not be available or applied if:
- The migration uses an IPv6 network.
- TC is missing from the source server.
- The installed SMS-Agent version is earlier than 24.9.0.
Migration Settings (Optional)
Migration Method
Linux block-level
Migration and synchronization are performed by block. This method is efficient, but the compatibility is poor.
Linux file-level
Migration and synchronization are performed by file. This method is inefficient, but the compatibility is excellent.
Windows block-level
Migration and synchronization are performed by block. This method is very efficient and is the only migration method for Windows servers.
Enable Continuous Synchronization
No
After the full replication is complete, SMS will automatically launch the target server without synchronizing incremental data. To synchronize incremental data, you will need to click Sync in the Operation column.
Yes
After the full replication is complete, the migration will enter the continuous synchronization stage. During this stage, incremental data will be periodically synchronized from the source server to the target server, and you will be unable to use the target server since it has not been launched yet. To finish this stage, you will need to click Launch Target in the Operation column.
Resize Disks and Partitions
Disable
The disk and partition settings from the source server will be retained on the target server.
Enable
You can resize the disks and partitions for the target server. For details, see Resizing Disks and Partitions.
Start Target Upon Launch
No
The target server will be stopped after the migration is complete.
Yes
The target server will be started after the migration is complete.
Measure Network Performance
No
Network performance will not be measured.
Yes
Before the full migration starts, the system will measure the packet loss rate, network jitter, network latency, bandwidth, memory usage, and CPU usage for the source server. For details, see How Do I Measure the Network Performance Before the Migration?
Enable Concurrency
No
By default, one process is used for migration and synchronization.
Yes
You can specify the maximum number of processes the Agent can start concurrently for migration and synchronization tasks, respectively. Enabling concurrency is only available for Linux file-level migrations. For more information, see How Do I Set the Number of Concurrent Processes for Linux File-Level Migrations?
Transit IP Address
-
For a migration over a private line, you can configure the transit IP address.
Resource Limits (Optional)
CPU Limit
-
These options are only available for Linux migrations. For details, see How Do I Limit Resource Allocation for the Agent in a Linux Migration?
Memory Limit
Disk Throughput Limit
Verify Data Consistency
If this option is enabled, the system will automatically verify data consistency after the full replication is complete. This is a quick verification, and only the file size and last modification time will be verified. You can modify the verification policy when you launch an incremental synchronization.
- Enable Hash Verification: If this option is enabled, the system will generate and compare hash values for each file to be verified. Hash verification is recommended when individual files are large and important. Enabling this option will increase CPU and disk I/O overheads for the source server and extend the verification time.
CAUTION:
- Hash values cannot be calculated for files in use, so these files will be skipped during the verification.
- Enabling this option requires you to specify the verification scope, and only files in the specified scope will be verified.
- Verification Scope
- Under Exclude paths, enter the paths you want to exclude from the verification. A maximum of 30 paths can be entered. Use commas (,) to separate the paths. For example, /root/data,/var. Leaving it empty will initiate a full verification.
- Under Include paths, enter the paths you want to verify.
NOTICE:- If the entered paths are incorrect or empty, 0 will be displayed for them in the verification results.
- The more data you need to verify, the longer the verification will take. It is wise to narrow the verification scope to only key paths.
- The following paths will be excluded from consistency verification by default:
- Linux: /bin, /boot, /dev, /home, /etc, /lib, /media, /proc, /sbin, /selinux, /sys, /usr, /var, /run, and /tmp
- Windows: top-level directories of partitions, for example, C:\ and D:\
If you need to include any of the preceding excluded paths in the verification, refer to .
- Click Next: Configure Target in the lower right corner.
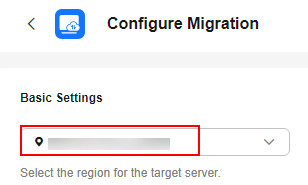
- In the Basic Settings area, select the region you are migrating to.
