Logging In to an MRS Cluster Node
This section describes how to log in to a node in an MRS cluster and manage or maintain the cluster. You can log in to a cluster node using VNC provided on the Elastic Cloud Server (ECS) console. For more information about ECS, see What Is ECS? Alternatively, you can log in to a node using SSH key or password. If the local environment cannot directly access the node VPC, you need to bind an elastic IP address (EIP) to the node. For more information about EIP, see What Is Elastic IP?
|
Access Method |
Access Scenario |
Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
|
SSH |
Routine node access, to install cluster clients, check role configuration files or log files of cluster components, and query data files required by upper-layer cluster jobs and so on. |
You need to bind an EIP to the ECS and add a security group rule to allow inbound traffic. If the ECS is accessed through a private network, for example, through a VPN or Direct Connect connection, you do not need to bind an EIP to the ECS. |
|
VNC (Remote Login from ECS Console) |
To remotely log in to an ECS for maintenance in case of emergency. |
No EIPs are required. |
Prerequisites
- When logging in to an MRS cluster node using SSH, bind an EIP to the node before login if the local environment cannot directly access the MRS cluster network.
- When logging in to an MRS cluster node using SSH, add an inbound rule to the security group of the MRS cluster.
Set the source address to the client IPv4 address/32 (or client IPv6 address/128) and the port number is 22. For details, see Adding Security Group Rules..
Video Tutorial
This video shows how to log in to an MRS cluster node using SSH and VNC.
The UI may vary depending on the version. This tutorial is for reference only.
Logging In to an MRS Cluster Node
You can log in to the node using SSH or remotely log in to the node using VNC on ECS console. The node login method depends on the node password type selected during MRS cluster creation.
Logging In to a Node on a Local Windows OS
To log in to a cluster node on a local Windows OS, perform the following operations:
- Log in to the MRS console.
- Choose Active Clusters and click the name of the target cluster to access cluster details page.
- On the Nodes tab, click the name of the target node to log in to the ECS console.
To log in to the active or standby management node of the MRS cluster, see Checking MRS Active/Standby Management Nodes.
- Click the EIPs tab, click Bind EIP to bind an EIP to the ECS, record the IP address, and click OK. If an EIP has been bound, skip this step.
If no EIP is available, click Buy EIP and purchase an EIP as prompted.
Figure 1 Binding an EIP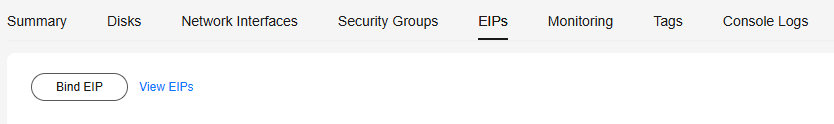
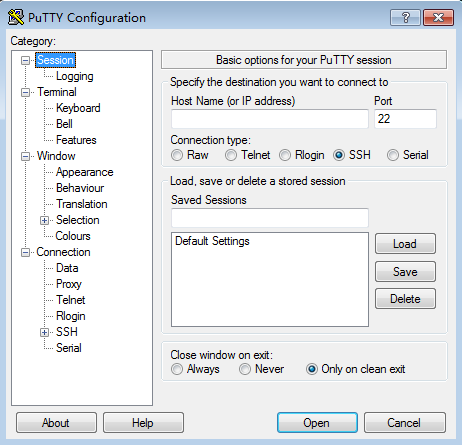
- Run the SSH login software, such as PuTTY.
- Click Session.
- Host Name (or IP address): Enter the EIP bound to the ECS.
- Port: Enter 22.
- Connection Type: Select SSH.
- Saved Sessions: Task name, which can be clicked for remote connection when you use PuTTY next time
Figure 2 Clicking Session
- Click Window and select UTF-8 for Remote character set: in Translation.
- Click Open to log in to the ECS.
If you log in to the ECS for the first time, PuTTY displays a security warning dialog box, asking you whether to accept the ECS security certificate. Click Yes to save the certificate to your local registry.
- After the SSH connection to the ECS is set up, enter the username and password as prompted to log in to the ECS.
The username is root, and the password is the one you set when creating the MRS cluster.
