使用C/C++重构代码
重构是通过改变现有程序结构而不改变其功能和用途来提高代码的可重用性和可维护性。
CodeArts IDE提供了多种重构方法,在使用重构之前,请确保compile_commands.json文件已自动导入。构建文件会生成在项目根目录下,如cmake-build-debug目录。具体请参见在CodeArts IDE for C/C++加载CMake工程。
选择需重构的代码块,如有可用的重构操作,代码处会出现黄色小灯泡 提示,或右键菜单选择“重构”查看可用的重构操作。
提示,或右键菜单选择“重构”查看可用的重构操作。
提取重构(Extraction refactoring)
CodeArts IDE for C/C++ 支持将字段、方法和参数提取到新类中,根据提取的内容会提供不同的重构类型。
- 提取函数/方法(Extract method)
将选定的语句或表达式提取到文件中的新方法或新函数。在选择提取函数/方法重构后,输入提取的方法/函数的名称。
图1 提取函数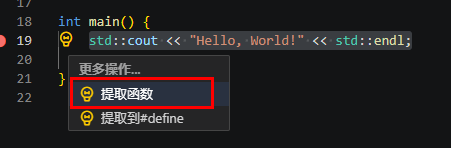
执行重构示例
重构前:
int main() { std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl; return 0; }重构后:
void extracted() { std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl; } int main() { extracted(); return 0; } - 提取表达式到变量(Extract subexpression to variable)
将选定的表达式提取为文件中的新变量。
图2 提取表达式到变量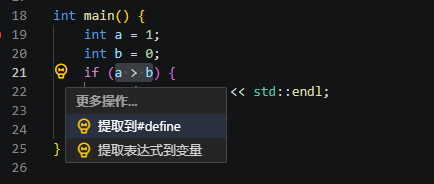
执行重构示例
重构前:
int main() { int a = 1; int b = 0; if (a > b) std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl; }重构后:
int main() { int a = 1; int b = 0; auto comparisonResult = a > b; if (comparisonResult) std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl; }
定义构造函数(Define constructor)
在每次创建类时,可以自动定义类的构造函数,并且初始化成员。当单击或选中类名时,可以单击左侧黄色灯泡选择定义构造函数。
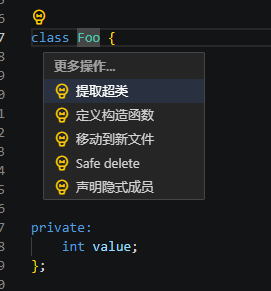
执行重构示例
重构前:
class Bar {
int value = 1;
}
重构后:
class AbstractBar {
int value = 1;
};
class Bar : public AbstractBar {}
基于声明排序函数(Sort functions to declarations)
根据头文件中的声明顺序,排序当前定义函数/方法的顺序。当单击或选中当前函数/方法定义时,重构选项可用。
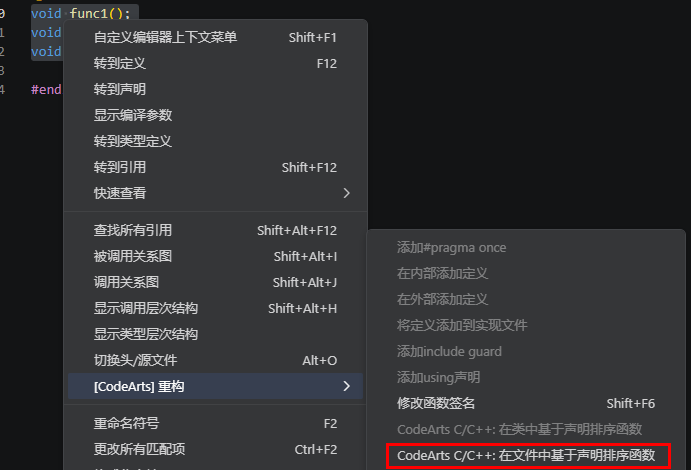
执行重构示例
重构前:
void func1();
void func2();
void func2()
{
return 0;
}
void func1()
{
return 0;
}
重构后:
void func1();
void func2();
void func1()
{
return 0;
}
void func2()
{
return 0;
}
将定义添加到实现文件(Add definition to implementation file)
选中头文件,将定义添加到实现文件中。当单击或选中当前函数/方法时,重构选项可用。
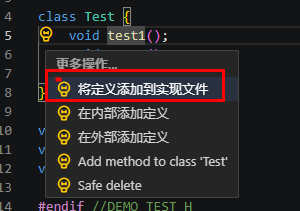
执行重构示例
重构前:
class test {
int testAdd();
}
重构后:
// test.h文件
class test {
int testAdd();
}
// test.cpp文件
int test::testAdd()
{
/* Not implemented yet */
return {};
}
交换if分支(Swap if branches)
若当前条件只有if和else分支,选中代码片段后,选择交换if分支,可自动交换if和else分支。
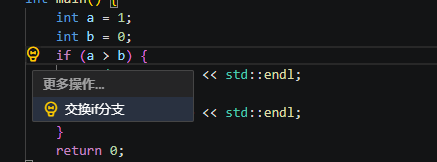
执行重构示例
重构前:
int main()
{
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
if (a < b) {
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Hello, Today!" << std::endl;
}
}
重构后:
int main()
{
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
if (a < b) {
std::cout << "Hello, Today!" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
}
}
内联变量(Inline variable)
该功能可以用相应的值替换所有引用。假设计算值总是产生相同的结果。选中需要替换的内容,重构选项可用。
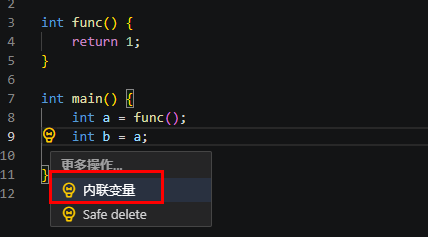
执行重构示例
重构前:
int main()
{
int a = func();
int b = a;
}
重构后:
int main()
{
int b = func();
}
内联函数(Inline function)
该功能尝试使用适当的代码内联所有函数用法。它只能处理简单的功能,不支持内联方法、函数模板、主函数和在系统头文件中声明的函数,该功能可以内联所有函数引用。
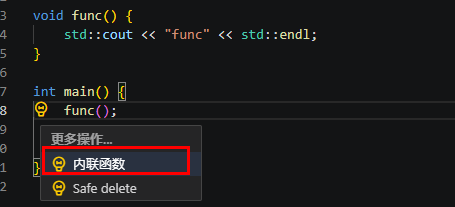
执行重构示例
重构前:
int func(){
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int a = func();