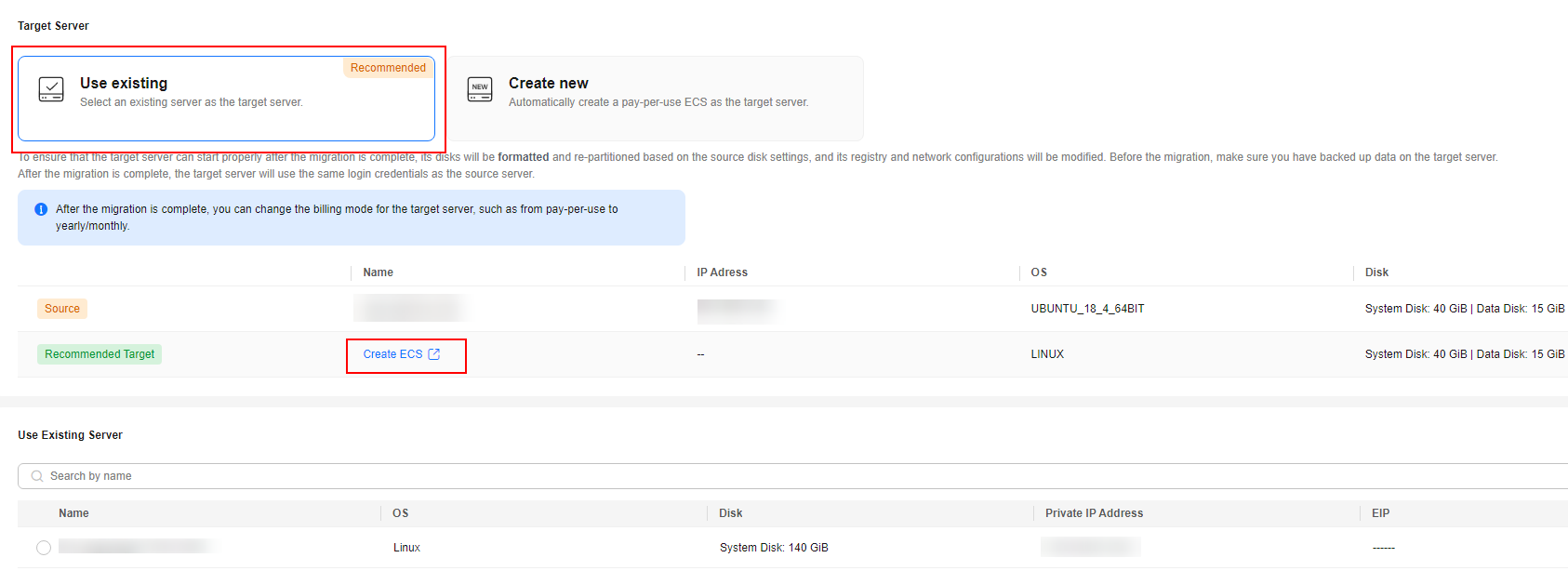
- In the Target Server area, choose whether to use an existing cloud server or create a new one as the target server. For details about the requirements on target servers, see .
- Use existing
In the list of existing servers, select one that meets the specifications requirements displayed in the Recommended Target row. If no existing server meets the requirements, click Create ECS and purchase an ECS with the required specifications. For details, see Purchasing an ECS.
You can select a pay-per-use or yearly/monthly ECS.
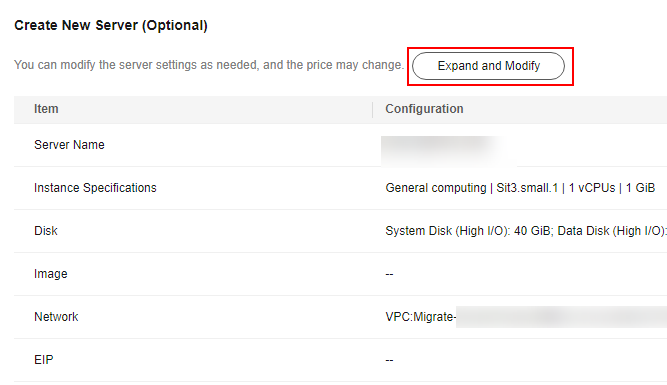
- Create new
The system automatically presets the name, AZ, specifications, disk specifications, EIP, VPC, subnet, and security group for the target server. You can also click Expand and Modify to manually modify the server settings.
- If you select Recommended for Server Template, the system will automatically create a VPC, subnet, and security group and select an AZ and disk type for the target server. You can also manually adjust the settings recommended by the system.
