Creating Derivative Metrics
Derivative metrics are aggregated from the modifiers and dimensions of atomic metrics. Therefore, their modifiers and dimensions are derived from the attributes of atomic metrics as well. When a derivative metric is published, a summary table is automatically generated, which can be viewed in the Automatically Aggregated area on the Summary Table tab page.
Derivative metric = Atomic metric + Dimension + Time filter + General filter
- Atomic metric specifies the statistical standards, namely, the computing logic.
- Dimension is the perspective to observe and analyze business data and assist in data aggregation, drilling, slicing, and analysis, and used as a GROUP BY condition in SQL statements.
- Time filter is a standard definition of a time condition.
- General filter collects statistics on the business scope and select the records that meet the business rules (similar to the WHERE clause in SQL statements, excluding the time range).
Prerequisites
- An atomic metric has been created and approved.
- A dimension and time filter have been created and approved. This prerequisite is required only if the derivative metric will use the statistical dimension or time filter.
Constraints
A maximum of 5,000 derivative metrics can be created in a workspace.
Creating and Publishing a Derivative Metric
- On the DataArts Studio console, locate a workspace and click DataArts Architecture.
- On the DataArts Architecture page, choose in the left navigation pane. On the displayed page, click the Derivative Metrics tab.
- Select a subject from the subject tree on the left and click Create.
- On the page displayed, set the parameters.
Figure 1 Creating a derivative metric
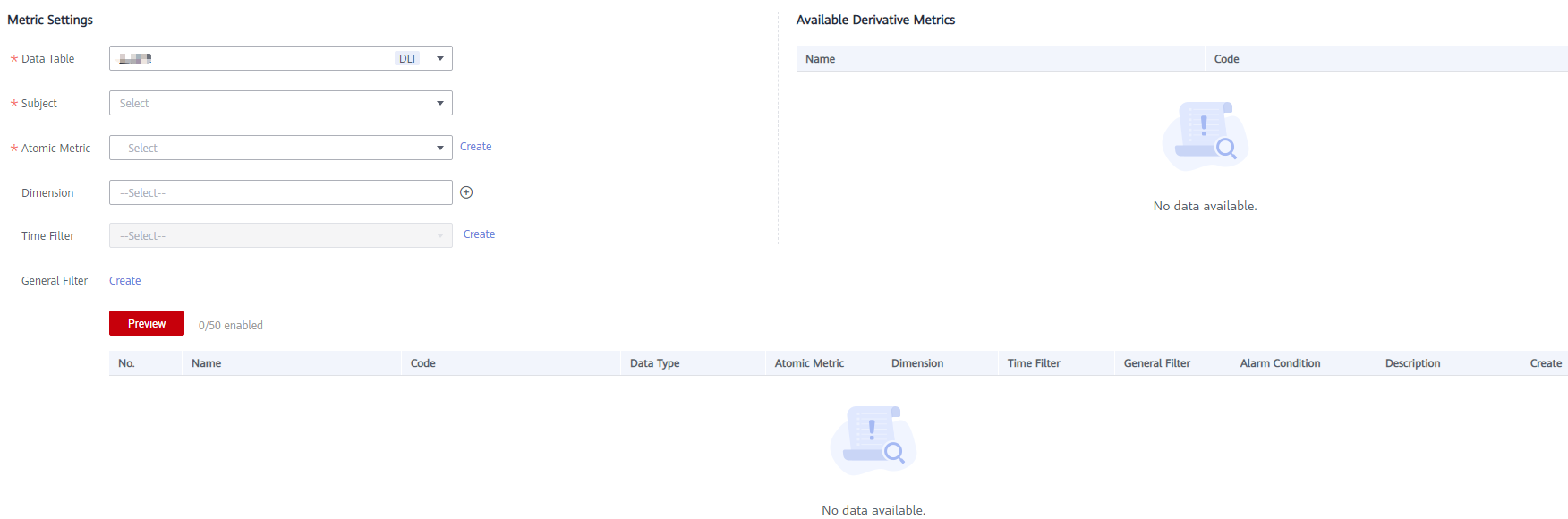
Table 1 Parameters for creating a derivative metric Parameter
Description
*Data Table
Select an asset table from the drop-down list box.
*Subject
Subject information.
*Atomic Metric
Select an atomic metric.
Dimension
Select one or more dimensions from the drop-down list box. Only the attributes in the fact table associated with the atomic metrics can be selected.
Time Filter
Select the required time filter from the drop-down list and select the associated field. Some time filters are preconfigured in the system. If the available time filters cannot meet the requirements, customize one. See Creating Time Filters for details.
General Filter
To set general filters, click Create. It must start with a letter. Only letters, digits, and underscores (_) are allowed.
