Before You Start
Intended Audience
The Identity and Access Management (IAM) service is intended for administrators, including:
- Account root user (with full permissions for all services, including IAM)
- IAM users added to the admin group (with full permissions for all services, including IAM)
- IAM users assigned the IAMFullAccessPolicy permissions to access IAM
If you want to view, audit, and trace the records of key operations performed on IAM, enable Cloud Trace Service (CTS). For details, see IAM Operations Supported by CTS.
Accessing the IAM Console
- Log in to Huawei Cloud and click Console in the upper right corner.
Figure 1 Accessing the console

- On the management console, hover over the username in the upper right corner, and choose Identity and Access Management from the drop-down list.
Figure 2 Accessing the IAM console

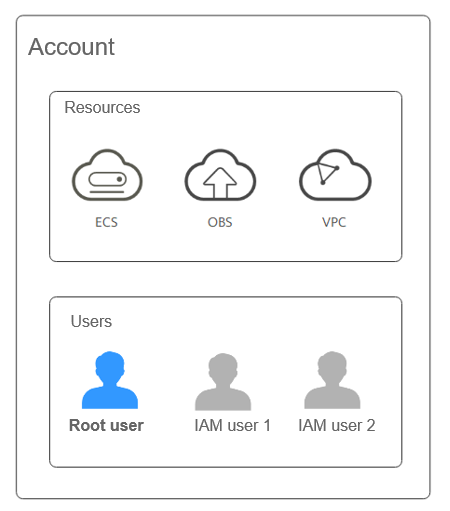
Accounts
An account is created after you sign up for Huawei Cloud. This account owns your Huawei Cloud resources and makes payments for the use of these resources. The root user of the account has full access permissions for these resources and services. You cannot modify or delete your account in IAM, but you can do so in My Account.
After you log in to your account, you will see a user marked Enterprise administrator on the Users page of the IAM console.
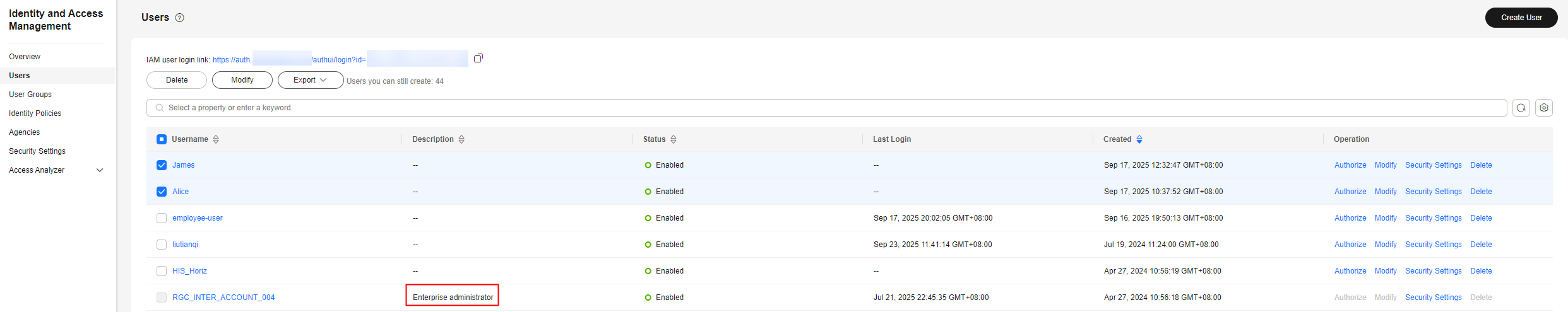
IAM User
Administrators can create users in IAM and assign permissions for specific resources. As shown in the following figure, James is an IAM user created by an administrator. IAM users can log in to Huawei Cloud using their account name, usernames, and passwords, and then use resources based on the assigned permissions. IAM users do not own resources and cannot make payments for using cloud services.