- If Create new is selected for VPC, SMS automatically creates a VPC for the target server based on the following rules:
If the source server's IP address is 192.168.X.X, SMS creates a VPC and a subnet that both belong to network range 192.168.0.0/16.
If the source IP address is 172.16.X.X, SMS creates a VPC and a subnet that both belong to network range 172.16.0.0/12.
If the source server's IP address is 10.X.X, SMS creates a VPC and a subnet that both belong to network range 10.0.0.0/8.
- If Create new is selected for Security Group, the system automatically creates a security group for the target server and allows traffic to the target server over certain ports:
Windows: ports 8899, 8900, and 22
Linux: port 22 for file-level migration
Linux: ports 8900 and 22 for block-level migration
- If Create new is selected for VPC, SMS automatically creates a VPC for the target server based on the following rules:
- You can also can choose your own server template.Then the VPC, subnet, security group, AZ, and disk settings will be preconfigured based on that template. You have the flexibility to adjust these preset settings as needed. To learn how to create a server template, see Creating a Server Template.
- Configure advanced disk settings.
- Data disks must be either VBD or SCSI. VBD is the default device type for data disks. For details about disk device types, see Device Types and Usage Instructions.
- Data disks can be created as shared disks. For details about shared disks, see Shared EVS Disks and Usage Instructions.
- For target servers newly created by the system, system and data disks can be encrypted. For details about shared disks, see Shared EVS Disks and Usage Instructions. To enable disk encryption, you need to create an agency to authorize EVS to access KMS. After the authorization is successful, configure the following parameters:
