How Do I Grant the Permissions of a Schema to a Specified GaussDB(DWS) User?
This section explains how to give query permission for schema-level permissions. If you need other permissions, see How Do I Grant Table Permissions to a User?
- Permission for a table in a schema
- Permission for all the tables in a schema
- Permission for tables to be created in the schema

The VACUUM, DROP, and ALTER permissions on foreign tables cannot be granted to users.
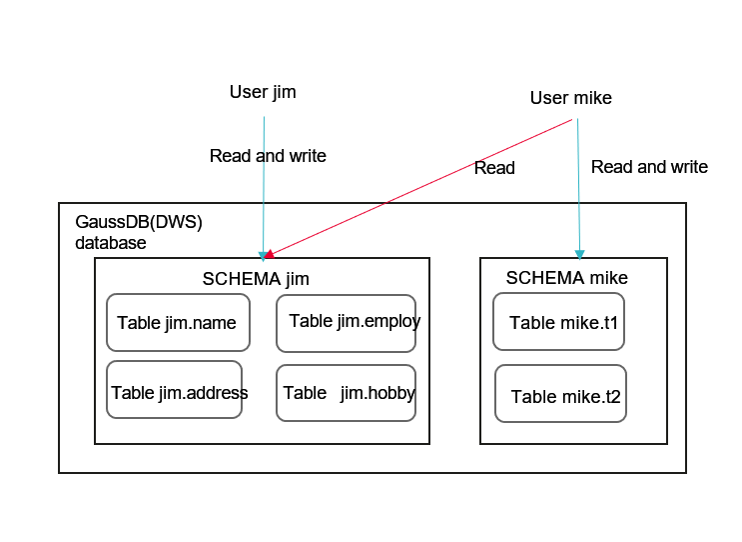
Assume that there are users jim and mike, and two schemas named after them. User mike needs to access tables in schema jim, as shown in Figure 1.
- Connect to your database as dbadmin. Run the following statements to create users jim and mike. Two schemas will be created and named after the users by default.
1 2
CREATE USER jim PASSWORD '{password}'; CREATE USER mike PASSWORD '{password}';
- Create tables jim.name and jim.address in schema jim.
1 2
CREATE TABLE jim.name (c1 int, c2 int); CREATE TABLE jim.address (c1 int, c2 int);
- Grant the access permission of schema jim to user mike.
1GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA jim TO mike;
- Grant user mike the permission to query table jim.name in schema jim.
1GRANT SELECT ON jim.name TO mike;
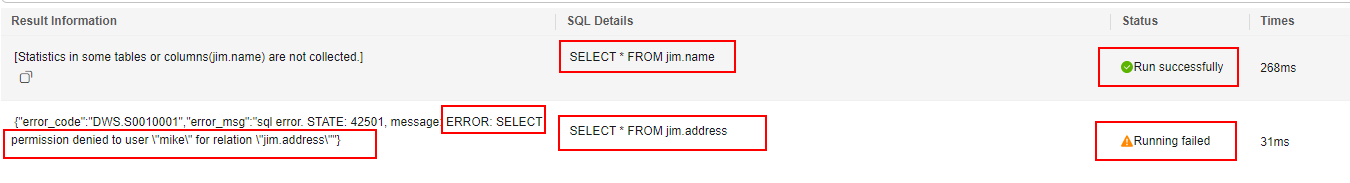
- Start a new session and connect to the database as user mike. Verify that user mike can query the jim.name table but not the jim.address table.
1 2
SELECT * FROM jim.name; SELECT * FROM jim.address;
- In the session started by user dbadmin, grant user mike the permission to query all the tables in schema jim.
1GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA jim TO mike;
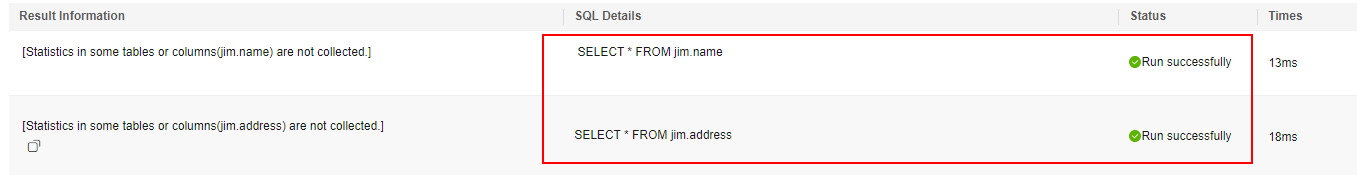
- In the session started by user mike, verify that mike can query all tables.
1 2
SELECT * FROM jim.name; SELECT * FROM jim.address;
- In the session started by user dbadmin, create table jim.employ.
1CREATE TABLE jim.employ (c1 int, c2 int);
- In the session started by user mike, verify that user mike does not have the query permission for jim.employ. It indicates that user mike has the permission to access all the existing tables in schema jim, but not the tables to be created in the future.
1SELECT * FROM jim.employ;

- In the session started by user dbadmin, grant user mike the permission to query the tables to be created in schema jim. Create table jim.hobby.
1 2
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES FOR ROLE jim IN SCHEMA jim GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO mike; CREATE TABLE jim.hobby (c1 int, c2 int);
- In the session started by user mike, verify that user mike can access table jim.hobby, but does not have the permission to access jim.employ. To let the user access table jim.employ, you can grant permissions by performing 4.
1SELECT * FROM jim.hobby;

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.