Account Root User
When you create an account, an account root user with the same name as the account is created by default.
Conceptually, the account root user is also an IAM user and has the same capabilities.
However, there are some use constraints on the root user.
Constraint 1: The root user has default authorizations.
By default, the account root user is granted full access to all resources in the account and can assign permissions to IAM users.
Constraint 2: The permissions of the root user cannot be changed.
You cannot grant permissions to or revoke permissions from the root user, or add the user to or remove it from a user group.
Constraint 3: The root user cannot be deleted.
- You are strongly advised not to use the root user to perform routine tasks.
- You should keep the root user credentials secure.
IAM Users and Accounts
Conceptual model
- Account: An account is the entity that owns resources, uses resources, and pays for resources. An account does not directly use resources.
- IAM users: IAM users use resources in an account.
Usage habits
- Account root user: When you create an account, an IAM user with the same name as the account is created by default. It has to comply with the use constraints.
- IAM user: An IAM user is manually created after an account is created. IAM users can be modified and deleted.
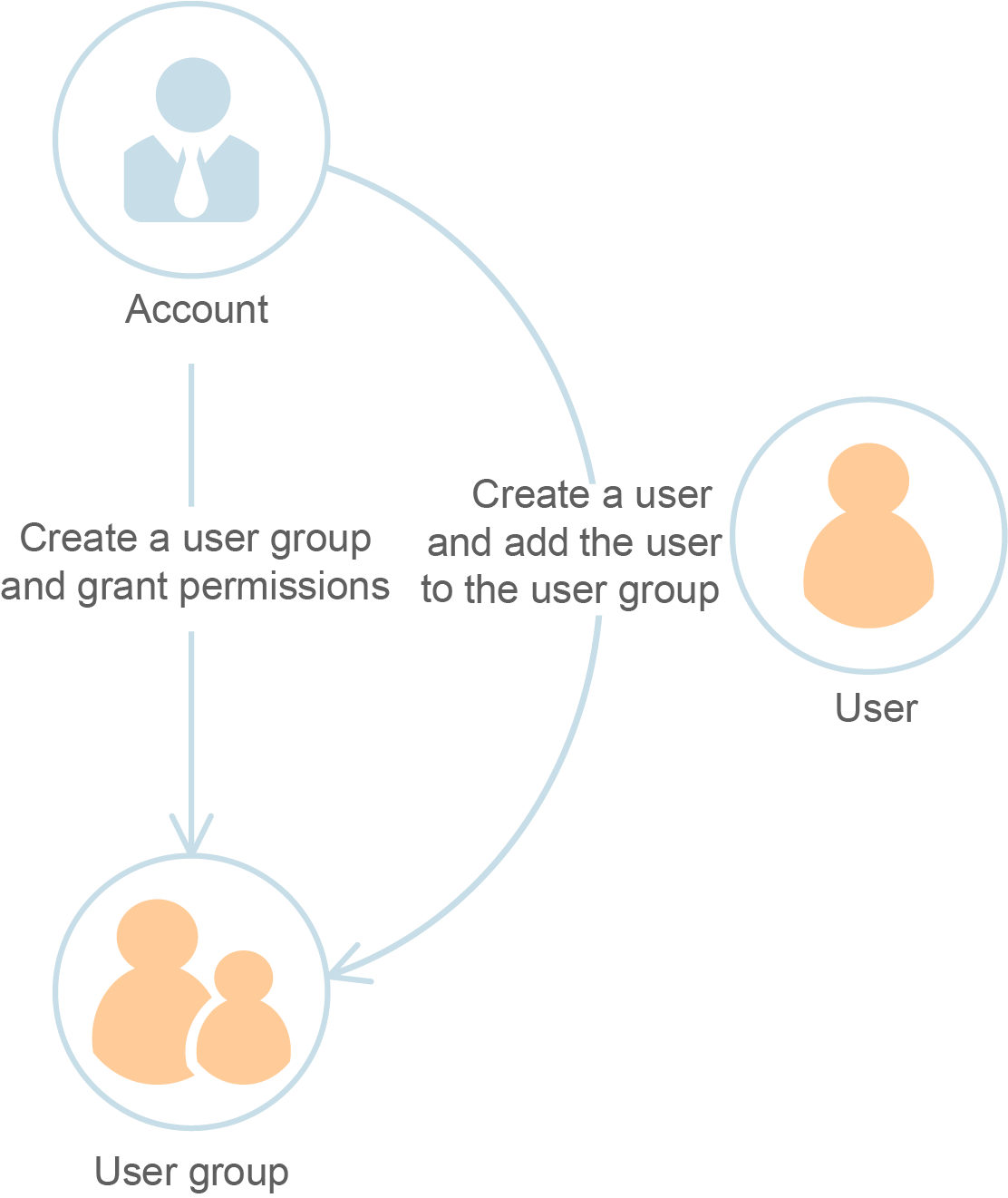
User Group
An IAM user group is a collection of IAM users. User groups let you specify permissions for multiple users, which can make it easier to manage the permissions for those users. After an IAM user is added to a user group or granted permissions, the user can perform operations on cloud services and resources as specified by the permissions. If a user is added to multiple user groups, the user inherits the permissions assigned to all these groups.
The default user group admin has all permissions required to use all of the cloud resources. Users in this group can perform operations on all the resources, including but not limited to creating user groups and users, modifying permissions, and managing resources.
Permissions
- IAM provides system-defined identity policies to define typical cloud service permissions. These policies cannot be modified and can only be used to assign permissions. If you cannot find system-defined identity policies for a specific cloud service in IAM when you are trying to assign permissions to users, user groups, agencies, or trust agencies, it means the cloud service does not support identity policies so far. In this case, you can submit a service ticket to request the permissions to be predefined in IAM.
- If system-defined identity policies cannot meet your requirements, you can create custom identity policies for more refined access control. You can create custom identity policies in the visual editor or in JSON view.
For example, when an IAM user granted only ECS permissions attempts to access other services, the system will display a message indicating that they do not have the required permissions to do so.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