- Select an existing key
Select a key from the drop-down list. You can select one of the following keys:
Default keys: After the KMS access permissions have been granted to EVS, the system automatically creates a default key and names it evs/default.
Custom keys: You can choose an existing key or create a new one. For details about how to create a key, see Creating a Key.
- Enter a key ID
Enter the ID of a key shared from another user. Ensure that the key is in the target region. For details, see Creating a Grant.

- Before the migration is complete, do not disable or delete the key used, or the migration will fail.
- The encryption attribute of a disk cannot be modified after the disk is created.
- Keys can be shared with accounts, not users.
- Select an existing key
- If you select Recommended for Server Template, the system will automatically create a VPC, subnet, and security group and select an AZ and disk type for the target server. You can also manually adjust the settings recommended by the system.
- Use existing
- Click Next: Confirm in the lower right corner.
Figure 2 The configuration confirmation page
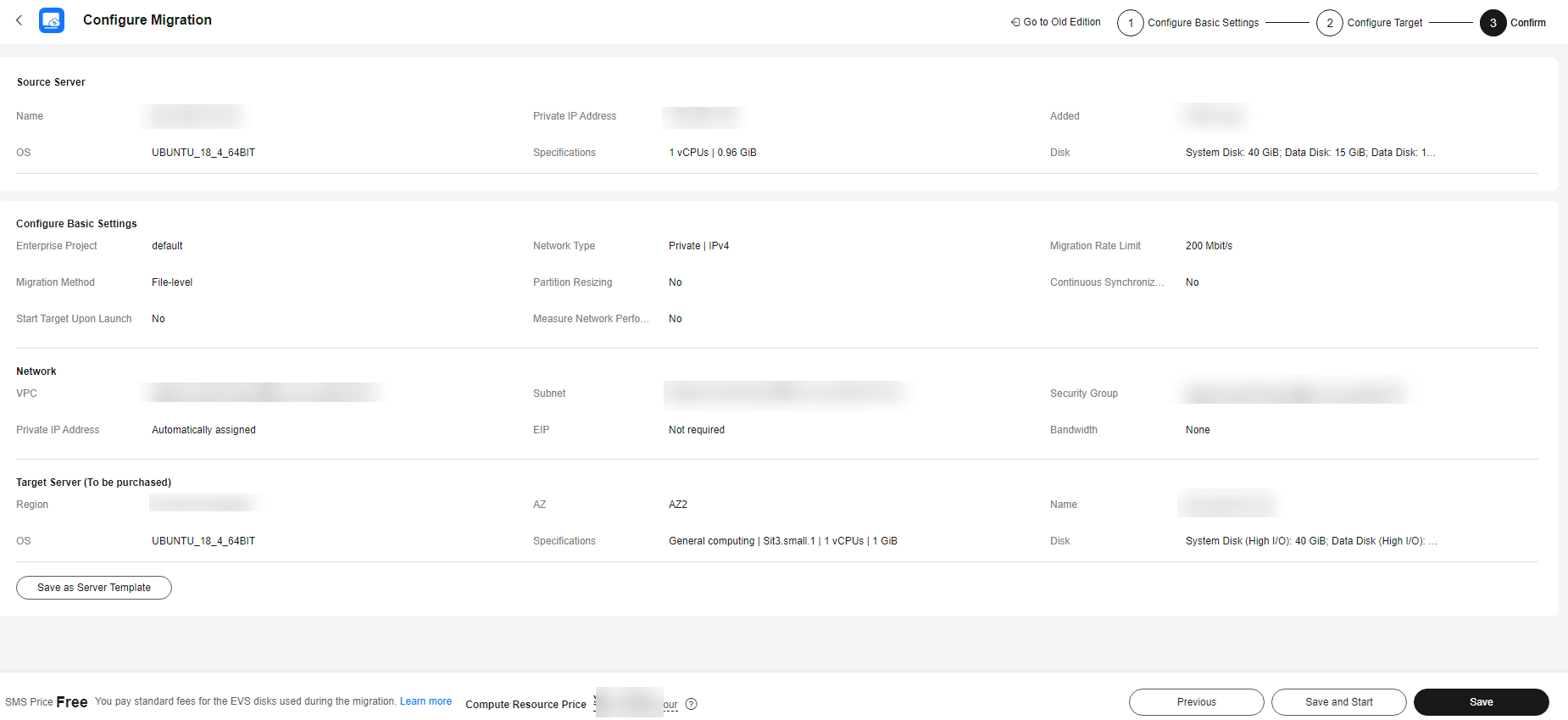
- (Optional) Click Save as Server Template. In the displayed Create Server Template dialog box, enter a template name and click OK to save the target server settings as a template.
Save as Server Template is available only when you select Create new for Server.
Figure 3 Create Server Template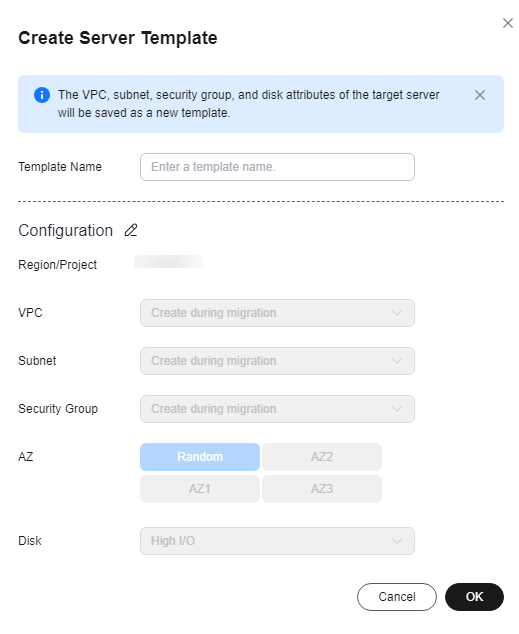
- Confirm the configuration and click Save. In the displayed dialog box, read the migration conditions and click OK.
