Using the Windows gsql Client to Connect to a Cluster
This section describes how to connect to a database through an SQL client after you create a data warehouse cluster and before you use the cluster's database. DWS provides the Windows gsql client that matches the cluster version for you to access the cluster through the cluster's public or private network address.
Procedure
- Install and run the gsql client on the local Windows server (in Windows CLI). Windows Server 2008/Windows 7 and later are supported.
- Download the Windows gsql client by referring to Downloading the Client and decompress the package to a local folder.
- On the local server, click Start, search for cmd, and run the program as the administrator. Alternatively, press Win+R to open the Windows CLI.
- Set environment variables. For a 32-bit OS, select the x86 folder. For a 64-bit OS, select the x64 folder.
Method 1: Configure environment variables in the Windows CLI. Open the command prompt and run the set path=<window_gsql>;%path% command, where <window_gsql> indicates the folder path where the Windows gsql client was decompressed to in the previous step. For example:
1set path=C:\Users\xx\Desktop\dws_8.1.x_gsql_for_windows\x64;%path%
Method 2: In the Control Panel window, search for System and click View advanced system settings. Click the Advanced tab, and click Environment Variables. Select the Path parameter and click Edit. Add the gsql path in the parameter value. For example:
Figure 1 Configuring Windows environment variables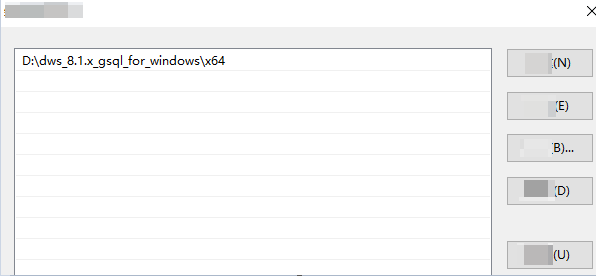
- (Optional) To connect to the cluster in SSL mode, configure SSL authentication parameters on the server where the client is installed. For details, see Establishing Secure TCP/IP Connections in SSL Mode.

The SSL connection mode is more secure than the non-SSL mode. You are advised to connect the client to the cluster in SSL mode.
- In the Windows CLI, run the following command to connect to the database in the DWS cluster using the gsql client:
1gsql -d <Database_name> -h <Cluster_address> -U <Database_user> -p <Database_port> -W <Cluster_password> -r
The parameters are as follows:
- Database name: Enter the name of the database to be connected. If you use the client to connect to the cluster for the first time, enter the default database gaussdb.
- Cluster address: For details about how to obtain this address, see Obtaining the Connection Address of a DWS Cluster. If a public network address is used for connection, set this parameter to the public network domain name. If a private network address is used for connection, set this parameter to the private network domain name. If ELB is used for connection, set this parameter to ELB Address.
- Database user: Enter the username of the cluster's database. If you use the client to connect to the cluster for the first time, set this parameter to the default administrator configured during cluster creation, for example, dbadmin.
- Database port: Enter the database port set during cluster creation.
For example, run the following command to connect to the default database gaussdb in the DWS cluster:
1gsql -d gaussdb -h 10.168.0.74 -U dbadmin -p 8000 -W password -r
If the following information is displayed, the connection succeeded:
1gaussdb=>
Precautions
- The default character encoding of the Windows command prompt is GBK, and the default value of client_encoding of Windows gsql is GBK. Some characters encoded using UTF-8 cannot be displayed in Windows gsql.
Suggestion: Ensure the file specified using -f uses UTF-8 encoding, and set the default encoding format to UTF-8 (set client_encoding='utf-8';).
- Paths in Windows gsql must be separated by slashes (/), or an error will be reported. In a meta-command, the backslash (\) indicates the start of a meta-command. If the backslash is enclosed in single quotation marks ('\'), it is used for escape.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
gaussdb=> \i D:\test.sql D:: Permission denied postgres=> \i D:/test.sql id ---- 1 (1 row)
- To use the \! metacommand to run a system command in Windows gsql, be sure to use the path separator required by the system command. Generally, the path separator is a backslash (\).
