Managing Cost Categories
Important Notes
After you create or edit a cost category, it can take up to four hours for your cost and usage details to be categorized.
You can create up to 10 cost categories.
Creating a Cost Category
- Log in to Cost Center.
- Choose Cost Organization > Cost Categories.
- Click Create Cost Category.
- Define category rules to group your costs.
You can define up to 20 rules for each category.
- Specify a category name.
Enter a name to uniquely identify your cost category. The name cannot be changed once your cost category is created.
- Configure a look-back period.
You can select any specified month from the previous 12 months.
- Define category rules.
Category rules are executed in prioritized order.
An enterprise master account can select enterprise projects by linked account, except the default enterprise project and those not categorized.
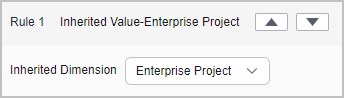
- Use existing rules for a cost category. This method lets you flexibly define a rule that dynamically inherits the value of a cost category or enterprise project to group your costs. You are advised to use the existing rules.
You can choose to group costs by enterprise project, as shown in the following figure.
- Define new rules. You can also associate multiple conditions for a cost category by using logical operators.
Table 1 Logical operators Logical Operator
Description
Example
And
Indicates that all conditions must be met.
If the logical operator is set to And and all of conditions 1, 2, and 3 are met, the rule can be used to categorize the costs.
Or
Indicates that any of configured conditions needs to be met.
If the logical operator is set to Or and any of the conditions (1, 2, and 3) is met, the rule can be used to categorize the costs.
One logical operator can be used to associate a maximum of five conditions. If multiple operators are involved, use nested logic. For details, see Calculation Logic.
- Use existing rules for a cost category. This method lets you flexibly define a rule that dynamically inherits the value of a cost category or enterprise project to group your costs. You are advised to use the existing rules.
- Group uncategorized costs.
All costs that do not comply with the rules you defined will be grouped into the default group Uncategorized. You can rename the group, for example, Shared Costs.
- Specify a category name.
- (Optional) Split shared costs.
When you use existing rules, the source and target values become available four hours after you create the cost category.
You cannot view cost splitting details in real time, including the cost of a split source and the percentage used for proportionally allocation, in a cost category you created. You are advised to create cost splitting rules four hours after you create a cost category.
Field
Description
Source Value
Shared costs you want to split, which can be either of the following:
Target Value
The cost categories you want to split your costs across
Allocation Method
- Proportionally: Allocate your costs in proportion to the weight of each target value.
Example: Suppose the value of target B is $800 USD and the value of target C is $200 USD. As the ratio of target B to target C is 4:1, 80% of the source value will be allocated to target B and 20% to target C.
- Evenly: Allocate your costs evenly across your target values.
Example: Suppose there are two target values (A and B). With this method, the source value is evenly allocated to A and B, 50% for each.
- Custom: Allocate your costs based on a custom percentage for each target value. The percentages must add up to 100%.
- Proportionally: Allocate your costs in proportion to the weight of each target value.
- Click Create.
Editing a Cost Category
- Log in to Cost Center.
- Choose Cost Organization > Cost Categories.
- Click Edit in the Operation column of the cost category you want to modify the configured category rules and cost splitting rules.

Deleting a Cost Category
- Log in to Cost Center.
- Choose Cost Organization > Cost Categories.
- Click Delete in the Operation column of the cost category you want to delete.

Calculation Logic
- Default logic: One logical operator can be used to associate a maximum of five conditions.
As shown in the following figure, a logical operator (And) is used to associate the three conditions. All these three conditions must be met at the same time so that the rule can be used to categorize costs.
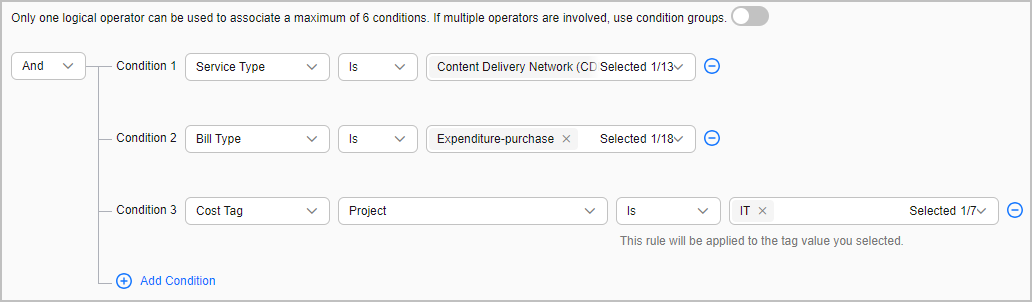
The following is an example of condition settings:
Example condition 1: Cost Tag project Is IT. When the value of the cost tag project is IT, this rule will be used to categorize costs.
Example condition 2: Cost Tag project Is not IT. When the value of the cost tag project is not IT, this rule will be used to categorize costs.

- When you use cost tags to group your costs, if the operator is Is not, the rule will not be used to categorize the costs that do not have tags.
Example: The key of a cost tag is project, and the key values are IT1, IT2, and IT3. If you configure a condition where Cost Tag project Is not IT1, the costs whose cost tag values are IT2 and IT3 will be grouped. Costs that do not have the cost tag project will not be grouped.
- When you use enterprise projects to group your costs, if the operator is Is not, the rule will be used to categorize the costs that do not belong to any enterprise projects.
Example: There are three enterprise projects (project 1, project 2, and project 3). If you configure a condition where Enterprise Project Is not project 1, costs that do not have enterprise projects as well costs whose enterprise projects are project 2 and project 3 will be grouped.
Example condition 3: Cost Tag project Starts with IT. When the value of the cost tag project starts with IT, this rule will be used to categorize costs.
Example condition 4: Cost Tag project Is absent. If the cost tag project is not used, this rule will be used to categorize costs.
Table 2 Conditional operators supported by different dimensions Dimension
Is
Is Not
Starts With
Is Absent
Linked Account
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
Not Supported
Service Type
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
Not Supported
Bill Type
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
Not Supported
Cost Tag
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Enterprise Project
Supported
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
Cost Category
Supported
Supported
Supported
Not Supported
- When you use cost tags to group your costs, if the operator is Is not, the rule will not be used to categorize the costs that do not have tags.
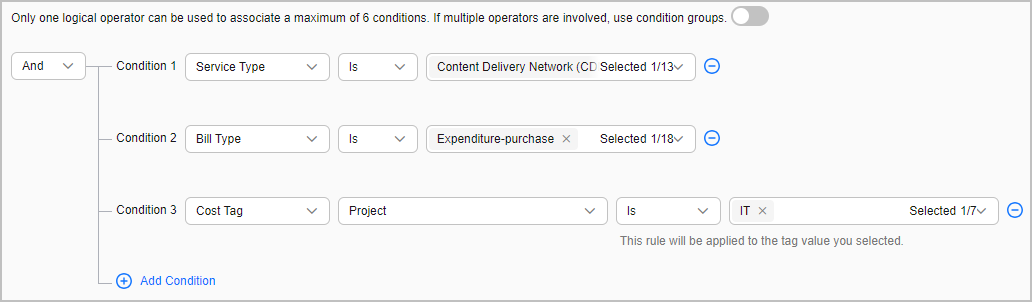
- Nested logic: Two logical operators can be used to associate up to five conditions.
As shown in the following figure, two logical operators are used to associate five conditions in a nested manner.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