If you want to start the migration immediately, click Save and Start. In the displayed dialog box, read the migration conditions and click OK.Figure 4 Saving the configuration
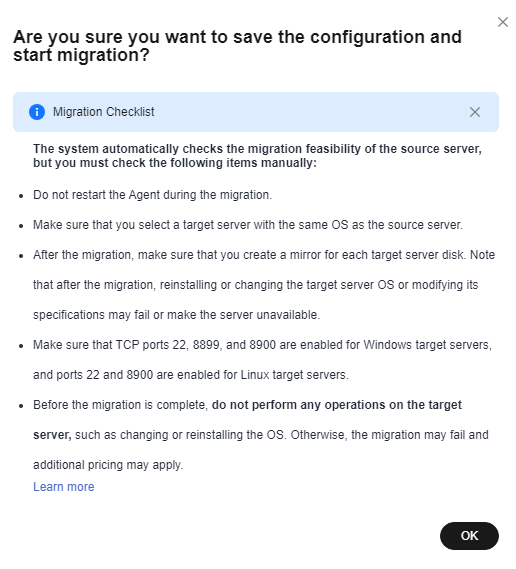 Figure 5 Saving the configuration and starting the migration
Figure 5 Saving the configuration and starting the migration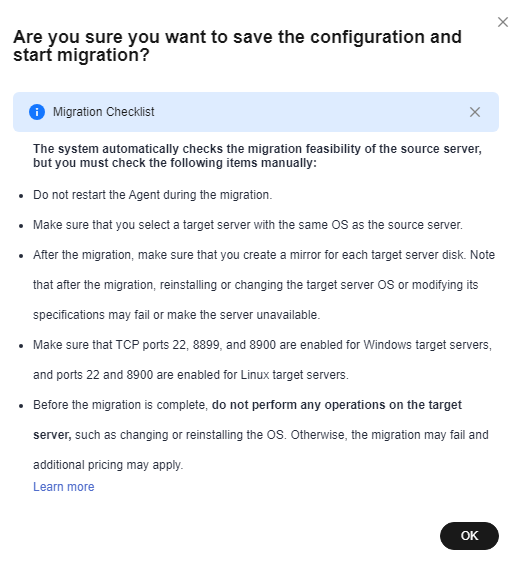
If Target Configuration and Ready show up in the Migration Stage/Status column, the target server has been configured.
Resizing Disks and Partitions
You can choose whether to migrate source partitions and then resize the paired target partitions as needed.
Resizing Disks and Partitions on Windows
- On the Configure Migration page, on Configure Basic Settings tab, expand Migration Settings (Optional), enable Resize Disks and Partitions, and click Resize Disks and Partitions.
- Click Resize Disk and adjust the size of each disk as required. As shown in Resizing disks and partitions (Windows), you can view the resized disks at the bottom of the window.
- If the total partition size after resizing is larger than the disk size, you need to expand the disk capacity to fit the partition size.
- If the total partition size after resizing is much smaller than the disk size, you can downsize the disk.
- Click Next: Confirm. Confirm the configurations and click OK.

