Configuring HTTP/HTTPS for a LoadBalancer Service
By default, a Layer 4 TCP/UDP listener is created for a LoadBalancer Service. You can also configure HTTP/HTTPS listeners for more refined and diverse task scheduling and to ensure secure access to applications from external networks.
Notes and Constraints
- Only clusters of v1.19.16 or later support HTTP or HTTPS.
Table 1 Scenarios where a load balancer supports HTTP or HTTPS ELB Type
Application
Whether to Support HTTP or HTTPS
Description
Dedicated load balancer
Interconnecting with an existing load balancer
Supported
- For versions earlier than v1.19.16-r50, v1.21.11-r10, v1.23.9-r10, v1.25.4-r10, or v1.27.1-r10, load balancer specifications must support both layer-4 and layer-7 routing.
- For v1.19.16-r50, v1.21.11-r10, v1.23.9-r10, v1.25.4-r10, v1.27.1-r10, and later versions, load balancer specifications must support layer-7 routing.
Automatically creating a load balancer
Supported
- For versions earlier than v1.19.16-r50, v1.21.11-r10, v1.23.9-r10, v1.25.4-r10, or v1.27.1-r10, load balancer specifications must support both layer-4 and layer-7 routing.
- For v1.19.16-r50, v1.21.11-r10, v1.23.9-r10, v1.25.4-r10, v1.27.1-r10, and later versions, load balancer specifications must support layer-7 routing.
- Do not connect an ingress and an HTTP/HTTPS Service to the same listener of the same load balancer. Otherwise, a port conflict occurs.
Step 1: Deploy a Sample Application
This section uses a Nginx Deployment as an example.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Workloads. In the upper right corner, click Create Workload.
- In the Basic Info area, enter the workload name. In this example, the workload name is nginx. Retain the default settings for other parameters.
- In Container Information under Container Settings, specify the image name and tag. Retain the default settings for other parameters.
Parameter
Example
Image Name
Click Select Image. In the displayed dialog box, click Open Source Images under SWR Shared Edition, search for nginx, select it, and click OK.
Image Tag
Select the latest image tag.
- Retain the default settings for other parameters and click Create Workload.
Step 2: Create a LoadBalancer Service and Configure HTTP or HTTPS
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Services & Ingresses. In the upper right corner, click Create Service.
- Configure Service parameters. In this example, only mandatory parameters required for using HTTP/HTTPS are listed. For details about how to configure other parameters, see Using the CCE Console.
- Service Name: Specify a Service name, which can be the same as the workload name.
- Service Type: Select LoadBalancer.
- Selector: Add a label and click Confirm. The Service will use this label to select pods. You can also click Reference Workload Label to use the label of an existing workload. In the dialog box that is displayed, select a workload and click OK.
- Load Balancer: Select a load balancer type and creation mode.
- A load balancer can be dedicated or shared. To enable HTTP/HTTPS on the listener port of a dedicated load balancer, the type of the load balancer must be Application (HTTP/HTTPS) or Network (TCP/UDP) & Application (HTTP/HTTPS).
- This section uses an existing load balancer as an example. For details about the parameters for automatically creating a load balancer, see Table 1.
- Ports
- Protocol: Select TCP. If you select UDP, HTTP and HTTPS will be unavailable.
- Service Port: the port used by the Service. The port number ranges from 1 to 65535.
- Container Port: the port that the workload listens on. For example, Nginx uses port 80 by default.
- Frontend Protocol: specifies whether to enable HTTP/HTTPS on the listener port. For a dedicated load balancer, to use HTTP/HTTPS, the type of the load balancer must be Application (HTTP/HTTPS).
- Listener
- SSL Authentication: Select this option if HTTPS is enabled on the listener port. This parameter is available only in clusters of v1.23.14-r0, v1.25.9-r0, v1.27.6-r0, v1.28.4-r0, or later versions.
- One-way authentication: Only the backend server is authenticated. If you also need to authenticate the identity of the client, select two-way authentication.
- Two-way authentication: Both the clients and the load balancer authenticate each other. This ensures only authenticated clients can access the load balancer. No additional backend server configuration is required if you select this option.
- CA Certificate: If SSL Authentication is set to Two-way authentication, add a CA certificate to authenticate the client. A CA certificate is issued by a Certificate Authority (CA) and is used to verify the issuer of the client's certificate. If HTTPS mutual authentication is enabled, HTTPS connections can be established only if the client provides a certificate issued by a specific CA.
- Server Certificate: If HTTPS is enabled on the listener port, you must select a server certificate.
- SNI: If HTTPS is enabled on the listener port, you must determine whether to add an SNI certificate. Before adding an SNI certificate, ensure the certificate contains a domain name.
- Security Policy: If HTTPS is enabled on the listener port, you can select a security policy. This parameter is available only in clusters of v1.23.14-r0, v1.25.9-r0, v1.27.6-r0, v1.28.4-r0, or later versions.
- Backend Protocol: If HTTPS is enabled on the listener port, HTTP or HTTPS can be used to access the backend server. The default value is HTTP. This parameter is available only in clusters of v1.23.14-r0, v1.25.9-r0, v1.27.6-r0, v1.28.4-r0, or later versions.
