Configuring a DNS Server for Domain Name Resolution
Scenarios
A DNS server is used to resolve domain names of SFS Turbo file systems. For details about DNS server IP addresses, see What Are Huawei Cloud Private DNS Server Addresses?
By default, the IP address of the DNS server is automatically configured on ECSs when ECSs are created. No manual configuration is needed except when the resolution fails due to a change in the DNS server IP address.
Windows Server 2012 is used as an example in the operation procedure for Windows.
Procedure (Linux)
- Log in to the ECS as user root.
- Run vi /etc/resolv.conf to edit the /etc/resolv.conf file. Add the DNS server IP address above the existing name server information, as shown in Figure 1.
The format is as follows:
nameserver 100.125.1.250
- Press Esc, enter :wq, and press Enter to save and exit.
- Check whether the IP address is successfully added.
cat /etc/resolv.conf
- Check whether the file system domain name can be resolved.
nslookup <file-system-domain-name>
Obtain the file system domain name from the file system shared path.
- (Optional) If DHCP is configured for the ECS, edit the /etc/resolv.conf file to prevent the file from being automatically modified upon an ECS startup, and to prevent the DNS server IP address added in 2 from being reset.
- Lock the file.
- Check whether the file is locked.
If the information shown in Figure 2 is displayed, the file is locked.
Procedure (Windows)
- Go to the ECS console and log in to the ECS running Windows Server 2012.
- Click This PC in the lower left corner.
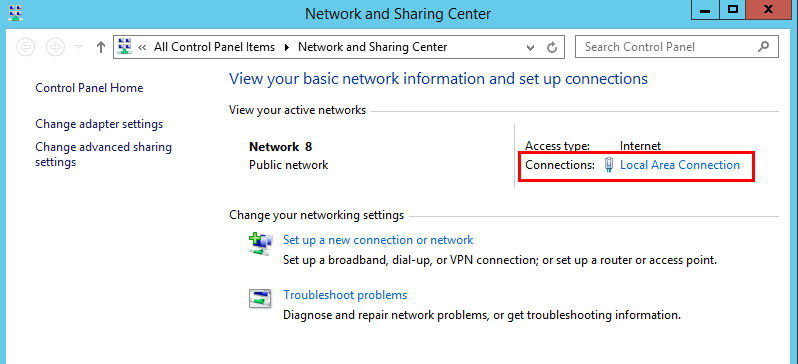
- On the displayed page, right-click Network and choose Properties from the drop-down list. The Network and Sharing Center page is displayed, as shown in Figure 3. Click Local Area Connection.
- In the Activity area, select Properties.
Figure 4 Local area connection

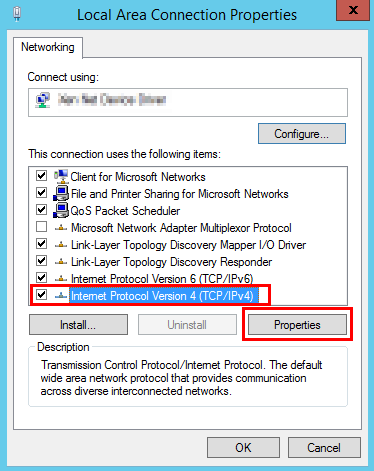
- In the displayed Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
Figure 5 Local area connection properties
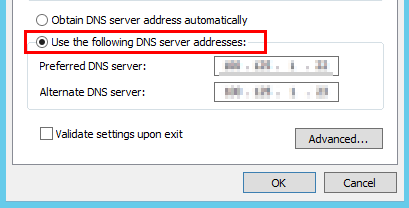
- In the displayed dialog box, select Use the following DNS server addresses: and configure the DNS server IP address, as shown in Figure 6. The DNS server IP address is 100.125.1.250. After the configuration is complete, click OK.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot