Encrypting and Decrypting Data Through Cross-region DR
Scenario
If a fault occurs during encryption or decryption in a region, you can use KMS to implement cross-region DR encryption and decryption, ensuring service continuity.
Solution
If KMS is faulty in one or multiple regions, encryption and decryption can be completed as long as a key in the key ring is available.
A cross-region key can use the CMKs of multiple regions to encrypt a piece of data and generate unique data ciphertext. To decrypt the data, you simply need to use a key ring that contains one or more available CMKs that were used for encrypting the data.
Process
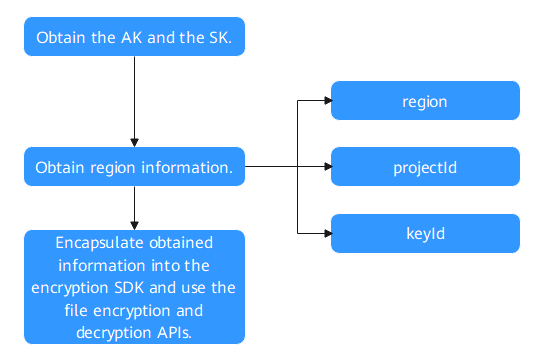
Procedure
- Obtain the AK and the SK.
- ACCESS_KEY: Access key of the Huawei account. For details, see How Do I Obtain an Access Key (AK/SK)?
- SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: Secret access key of the Huawei account. For details, see How Do I Obtain an Access Key (AK/SK)?
- PROJECT_ID: site project ID. For details, see Obtaining a Project ID.
- KMS_ENDPOINT: endpoint for accessing KMS.
- There will be security risks if the AK/SK used for authentication is directly written into code. Encrypt the AK/SK in the configuration file or environment variables for storage.
- In this example, the AK/SK stored in the environment variables are used for identity authentication. Configure the environment variables HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK and HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK in the local environment first.
- Obtain region information.
- Log in to the DEW console.
- Hover over the username in the upper right corner and choose My Credentials from the drop-down list.
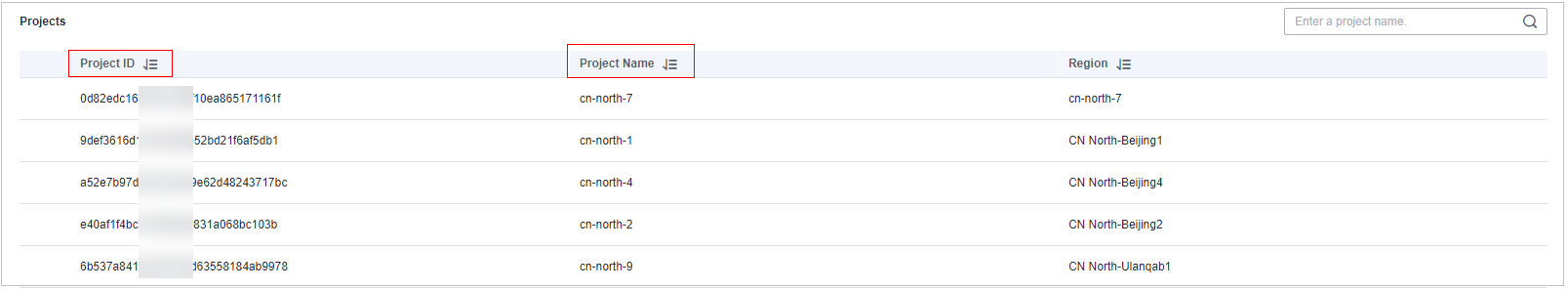
- Obtain the Project ID and Project Name.
Figure 1 Obtaining the project ID and project name
- Click
 on the left and choose .
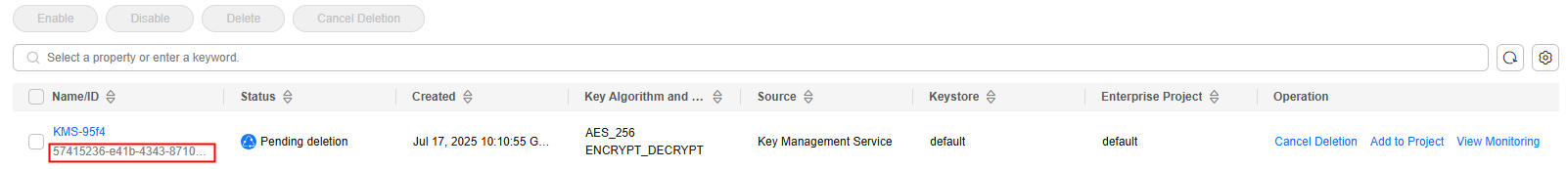
on the left and choose . - Obtain the ID of the CMK (KEYID) to be used in the current region.
Figure 2 Obtaining the CMK ID
- Use the key ring for encryption and decryption.
public class KmsEncryptionExample { private static final String ACCESS_KEY = System.getenv("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK"); private static final String SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = System.getenv("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK"); private static final String PROJECT_ID_1 = "<projectId1>"; private static final String REGION_1 = "<region1>"; private static final String KEYID_1 = "<keyId1>"; public static final String PROJECT_ID_2 = "<projectId2>"; public static final String REGION_2 = "<region2>"; public static final String KEYID_2 = "<keyId2>"; // Data to be encrypted private static final String PLAIN_TEXT = "Hello World!"; public static void main(String[] args) { // CMK list List<KMSConfig> kmsConfigList = new ArrayList<>(); kmsConfigList.add(new KMSConfig(REGION_1, KEYID_1, PROJECT_ID_1)); kmsConfigList.add(new KMSConfig(REGION_2, KEYID_2, PROJECT_ID_2)); // Construct encryption-related information. HuaweiConfig multiConfig = HuaweiConfig.builder().buildSk(SECRET_ACCESS_KEY) .buildAk(ACCESS_KEY) .buildKmsConfig(kmsConfigList) .buildCryptoAlgorithm(CryptoAlgorithm.AES_256_GCM_NOPADDING) .build(); // Select a key ring. KMSKeyring keyring = new KmsKeyringFactory().getKeyring(KeyringTypeEnum.KMS_MULTI_REGION.getType()); HuaweiCrypto huaweiCrypto = new HuaweiCrypto(multiConfig).withKeyring(keyring); // Encryption context Map<String, String> encryptContextMap = new HashMap<>(); encryptContextMap.put("key", "value"); encryptContextMap.put("context", "encrypt"); // Encryption CryptoResult<byte[]> encryptResult = huaweiCrypto.encrypt(new EncryptRequest(encryptContextMap, PLAIN_TEXT.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))); // Decryption CryptoResult<byte[]> decryptResult = huaweiCrypto.decrypt(encryptResult.getResult()); Assert.assertEquals(PLAIN_TEXT, new String(decryptResult.getResult())); } }
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