Logging In to the Node on a Local Linux OS
To log in to a cluster node on a local Linux OS, bind an EIP to the ECS by referring to Step 1 to Step 4, and then run the following command in the CLI to log in to the ECS:
ssh EIP bound to the ECS
Logging In to a Node on a Local Windows OS
To log in to the Linux ECS from local Windows, perform the operations described in this section. The following procedure uses PuTTY as an example to log in to the ECS.
- Log in to the MRS console.
- Choose Active Clusters and click the name of the target cluster to access cluster details page.
- On the Nodes tab, click the name of the target node to log in to the ECS console.
To log in to the active or standby management node of the MRS cluster, see Checking MRS Active/Standby Management Nodes.
- Click the EIPs tab, click Bind EIP to bind an EIP to the ECS, and record the EIP. If an EIP has been bound to the ECS, skip this step.
- Check whether the private key file has been converted to .ppk format.
- Run the SSH login software, such as PuTTY.
- In the Actions area, click Load and import the private key file you used during ECS creation.
Ensure that the private key file is in the format of All files (*.*).
- Click Save private key.
- Save the converted private key,
for example, kp-123.ppk, to a local directory.
- Run PuTTY.
- Choose Connection > Data. Enter the image username in Auto-login username.
The default username for logging in to the MRS cluster node image is root.
- Choose Connection > SSH > Auth. In the last configuration item Private key file for authentication, click Browse and select the private key file in .ppk format or the private key file saved in Step 9.
- Click Session.
- Host Name (or IP address): Enter the EIP bound to the ECS.
- Port: Enter 22.
- Connection Type: Select SSH.
- Saved Sessions: Task name, which can be clicked for remote connection when you use PuTTY next time
Figure 3 Clicking Session

- Click Open to log in to the ECS.
If you log in to the ECS for the first time, PuTTY displays a security warning dialog box, asking you whether to accept the ECS security certificate.
Click Yes to save the certificate to your local registry.
Logging In to the ECS from Local Linux
To log in to the Linux ECS from local Linux, perform the operations described in this section.
The following procedure uses private key file kp-123.pem as an example to log in to the ECS. The name of your private key file may differ.
- On the Linux CLI, run the following command to change operation permissions:
chmod 400 /path/kp-123.pem
In the preceding command, path indicates the path for storing the private key file.
- Run the following command to log in to the ECS:
ssh -i /path/kp-123.pemDefault username@EIP
For example, if the default username is root and the EIP is xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, run the following command:
ssh -i /path/kp-123.pem root@xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
In the preceding command:
- path indicates the path where the key file is saved.
- EIP indicates the EIP bound to the ECS.
- The image username is root for cluster nodes.
- Log in to the MRS console.
- Choose Active Clusters and click the name of the target cluster to access cluster details page.
- On the Nodes tab, click the name of the target node to log in to the ECS console.
To log in to the active or standby management node of the MRS cluster, see Checking MRS Active/Standby Management Nodes.
- Click Remote Login in the upper right corner. In the displayed dialog box, click Log In in the VNC Login area.
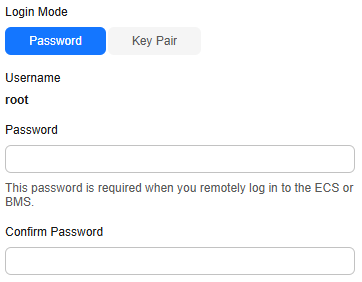
- Enter the username and password for logging in to the Master node as prompted.
- If you select Password for Login Mode, you need to enter root in Username and the password you set during cluster creation in Password.
Figure 4 Selecting password as the login mode
- If you select Key Pair for Login Mode when creating a cluster, perform the following operations to log in to the cluster:
- After the cluster is created, assign an EIP and bind it to the Master node of the cluster. For details, see Assigning an EIP and Binding It to an ECS.
- Remotely log in to the Master node in SSH mode as user root using the key file.
- Run the following command to set the password for user root:
passwd root
- Go back to the login interface, and enter root and the password set in 5.b.iii to log in to the node.
- If you select Password for Login Mode, you need to enter root in Username and the password you set during cluster creation in Password.
Helpful Links
- To periodically change the password for the MRS cluster user to improve system security, see Changing the Passwords for System Users of an MRS Cluster.
- To reset the password of the user root in case of password loss or expiration, see Resetting the Password for Logging In to an ECS on the Management Console.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