After you click OK, disk and partition resizing cannot be disabled in this task. If you want to restore the original disk and partition settings, locate the source server and choose More > Delete in the Operation column. Then restart the Agent on the source server, and configure the target server again.
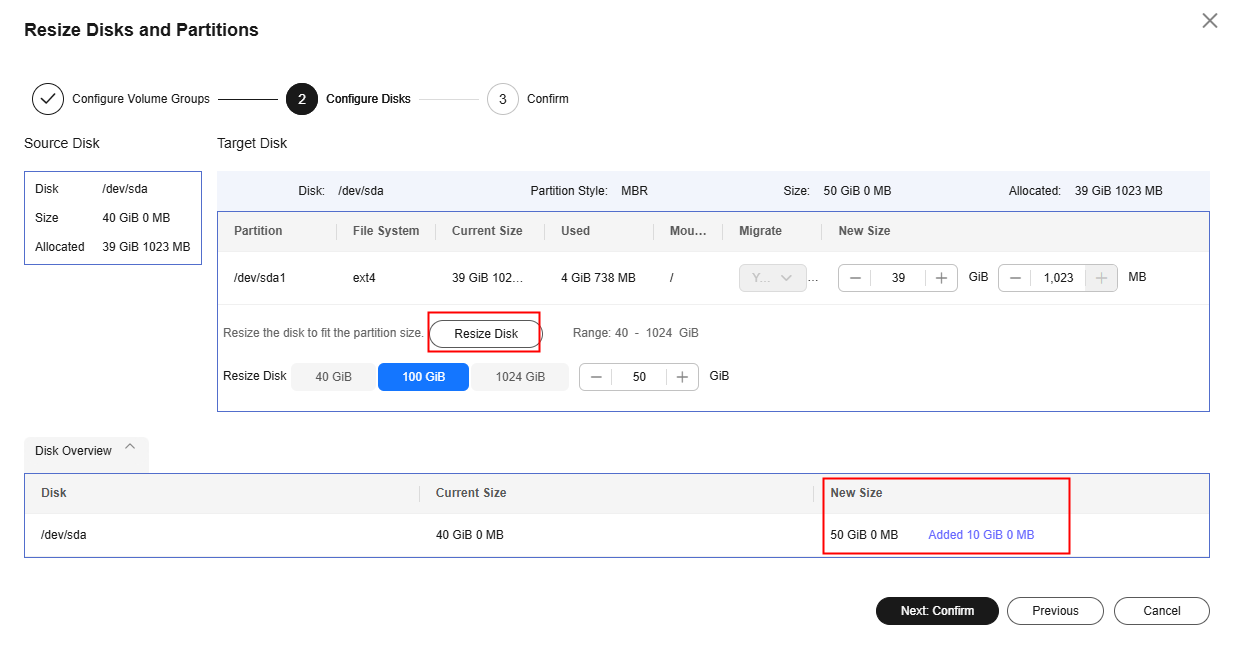
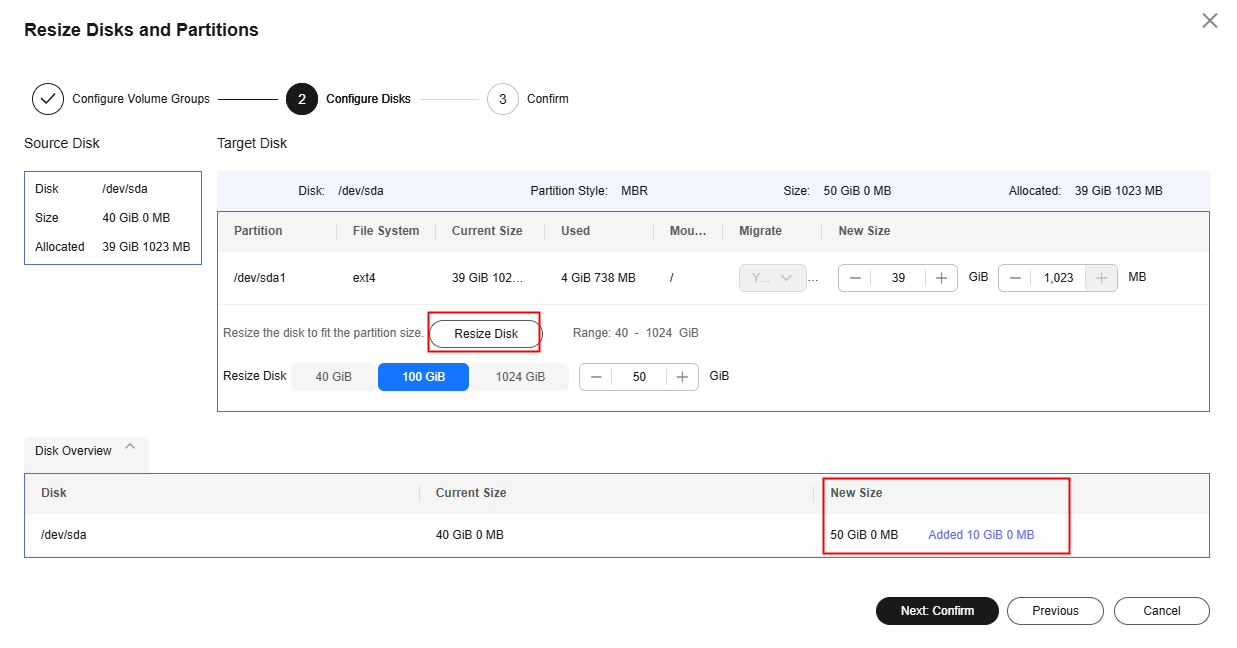
Resizing Disks and Partitions on Linux
- On the Configure Migration page, on Configure Basic Settings page, expand Migration Settings (Optional), enable Resize Disks and Partitions, and click Resize Disks and Partitions.
- Configure volume groups.
- If the source server uses LVM, you can resize logical and physical volumes.
- If the source server does not use LVM, skip this step.
- Click Next: Configure Disks.
- Click Resize Disk and adjust the size of each disk as required. As shown in Resizing disks and partitions (Linux), you can view the resized disks at the bottom of the window.
- If the total partition size after resizing is larger than the disk size, you need to expand the disk capacity to fit the partition size.
- If the total partition size after resizing is much smaller than the disk size, you can downsize the disk.
- Click Next: Confirm. Confirm the configurations and click OK.

After you click OK, disk and partition resizing cannot be disabled in this task. If you want to restore the original disk and partition settings, locate the source server and choose More > Delete in the Operation column. Then restart the Agent on the source server, and configure the target server again.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.