int b = a;
}
重构后:
int func(){
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int a = 1;
int b = a;
}
生成getter和setter(Generate getter and setter)
通过为生成getter和setter来封装选定的类属性。同时也可以选择只生成getter或者生成setter选项。
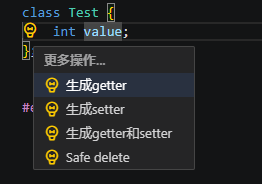
执行重构示例
重构前:
class AbstractFoo {
int value = 1;
};
重构后:
class AbstractFoo {
public:
int getValue() const;
void setValue(int NewValue);
private:
int value = 1;
};
int AbstractFoo::getValue() const
{
return value;
}
void AbstractFoo::setValue(int NewValue)
{
value = NewValue;
}
填充switch语句(Populate switch)
该功能可以自动填充switch语句。选中任意switch字段,并且单击黄色灯泡,选择填充switch语句。
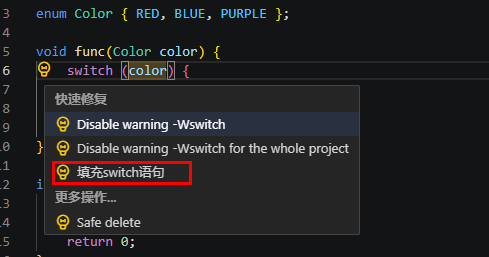
执行重构示例
重构前:
enum Color { RED, BLUE };
void getColor(Color color) {
switch (color) {
}
}
重构后:
enum Color { RED, BLUE };
void getColor(Color color) {
switch (color) {
case RED:
case BLUE:
break;
}
}
移除namespace(Remove using namespace)
移除namespace功能,会自动移除所有使用到的namespace。当光标单击或选中namesapace关键字时,重构选项可用。
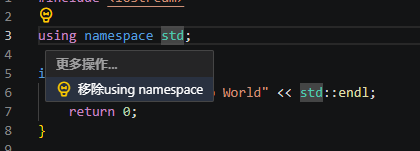
执行重构示例
重构前:
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello, World!" << endl;
}
重构后:
int main() {
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
}
添加定义
- 在内部添加定义(Add definition in-place)
在类内部生成当前函数/方法的函数定义。当光标移动到函数/方法时,单击“重构”,重构选项可用。
图12 在内部添加定义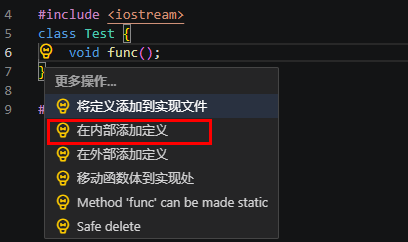
执行重构示例
重构前:
class Test { void func(); }重构后:
class Test { void func() { /* Not implemented yet */ } } - 在外部添加定义(Add definition out-of-place)
在类外部生成当前函数/方法的函数定义。当光标移动到函数/方法时,单击重构按钮,重构选项可用。
执行重构示例
重构前:
class Test { void func(); }重构后:
class Test { void func(); void Test::func() { /* Not implemented yet */ } }
展开宏(Expand macro)
在页面上添加展开宏(Expand macro),以便在可扩展/可折叠的部分提供内容。
执行重构示例
重构前:
#define TEST 1
int main() {
int a = TEST;
std::cout std:: << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
}
重构后:
#define TEST 1
int main() {
int a = 1;
std::cout std:: << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
}
替换为推导类型(Replace with deduced type)
展开auto type所隐藏的变量类型,并替换为推导类型。
执行重构示例
重构前:
void replaceType()
{
int b = 1;
auto a = b;
}
重构后:
void replaceType()
{
int b = 1;
int a = b;
}
移动函数体到声明处(Move function body to declaration)
该功能会将函数/方法的定义移动到声明的位置。
执行重构示例
重构前:
在test.cpp文件中,定义test函数。
void test()
{
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
}
重构后:
test.cpp文件中的test函数移动到test.h文件中。
inline void test()
{
std::cout std:: << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
}
移动函数体到实现处(Move function body to out-of-line)
该功能会将函数/方法的定义移动到对应的文件中。
执行重构示例
重构前:
在头文件中定义一个函数,光标放在函数名处。
void test() {
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
}
重构后:
头文件中定义函数,函数体移动到实现处。
void test();
转为原始字符串(Convert to raw string)
该功能可以将转义后的字符串转换为原始的字符串,当单击或选择了当前字符串,单击重构图标,重构选项可用。
执行重构示例
重构前:
int myPrint() {
std::cout << "\"a\"\n" << std::endl;
}
重构后:
int myPrint() {
std::cout << R"("a"
)" << std::endl;
}