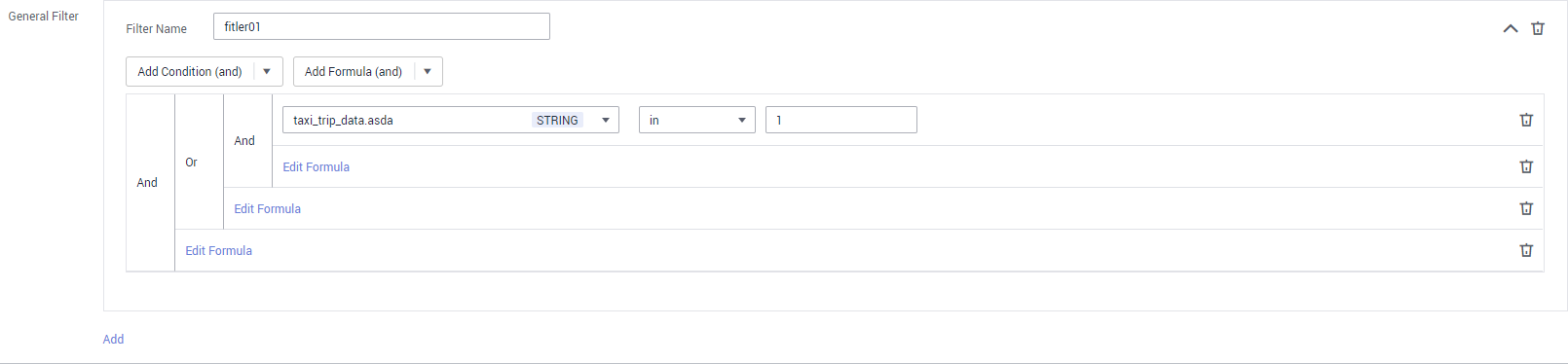
In the General Filter area shown in Figure 2, set the parameters as follows:
- Name specifies the name of a general filter.
- Under Add Condition (and), you can select And condition or Or condition to add a condition. After you specify the condition, select a field from the field drop-down list and set the parameters as prompted. You can add multiple conditions.
If the selected field is of the string type (for example, string or varchar) and the condition is set to in or not in, data can be imported from a lookup table. Click From lookup tables, set lookup tables and lookup table field, and click OK. A maximum of 50 fields can be imported from a lookup table.
You can click
 to delete unwanted conditions.
to delete unwanted conditions. - Under Add Formula (and), you can select And formula or OR formula to add a formula. Click Edit Formula if needed. In the dialog box displayed, select the required functions and fields and set the expression.
You can click
 to delete unwanted formulas.
to delete unwanted formulas.
Alarm Triggering Condition
An alarm triggering condition consists of derivative metrics and expressions. An expression consists of alarm parameters and logical operators. When a metric is running, the system calculates the result of the alarm condition expression and determines whether to trigger the alarm based on the result of the expression. If the expression result is true, the alarm will be triggered. Otherwise, no quality alarm will be triggered.
- After setting the parameters, click Preview to view the information about the derivative metric and define the name, code, data type, alarm condition, and description for the metric.
Table 2 Parameters for previewing a derivative metric Parameter
Description
Metric Name
It is automatically generated by the system based on parameters such as atomic metrics, statistical dimensions, and time filters. You can also customize it.
Metric Code
It is automatically generated by the system based on parameters such as atomic metrics, statistical dimensions, and time filters. You can also customize it.
Data Type
It is automatically generated by the system based on the data type of the atomic metric. You can also customize it.
Alarm Condition
An alarm condition expression consists of alarm parameters and logical operators. When a metric is running, the system calculates the result of the alarm condition expression and determines whether to trigger the alarm based on the result of the expression. If the expression result is true, the alarm will be triggered. Otherwise, no quality alarm will be triggered.
Description
A description of the derivative metric to create. Up to 600 characters are supported.
- In the lower part of the page, click Trial Run. In the dialog box displayed, click Trial Run to check whether the derivative metric can run properly.
If the trial run fails, locate the fault based on the error message, correct the configurations, and click Trial Run to try again.
- If the trial run is successful, click Publish.
- In the displayed dialog box, select a reviewer and click OK to submit a request.
If you have been added as a reviewer, you can select Auto-review and click OK. After the request is approved, the status changes to Published.
If you select multiple reviewers, the status changes to Published only after all reviewers have approved the publishing request. If any reviewer rejects the request, the status is Rejected.
- (Optional) Create and publish other derivative metrics by repeating 2 to 8.
- Wait for the reviewer to approve the application.
After the application is approved, the derivative metric is created.
Click the name of a derivative metric to view its details, relationship diagram, publishing history, and review history.
In the relationship diagram, you can view the lineage diagram of the derivative metric.
In the release history, you can view the differences between historical versions.
