CFW allows you to query logs generated within the last seven days. The following types of logs are available:
- Attack event logs: The events detected by attack defense functions, such as IPS, are recorded.
- Access control logs: All traffic that matches the access control policy are recorded.
- Traffic logs: All traffic passing through the firewall is recorded.
One or multiple types of logs can be recorded in LTS. You can view log data in the past 1 to 365 days. For details, see Log Management.
Constraints
- Logs can be stored for up to seven days.
- For each type of logs, up to 1,000 records can be viewed, and up to 100,000 records can be exported.
- Traffic logs are collected based on sessions. Data about a connection is not reported until connection is terminated.
- On the log query page, the geographical locations (source countries/regions) of IPv6 addresses cannot be displayed.
Checking Logs
Perform the following operations to view logs.
Attack Event Logs
- Log in to the CFW console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
- (Optional) Switch to another firewall instance. Select a firewall from the drop-down list in the upper left corner of the page.
- In the navigation pane, choose . On the Attack Event Logs tab, check the details about attack events in the past week.
Figure 1 Attack event logs
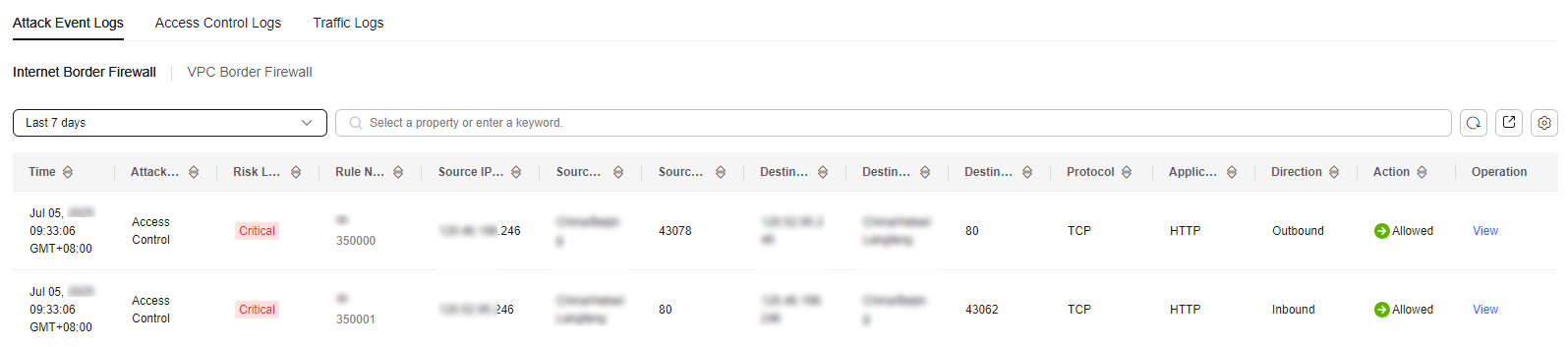
Table 1 Attack event log parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Time |
Time when an attack occurred. |
|
Attack Type |
Type of the attack event, including IMAP, DNS, FTP, HTTP, POP3, TCP, and UDP. |
|
Risk Level |
It can be Critical, High, Medium, or Low. |
|
Rule name/Rule ID |
Name and ID of the matched rule in the library. |
|
Source IP Address |
Source IP address of an attack event.
If the source IP address is a WAF back-to-source IP address, Source IP Address displays the WAF back-to-source IP address and the real IP address. The first IP address corresponding to X-Forwarded-For is displayed in RealIP, that is, the real IP address of the client. |
|
Source Country/Region |
Geographical location of the attack source IP address. |
|
Source Port |
Source port of an attack. |
|
Destination IP Address |
Attacked IP address. |
|
Destination Country/Region |
Geographical location of the attack target IP address. |
|
Destination Port |
Destination port of an attack. |
|
Protocol |
Protocol type of an attack. |
|
Application |
Application type of an attack. |
|
Direction |
It can be outbound or inbound. |
|
Action |
Action of the firewall. It can be Allow, Block, Block IP, or Discard. |
|
Operation |
You can click View to view the basic information and attack payload of an event. |
Access Control Logs
- Log in to the CFW console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
- (Optional) Switch to another firewall instance. Select a firewall from the drop-down list in the upper left corner of the page.
- In the navigation pane, choose . On the log query page, click the Access Control Logs tab to view details about access control traffic in the past week.
For details about how to modify the action taken on an IP address, see Configuring Protection Rules to Block or Allow Internet Border Traffic or Adding Blacklist or Whitelist Items to Block or Allow Traffic.
