Creating a Database Account
Scenarios
When you create a DB instance, account root is created at the same time by default. You can create other database accounts as needed.
Constraints
- The instance must be in the running state.
- This operation is not allowed for DB instances that are being restored.
Procedure
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the target instance name to go to the Summary page.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Databases and Accounts and then click the Accounts tab.
- On the displayed page, click Create Account.
- In the displayed dialog box, set required parameters and click OK.
Figure 1 Creating a database account
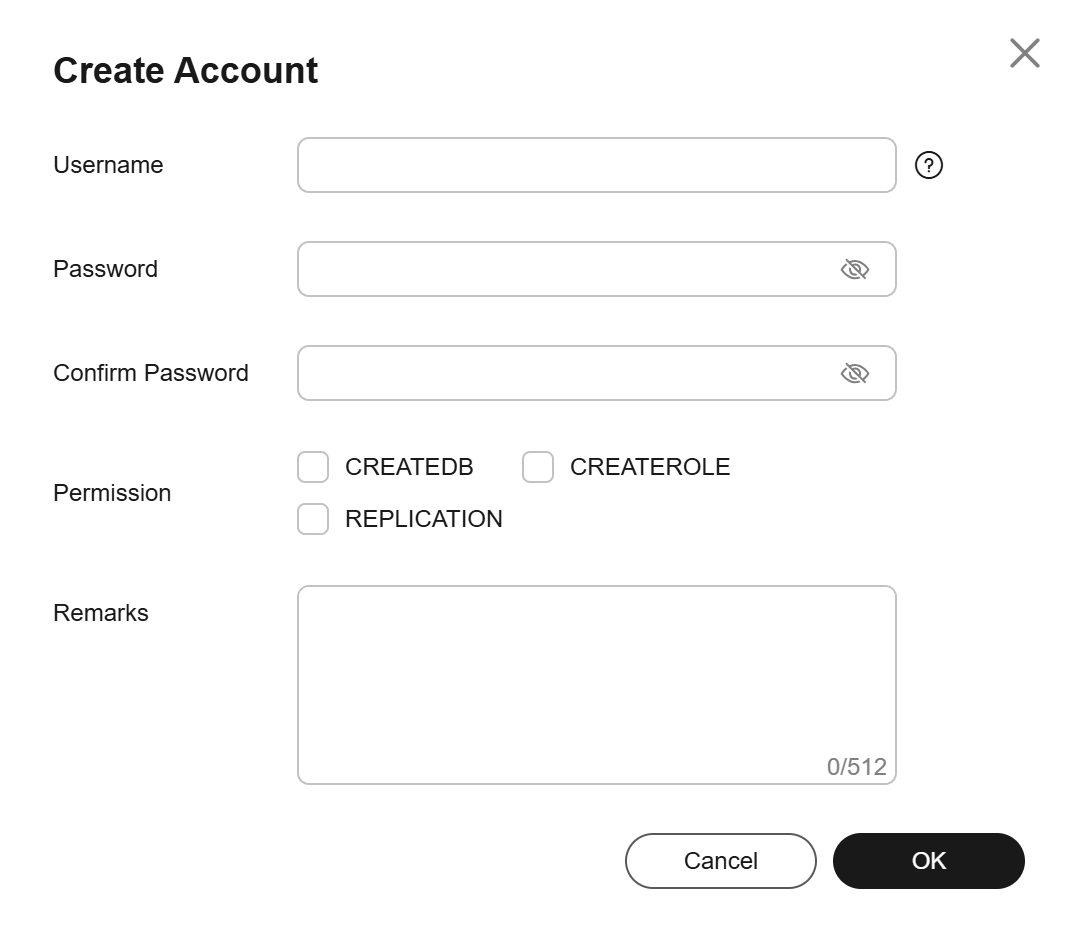
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Username
The username can contain 1 to 63 characters. It can include letters, digits, and underscores (_). It cannot start with pg or a digit and must be different from the system usernames. System users include rdsAdmin, rdsMetric, rdsBackup, rdsRepl, rdsProxy, rdsDdm, and rdsDisaster.
- rdsAdmin: a management account with the highest permissions. It is used to query and modify instance information, rectify faults, migrate data, and restore data.
- rdsRepl: a replication account, used to synchronize data from the primary instance to the standby instance or read replicas.
- rdsBackup: a backup account, used for backend backup.
- rdsMetric: a metric monitoring account used by watchdog to collect database status data.
- rdsProxy: the proxy account, which is automatically created when read/write splitting is enabled and is used for authentication when a database is connected through a read/write splitting address.
- rdsDdm: a DDM account.
- rdsDisaster: a DR account, used to set up cross-region DR.
Password
- The password must consist of 8 to 32 characters and contain at least three types of the following characters: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters (~!@#$%^*-_=+?,).
- The password cannot contain the username or the username spelled backwards.
- Using a weak password will cause account creation to fail. Enter a strong password to improve security and prevent security risks such as brute force cracking.
Permission
You can assign permissions, including CREATEDB, CREATEROLE, and REPLICATION, to the user.
- CREATEDB: indicates that the user has the permission to create a database. If this attribute is not specified, the user cannot create databases by default.
- CREATEROLE: indicates that the user has the permission to create other users. If this attribute is not specified, the user cannot be used to create new users by default.
- REPLICATION: indicates that the user can use streaming replication or logical replication. If this attribute is not specified, the user cannot be used to set up streaming replication or logical replication by default.
Remarks
The remarks can contain 0 to 512 characters.
- After the account is created, manage it on the Accounts page.
Privileges of the Root User
RDS for PostgreSQL provides permissions for the root user. To create objects on an RDS for PostgreSQL database without operation risks, escalate your account to root privileges when necessary.
The following table describes root privilege escalation in different versions.
|
Version |
Whether to Escalate Privileges |
Initial Version for Privilege Escalation |
|---|---|---|
|
pgcore9 |
No |
N/A |
|
pgcore10 |
No |
N/A |
|
pgcore11 |
Yes |
11.11 |
|
pgcore12 |
Yes |
12.6 |
|
pgcore13 |
Yes |
13.2 |
|
pgcore14 |
Yes |
14.4 |
|
pgcore15 |
Yes |
15.4 |
|
pgcore16 |
Yes |
16.2 |
|
pgcore17 or later |
Yes |
N/A |
Escalate to root privileges when you need to:
- Create an event trigger.
- Create a wrapper.
- Create a logical replication publication.
- Create a logical replication subscription.
- Query and maintain replication sources.
- Create a replication user.
- Create a full-text index template and parser.
- Run the vacuum command on a system table.
- Run the analyze command on a system table.
- Create an extension.
- Granting permissions on an object to a user.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





