Application Scenarios
Example Scenario
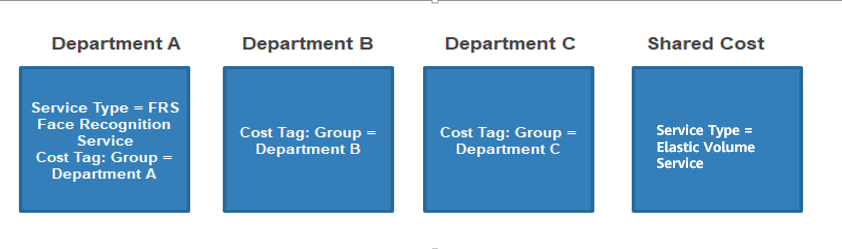
You want to allocate costs across Department A, Department B, and Department C in your company, and the department of most of the costs can be identified based on the tags configured for the resources. In addition, Department A uses the Face Recognition Service that does not support tag management, and an Elastic Volume Service (EVS) is shared across all departments.
As mentioned earlier, you can use the tag key Group and tag values Department A, Department B, and Department C to group most of your costs, as shown in the following figure.
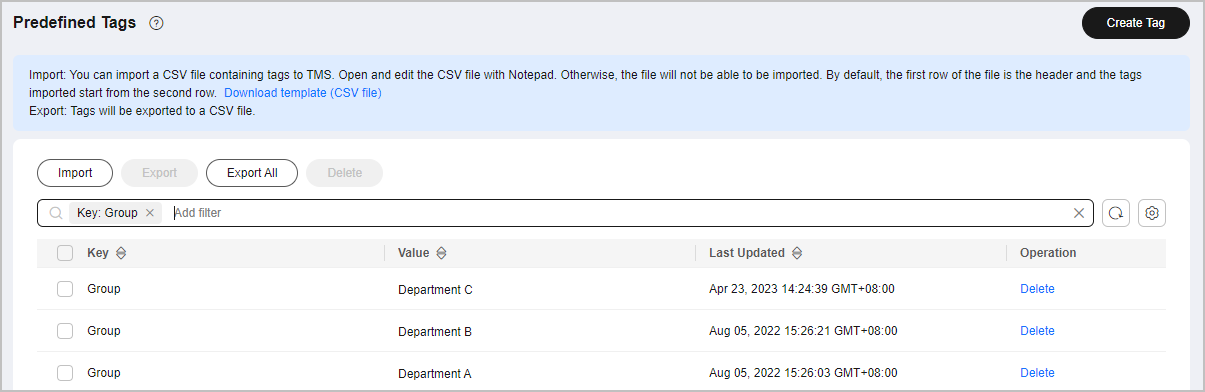
Step 1 Creating Cost Tags
Create tags before using cloud services. For details, see Creating Predefined Tags. For example, you can create the tag key Group with three tag values (Department A, Department B, and Department C).