Figure 2 Access control logs
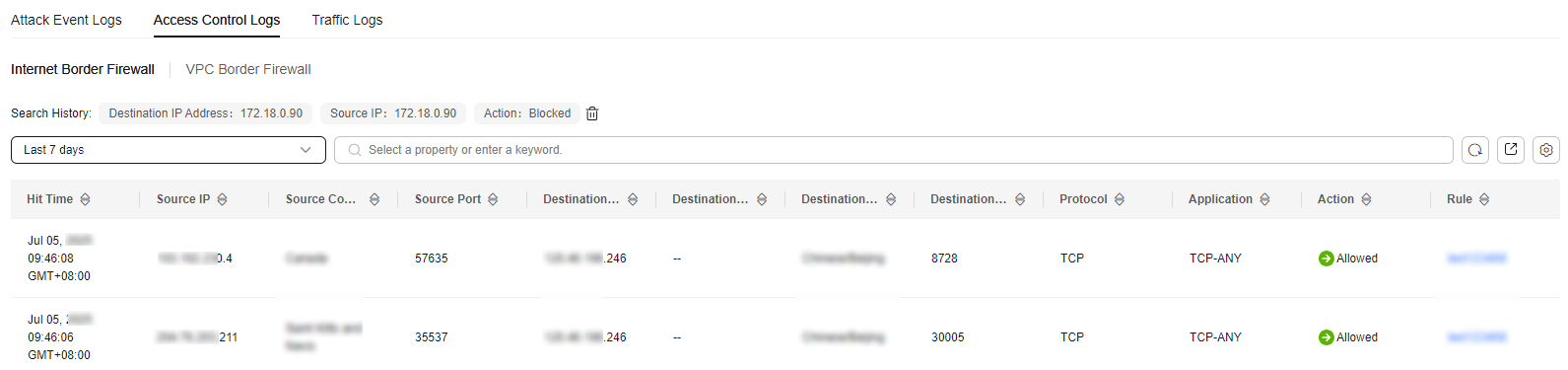
Table 2 Access control log parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Hit Time |
Time of an access. |
|
Source IP Address |
Source IP address of the access. |
|
Source Country/Region |
Geographical location of the source IP address. |
|
Source Port |
Source port for access control. It can be a single port or consecutive port groups (example: 80-443). |
|
Destination IP Address |
Destination IP address. |
|
Destination Host |
Destination domain name |
|
Destination Country/Region |
Geographical location of the destination IP address. |
|
Destination Port |
Destination port for access control. It can be a single port or consecutive port groups (example: 80-443). |
|
Protocol |
Protocol type for access control. |
|
Application |
Application type of the access traffic. |
|
Action |
Action taken on an event. It can be Observe, Block, or Allow. |
|
Rule |
Type of an access control rule. It can be a blacklist or whitelist. |
Traffic Logs
- Log in to the CFW console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
- (Optional) Switch to another firewall instance. Select a firewall from the drop-down list in the upper left corner of the page.
- In the navigation pane, choose . Click the Traffic Log tab to view the number of traffic bytes and packets in the past week.
Figure 3 Traffic logs
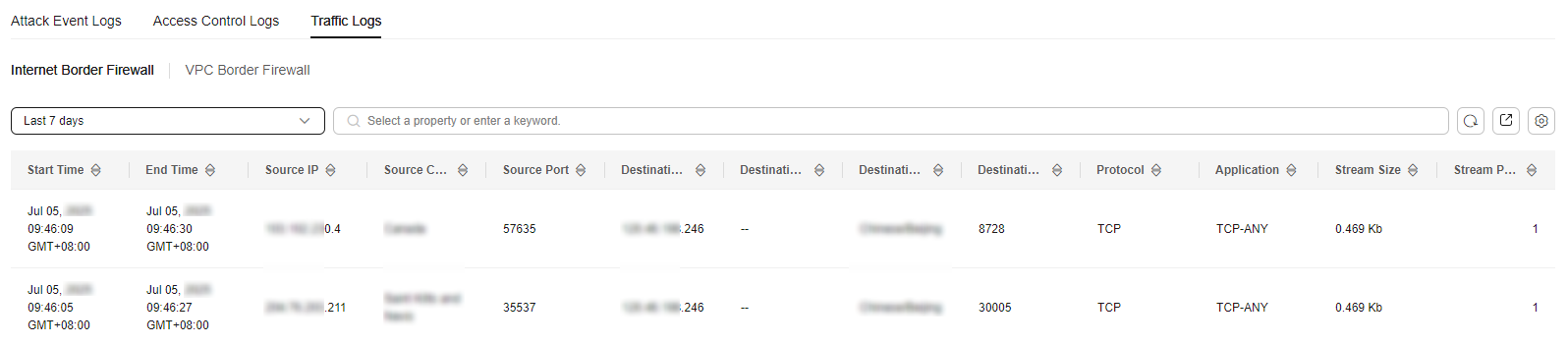
Table 3 Traffic log parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Start Time |
Time when traffic protection started. |
|
End Time |
Time when traffic protection ended. |
|
Source IP Address |
Source IP address of the traffic |
|
Source Country/Region |
Geographical location of the source IP address. |
|
Source Port |
Source port of the traffic. |
|
Destination IP Address |
Destination IP address. |
|
Destination Host |
Destination domain name |
|
Destination Country/Region |
Geographical location of the destination IP address. |
|
Destination Port |
Destination port of the traffic. |
|
Protocol |
Protocol type of the traffic. |
|
Application |
Application type of the access traffic. |
|
Stream Size |
Total number of bytes of protected traffic. |
|
Stream Packets |
Total number of protected packets. |
References
- Exporting logs: Click
 in the upper right corner of the log list to export the logs in the list.
in the upper right corner of the log list to export the logs in the list.
- CFW provides the network packet capture function. You can capture traffic by IP address, port number, or protocol type to quickly locate network faults and identify security risks. For details, see Network Packet Capture.
Follow-up Operations
- If improper blocking is recorded in access control logs, your normal workloads may have been blocked by IPS. In this case, check the policy configuration. For details about how to modify protection rules, see Managing Protection Rules. For details about how to modify the blacklist and whitelist, see Editing the Blacklist or Whitelist.
- If improper blocking is recorded in attack event logs, your normal workloads may be blocked by IPS.
- If the traffic from an IP address is improperly blocked, add it to the whitelist.
- If the traffic from multiple IP addresses is blocked, check logs to see whether it is blocked by a single rule or multiple rules.
 in the upper right corner of the log list to export the logs in the list.
in the upper right corner of the log list to export the logs in the list.