If multiple HTTPS Services are released, all listeners will use the same certificate configuration.
- SSL Authentication: Select this option if HTTPS is enabled on the listener port. This parameter is available only in clusters of v1.23.14-r0, v1.25.9-r0, v1.27.6-r0, v1.28.4-r0, or later versions.
- Click Create.
If a Service uses the HTTP or HTTPS protocol, it is important to take note of the following configuration requirements:
- Different ELB types and cluster versions have different requirements on flavors. For details, see Table 1.
- The two ports in spec.ports must correspond to those in kubernetes.io/elb.protocol-port. In this example, ports 443 and 80 are enabled with HTTPS and HTTP, respectively.
The following uses an automatically created dedicated load balancer as an example.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
# Specify the Layer 4 and Layer 7 flavors in the parameters for automatically creating a load balancer.
kubernetes.io/elb.autocreate: '
{
"type": "public",
"bandwidth_name": "cce-bandwidth-1634816602057",
"bandwidth_chargemode": "bandwidth",
"bandwidth_size": 5,
"bandwidth_sharetype": "PER",
"eip_type": "5_bgp",
"available_zone": [
""
],
"l7_flavor_name": "L7_flavor.elb.s2.small",
"l4_flavor_name": "L4_flavor.elb.s1.medium"
}'
kubernetes.io/elb.class: performance # A dedicated load balancer
kubernetes.io/elb.protocol-port: "https:443,http:80" # HTTP/HTTPS and port number, which must be the same as the port numbers in spec.ports
kubernetes.io/elb.cert-id: "17e3b4f4bc40471c86741dc3aa211379" # The certificate ID of the LoadBalancer Service
labels:
app: nginx
name: test
name: test
namespace: default
spec:
ports:
- name: cce-service-0
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
- name: cce-service-1
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
version: v1
sessionAffinity: None
type: LoadBalancer
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
kubernetes.io/elb.protocol-port |
String |
If a Service is TLS/HTTP/HTTPS-compliant, configure the protocol and port number in the format of "protocol:port". where,
In this example, ports 443 and 80 are enabled with HTTPS and HTTP, respectively. Therefore, the parameter value is https:443,http:80. |
|
kubernetes.io/elb.cert-id |
String |
ID of an ELB certificate, which is used as the TLS/HTTPS server certificate. How to obtain: Log in to the ELB console and choose Certificates. In the load balancer list, copy the ID under the target certificate name. |
Step 3: Access the Workload
- After the Service is created, copy the load balancer's EIP.
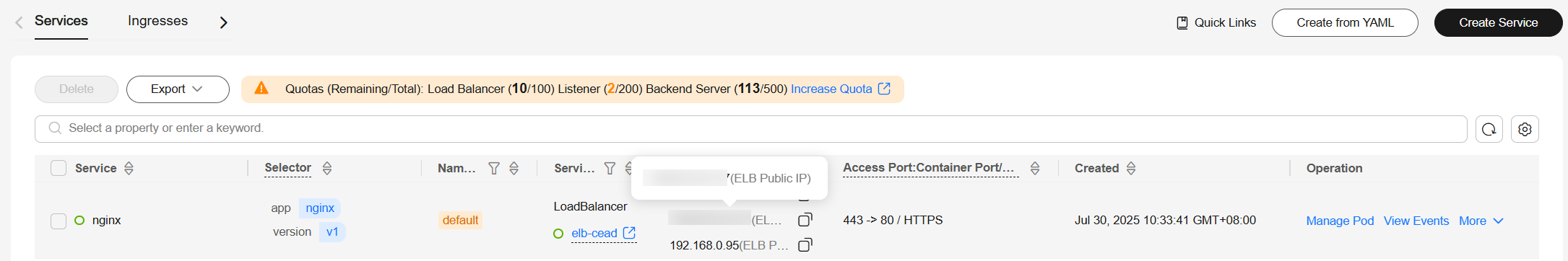
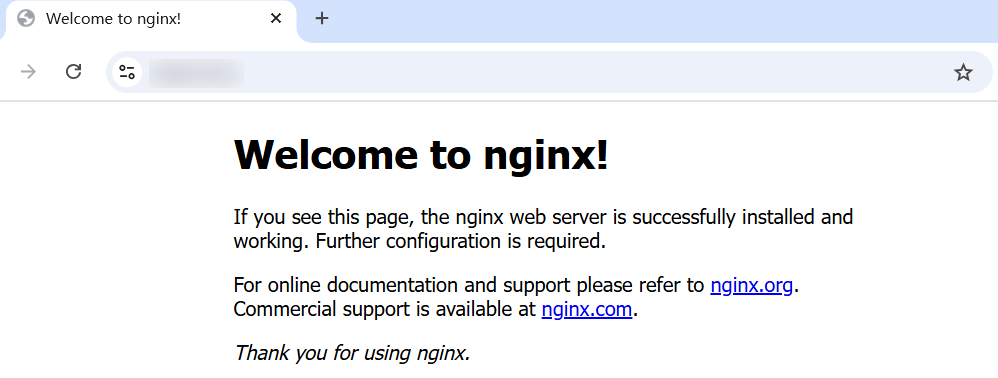
- Access the address via HTTPS in the browser.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