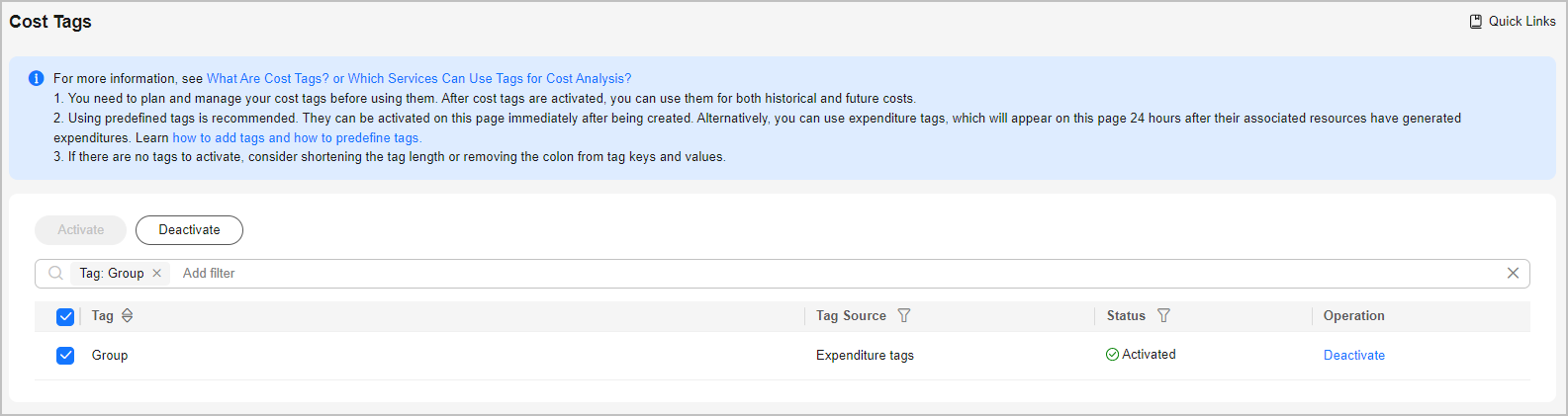
Step 2 Activating Cost Tags
Activate the created tag Group so that it can be applied to cost categories.
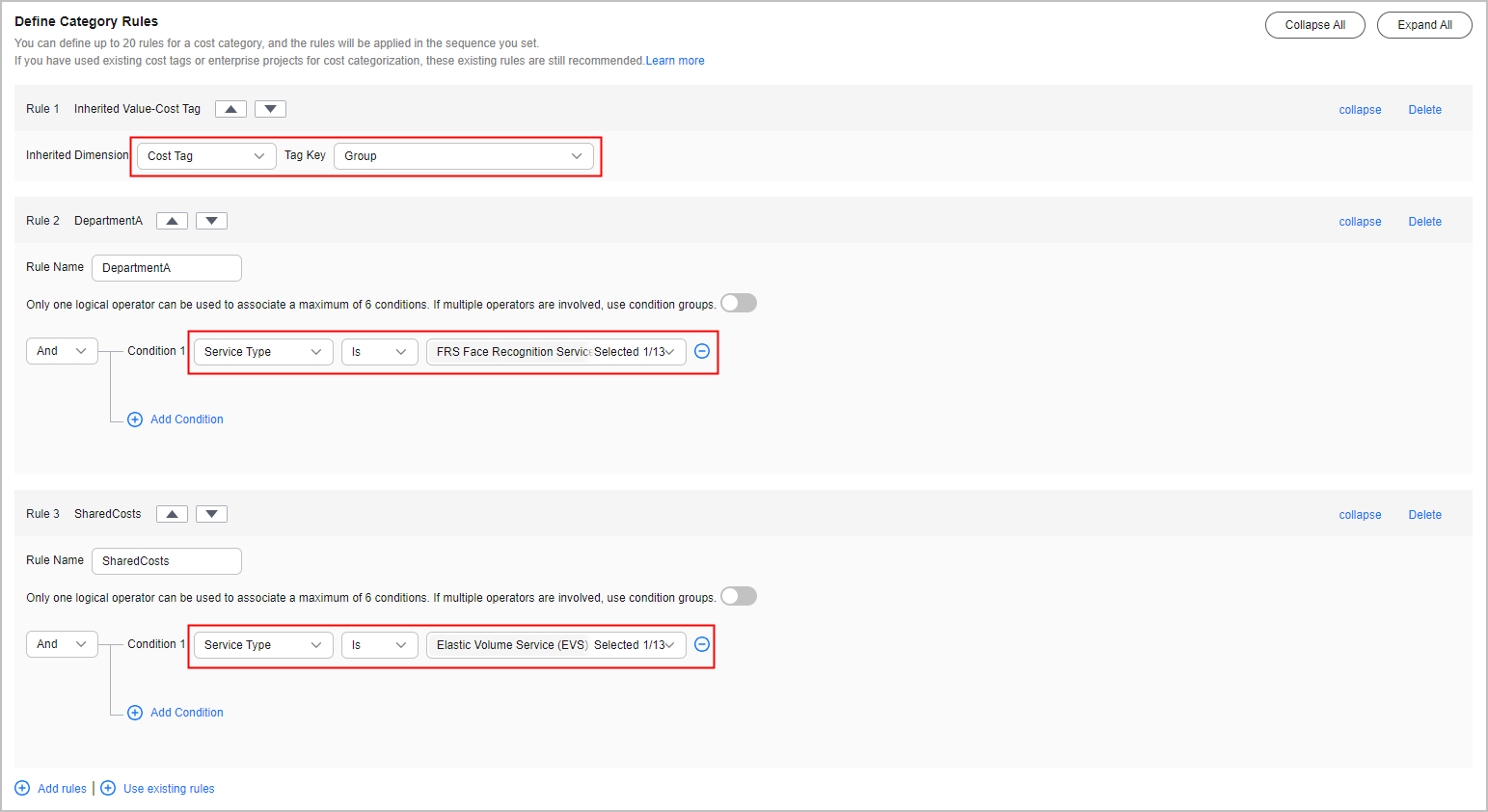
Step 3 Creating Cost Categories (Defining Rules)
|
Rule |
Type |
Content |
|---|---|---|
|
Rule 1: Inherited Value - Cost Tags |
Use existing rules.
NOTE:
If you have used existing cost tags or enterprise projects to group cost data, existing rules are recommended. Example: If rules are defined based on the cost tag Group, cost data will be grouped for DepartmentA, DepartmentB, and DepartmentC. |
Condition: Inherited Dimension is Cost Tag, and Tag Key is Group. |
|
Rule 2: Department A |
Add rules. |
Condition: Service Type is FRS Face Recognition Service. |
|
Rule 3: Shared costs |
Add rules. |
Condition: Service Type is Elastic Volume Service. |
|
Uncategorized costs |
- |
Costs that do not match the preceding rules. |
In this example, costs are amortized in the way described in Table 2.
Step 4 Creating Cost Categories (Allocating Shared Costs)
Four hours after the cost category is created, you can define cost splitting rules to split the shared costs across departments.
- Select Custom for Allocation Method to allocate 30% of the shared costs to Department A, 30% to Department B, and 40% to Department C.
- Select Custom for Allocation Method to allocate 50% of the uncategorized costs to Department A, 30% to Department B, and 20% to Department C.
There are three cost allocation methods:
- Proportionally: Allocate your costs in proportion to the weight of each target value.
Example: Suppose the value of target B is $800 USD and the value of target C is $200 USD. As the ratio of target B to target C is 4:1, 80% of the source value will be allocated to target B and 20% to target C.
- Evenly: Allocate your costs evenly across your target values.
Example: Suppose there are two target values (A and B). With this method, the source value is evenly allocated to A and B, 50% for each.
- Custom: Allocate your costs based on a custom percentage for each target value. The percentages must add up to 100%.