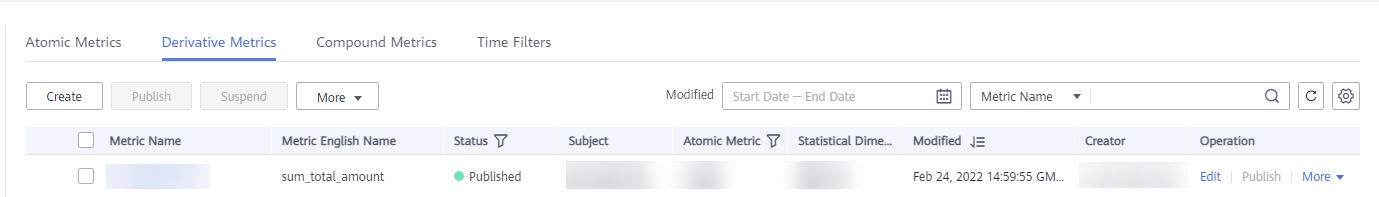
Managing a Derivative Metric
On the Derivative Metrics tab page, you can edit, publish, suspend, or delete derivative metrics.
- On the DataArts Architecture page, choose in the left navigation pane. On the displayed page, click the Derivative Metrics tab.
- Manage your derivative metrics as required. Refer to the following table for details.
- Edit a derivative metric.
- Click Edit to the right of the target derivative metric.
- On the page displayed, edit the derivative metric as required.
- In the lower part of the page, click Trial Run. In the dialog box displayed, click Trial Run to check whether the derivative metric can run properly.
If the trial run fails, locate the fault based on the error message, correct the configurations, and click Trial Run to try again.
- If the trial run is successful, click Publish.
- Publish a derivative metric.
- Click Publish to the right of the target derivative metric.
- In the Submit for Publication dialog box displayed, select a reviewer from the drop-down list box.
- Click OK.
- View the publish history.
- Select the target derivative metric and choose .
- On the page displayed, you can view the publish history and version comparison information of the metric.
- Preview an SQL statement.
- Select the target derivative metric and choose .
- On the page displayed, you can view or copy the SQL statement.
- Suspend a derivative metric.
The prerequisite for suspending a derivative metric is that the derivative metric is not referenced to any compound metrics.
- Choose on the right of the target derivative metric.
- In the Submit for Suspension dialog box displayed, select a reviewer from the drop-down list box.
- Click OK.
- View a summary table.
Currently, only details about automatically generated summary tables can be viewed. Choose on the right of the target derivative metric. The Summary Tables page is displayed.
- Delete a derivative metric.
The prerequisite for deleting a derivative metric is that the derivative metric is not referenced to any compound metrics.
- Select the target derivative metric and choose above the list.
- In the dialog box displayed, confirm the information and click Yes.
- Import derivative metrics.
You can import derivative metrics to the system quickly.
- Above the summary table list, choose More > Import.
Figure 4 Importing derivative metrics
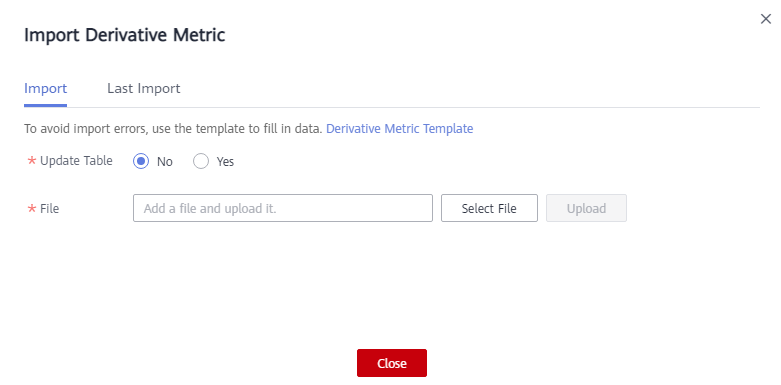
- Download the derivative metric template, and edit and save it.
- Choose whether to update existing data.
If a code in the template already exists in the system, the data is considered duplicate.
- No: If the data to be imported already exists in the system, the existing data in the system will not be replaced.
- Yes: If the data to be imported already exists in the system:
- If the existing data in the system is in draft state, the data will be replaced and new draft data will be generated.
- If the existing data in the system is in published state, expanded data will be generated.
- Click Select File and select the edited template to import.
- Click Upload. When the template is uploaded, the Last Import page is displayed. You can view the imported data.
- Click Close.
- Above the summary table list, choose More > Import.
- Exporting derivative metrics.
You can export derivative metrics to a local file.
- In the derivative metric list, select the metric to be exported.
- Above the derivative metric list, choose More > Export.
- You can export all the derivative metrics of a subject by selecting the subject in the subject list on the left.
- You can export all the derivative metrics of a workspace, as long as there are no more than 5,000 derivative metrics in the workspace.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.