1 2 3 4
gaussdb=> \! type D:/test.sql Incorrect syntax. gaussdb=> \! type D:\test.sql select 1 as id;
- Windows gsql does not support the \parallel meta-command.
1 2
gaussdb=> \parallel ERROR: "\parallel" is not supported in Windows.
- In Linux shell, single quotation marks ('') and double quotation marks ("") can be used to enclose strings. In Windows, only double quotation marks can be used.
1 2 3 4 5
gsql -h 192.168.233.189 -p 8109 -d postgres -U odbcuser -W password -c "select 1 as id" id ---- 1 (1 row)
If single quotation marks are used, an error will be reported and the input will be ignored.1 2 3 4 5 6
gsql -h 192.168.233.189 -p 8109 -d postgres -U odbcuser -W password -c 'select 1 as id' gsql: warning: extra command-line argument "1" ignored gsql: warning: extra command-line argument "as" ignored gsql: warning: extra command-line argument "id'" ignored ERROR: unterminated quoted string at or near "'select" LINE 1: 'select
- If Windows gsql is idle for a long time after a connection is established, the connection session times out, and an SSL error is reported. In this case, you need to log in again. The following error is reported:
1SSL SYSCALL error: Software caused connection abort (0x00002745/10053), remote datanode <NULL>, error: Result too large
- In Windows, press Ctrl+C to exit gsql. If Ctrl+C are pressed during input, the input will be ignored and you will be forced to exit gsql.
Enter as and press Ctrl+C. After \q is displayed, exit gsql.
1 2
gaussdb=> select 1 gaussdb=> as \q
- Windows gsql cannot connect to a database using the LATIN1 character encoding. The error information is as follows:
1gsql: FATAL: conversion between GBK and LATIN1 is not supported
- The location of the gsqlrc.conf file:
The default gsqlrc path is %APPDATA%/postgresql/gsqlrc.conf. You can also set the path using the PSQLRC variable.
1set PSQLRC=C:\Users\xx\Desktop\dws_8.1.x_gsql_for_windows\x64\gsqlrc.conf
- MSVCP100.dll may be missing in the Windows Server system. When you use gsql, the following error message is displayed.
Figure 2 Error message
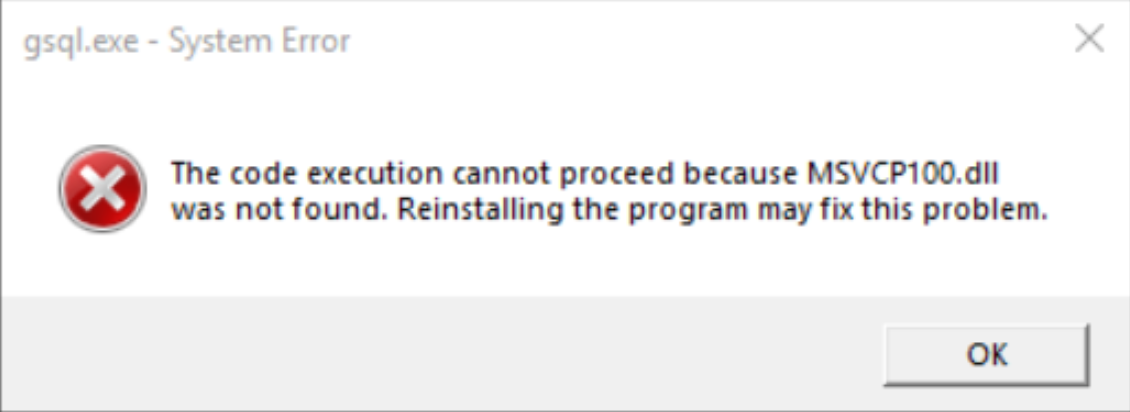
Solution: Add the MSVCP100.dll file. You can download the C++ redistributable program package and install the vcredist_x86.exe/vcredist_x64.exe package to supplement the required dynamic link library file.
gsql Command Reference
For more information about the gsql commands, see "Client Tools" > "Command Reference" in the Data Warehouse Service Tool Guide.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