Figure 2 Defining splitting rules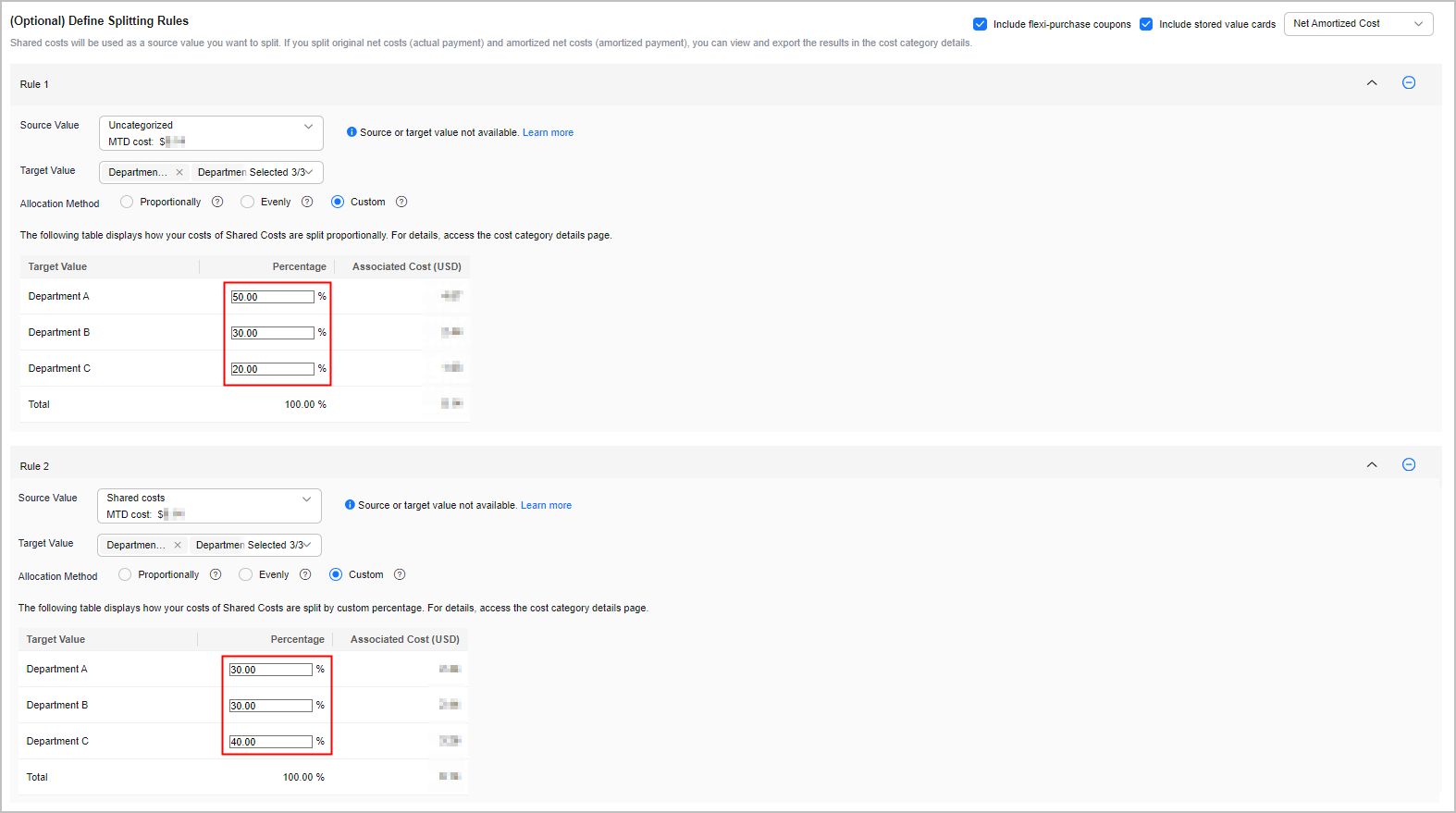
Table 3 Cost splitting rules Rule
Source Value
Target Value
Allocation Method
Content
Associated Cost ($)
Rule 1
Uncategorized costs
Department A
Department B
Department C
Custom
Department A: 50%
Department B: 30%
Department C: 20%
Department A: 100 x 50% = 50
Department B: 100 x 30% = 30
Department C: 100 x 20% = 20
Rule 2
Shared costs
Department A
Department B
Department C
Custom
Department A: 30%
Department B: 30%
Department C: 40%
Department A: 40 x 30% = 12
Department B: 40 x 30% = 12
Department C: 40 x 40% = 16
- Proportionally: Allocate your costs in proportion to the weight of each target value.
Step 5 Viewing Cost Splitting Results
|
Department |
Net Amortized Cost |
Split Amount |
Amount Allocated |
Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Department A |
100 |
50 + 12 |
162 |
33.06% |
|
Department B |
200 |
30 + 12 |
242 |
49.39% |
|
Department C |
50 |
20 + 16 |
86 |
17.55% |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






